Muscles Of The Arm And Forearm Anterior Advanced
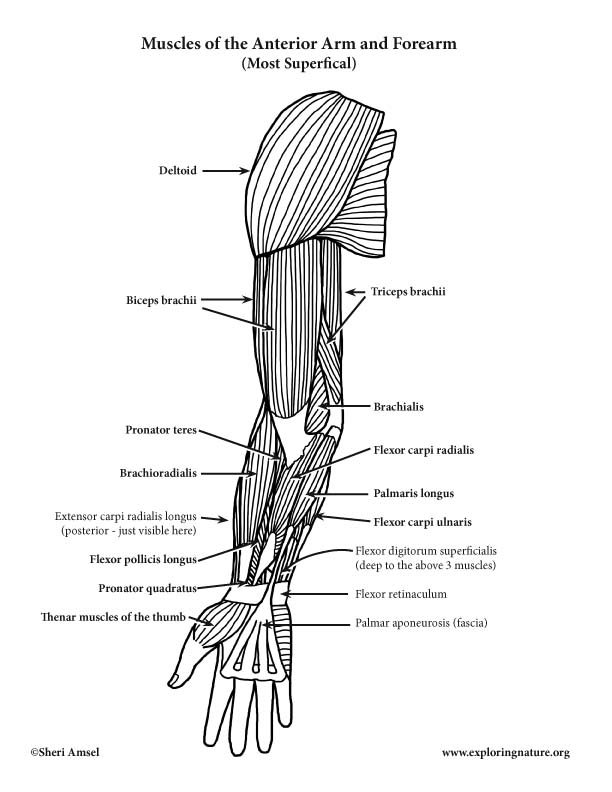
Muscles Of The Arm And Forearm Anterior Advanced Muscles that cross the elbow (moving the forearm) (anterior) 1) deltoid (visible, but not part of this group as it moves arm from the shoulder) 2) biceps brachii. a. actions: flexes and supinates forearm (supinate rotates forearm laterally) –. these act together for pulling tissue from tissue box, also a minor arm flexor. b. The superficial muscles in the anterior compartment are the flexor carpi ulnaris, palmaris longus, flexor carpi radialis and pronator teres. they all originate from a common tendon, which arises from the medial epicondyle of the humerus. flexor carpi ulnaris. the flexor carpi ulnaris has two origins.
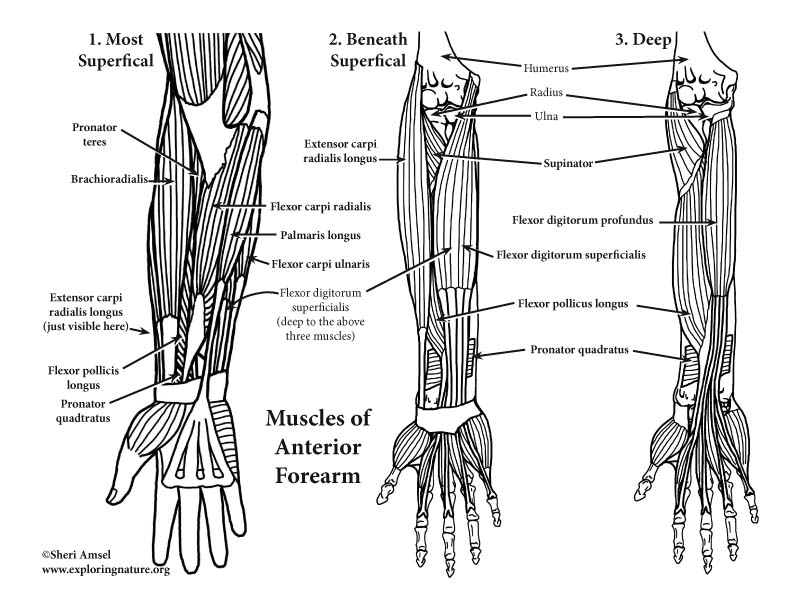
Arm And Forearm Muscles Anterior View Advanced Overview. the forearm is the portion of the arm distal to the elbow and proximal to the wrist. there are 2 0 muscles separated into two compartments in this article, we will discuss the anterior compartment of the forearm in the setting of their attachment points, function, innervation and vascular supply, while providing clinical examples to reinforce this information. The muscles of the upper limb can be divided into 6 different regions: pectoral, shoulder, upper arm, anterior forearm, posterior forearm, and the hand. there are 4 muscles of the pectoral region: pectoralis major, pectoralis minor, serratus anterior and subclavius. collectively, these muscles are involved in movement and stabilisation of the. The arm muscles are a group of five muscles located in the region between the shoulder and elbow joints. they are divided into two distinct compartments of the arm. the anterior (flexor) compartment contains the biceps brachii, coracobrachialis and brachialis muscles. the posterior (extensor) compartment contains only the triceps brachii muscle. The forearm is the section of the upper limb from the elbow to the wrist, whose bony structure is formed by the radius (laterally) and ulna (medially). two muscular compartments an anterior (flexor) and posterior (extensor) compartment contain together twenty muscles that act on the elbow and wrist joints, as well as carpometacarpal, metacarpophalangeal, and interphalangeal joints of the hand.
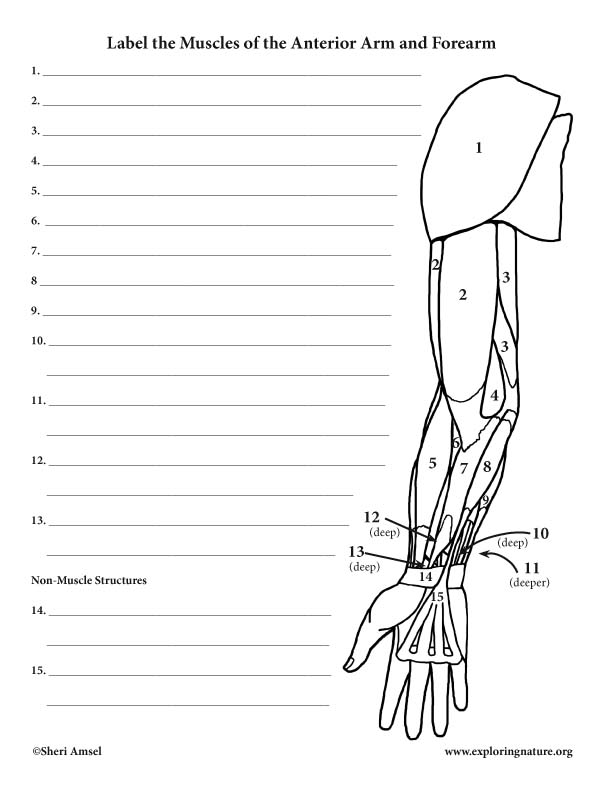
Muscles Of The Arm And Forearm Anterior вђ Labeling Page Advanced The arm muscles are a group of five muscles located in the region between the shoulder and elbow joints. they are divided into two distinct compartments of the arm. the anterior (flexor) compartment contains the biceps brachii, coracobrachialis and brachialis muscles. the posterior (extensor) compartment contains only the triceps brachii muscle. The forearm is the section of the upper limb from the elbow to the wrist, whose bony structure is formed by the radius (laterally) and ulna (medially). two muscular compartments an anterior (flexor) and posterior (extensor) compartment contain together twenty muscles that act on the elbow and wrist joints, as well as carpometacarpal, metacarpophalangeal, and interphalangeal joints of the hand. Muscles that cross the elbow (moving the forearm) (anterior) deltoid. biceps brachii. (visible, but not part of this group as it moves arm from the shoulder) actions: flexes and supinates forearm (supinate rotates forearm laterally) – these act together for pulling tissue from tissue box, also a minor arm flexor. The forearm muscles are divided into two compartments based on location and action: the anterior or flexor compartment and the posterior or extensor compartment. there are a total of 19 muscles in the forearm that help move not only the elbow and wrist joints but also the joints in the hand and fingers.

Comments are closed.