Muscle Tissue Review For Anatomy And Physiology
Muscular Tissue Skeletal Smooth And Cardiac Muscle Figure 4.4.1 – muscle tissue: (a) skeletal muscle cells have prominent striation and nuclei on their periphery. (b) smooth muscle cells have a single nucleus and no visible striations. (c) cardiac muscle cells appear striated and have a single nucleus. from top, lm × 1600, lm × 1600, lm × 1600. Chapter review. muscle is the tissue in animals that allows for active movement of the body or materials within the body. there are three types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. most of the body’s skeletal muscle produces movement by acting on the skeleton. cardiac muscle is found in the wall of the heart.

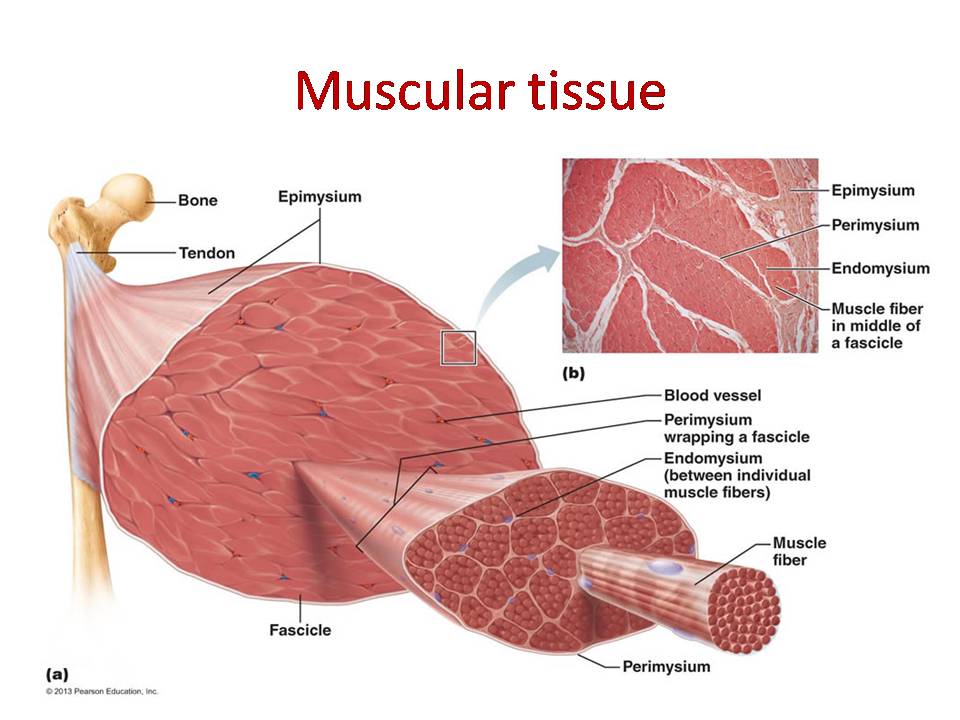
Muscle Tissue Human Physiology And Anatomy Lecture Slides Docsity Facial muscles. found in voluntary sphincters lips, urethra, and anus. table 10.1: muscle type – structure, function, location. figure 10.2 the three types of muscle tissue the body contains three types of muscle tissue: (a) skeletal muscle, (b) smooth muscle, and (c) cardiac muscle. Skeletal muscle fibers are organized into groups called fascicles. blood vessels and nerves enter the connective tissue and branch in the cell. muscles attach to bones directly or through tendons or aponeuroses. skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilize bones and joints, control internal movement, and generate heat. Chapter review. muscle is the tissue in animals that allows for active movement of the body or materials within the body. there are three types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. most of the body’s skeletal muscle produces movement by acting on the skeleton. cardiac muscle is found in the wall of the heart. 10.1 overview of muscle tissues . muscle is the tissue in animals that allows for active movement of the body or materials within the body. there are three types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. most of the body’s skeletal muscle produces movement by acting on the skeleton.
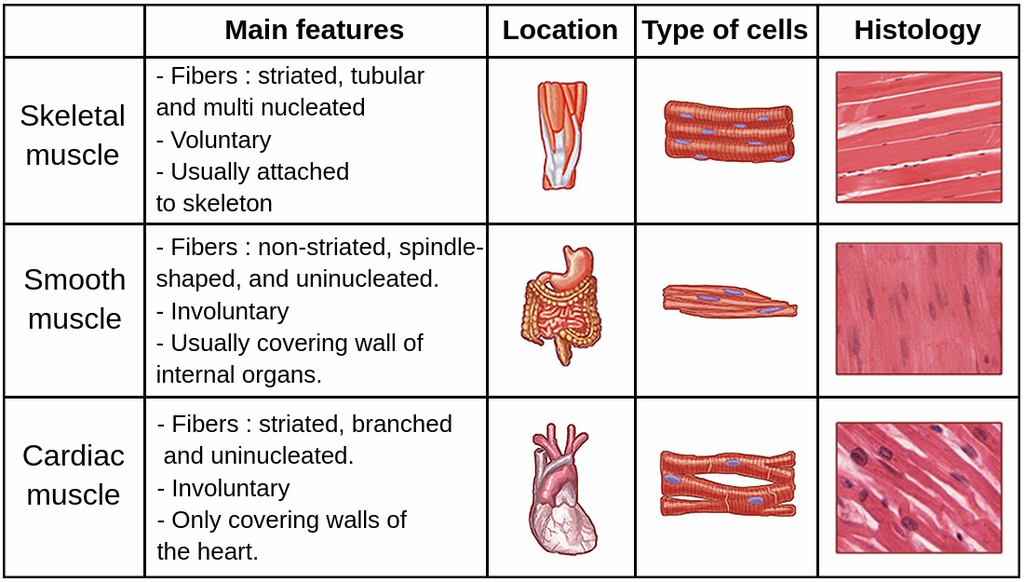
Muscular Tissue Its Types And Functions In Human Body Online Science Chapter review. muscle is the tissue in animals that allows for active movement of the body or materials within the body. there are three types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. most of the body’s skeletal muscle produces movement by acting on the skeleton. cardiac muscle is found in the wall of the heart. 10.1 overview of muscle tissues . muscle is the tissue in animals that allows for active movement of the body or materials within the body. there are three types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. most of the body’s skeletal muscle produces movement by acting on the skeleton. Skeletal muscle tissue is arranged in bundles surrounded by connective tissue. under the light microscope, muscle cells appear striated with many nuclei squeezed along the membranes. the striation is due to the regular alternation of the contractile proteins actin and myosin, along with the structural proteins that couple the contractile. Muscles and muscle tissue. this type of tissue is found in skeletal muscles and is responsible for the voluntary movements of bones. muscle is defined as a tissue primarily composed of specialized cells fibers which are capable of contracting in order to effect movement. this can relate to movement of the body or body parts with our external.

Muscle Tissues Skeletal Cardiac Smooth Basic Anatomy And Skeletal muscle tissue is arranged in bundles surrounded by connective tissue. under the light microscope, muscle cells appear striated with many nuclei squeezed along the membranes. the striation is due to the regular alternation of the contractile proteins actin and myosin, along with the structural proteins that couple the contractile. Muscles and muscle tissue. this type of tissue is found in skeletal muscles and is responsible for the voluntary movements of bones. muscle is defined as a tissue primarily composed of specialized cells fibers which are capable of contracting in order to effect movement. this can relate to movement of the body or body parts with our external.

Muscular System Anatomy And Physiology Muscular System Anatomy

Comments are closed.