Multiplication Strategies For 3rd Grade Elementary Shenanigans

Elementary Shenanigans Multiplication Strategies For 3rd Grade Here is a little peek inside our magic of math multiplication unit (unit 3 3rd grade). each lesson is strategically broken down into three sections. this helps keep our math block consistent, but the breakdown is also tied to research based practices. we begin with a quick 10 15 mini lesson, followed by independent guided practice, and. Learn 6 multiplication strategies for third grade and get some ideas for fun activities to practice each strategy. teach your third graders about equal groups, arrays, tape diagrams, skip counting, fact families, and repeated addition. knowing these strategies will help your third graders solve multiplication facts that they don't yet know.

Multiplication Strategies For 3rd Grade Elementary Shenanigans Explain that there are 3 groups and 4 counters in each. this is the same as saying 3×4. ask the kids to tell you the total amount of counters they used. their response should be 12. so 3×4=12. this is a good time to point out that when you add numbers you find the total. it’s the same with multiplication. This video helps you understand how to use multiplication strategies. grade 3. lessons 3.1, 3.2, and 3.5#multiplication #arrays #multiply. Multiplication can be a daunting task for students of all ages. however, with the right multiplication strategies in place, it can become a fun and easy process. in this article, we will discuss 7 multiplication strategies that will help students understand the why behind multiplication before learning how to do it. In bridges and number corner, grades 3 and 4. originally developed by math interventionists laurie kilts and kim hornbeck, these posters have been updated to reflect the multiplication fact strategy names and models used in bridges 2nd edition. grade level suggestions grades 3 & 4 display each poster after you have introduced or reviewed the.
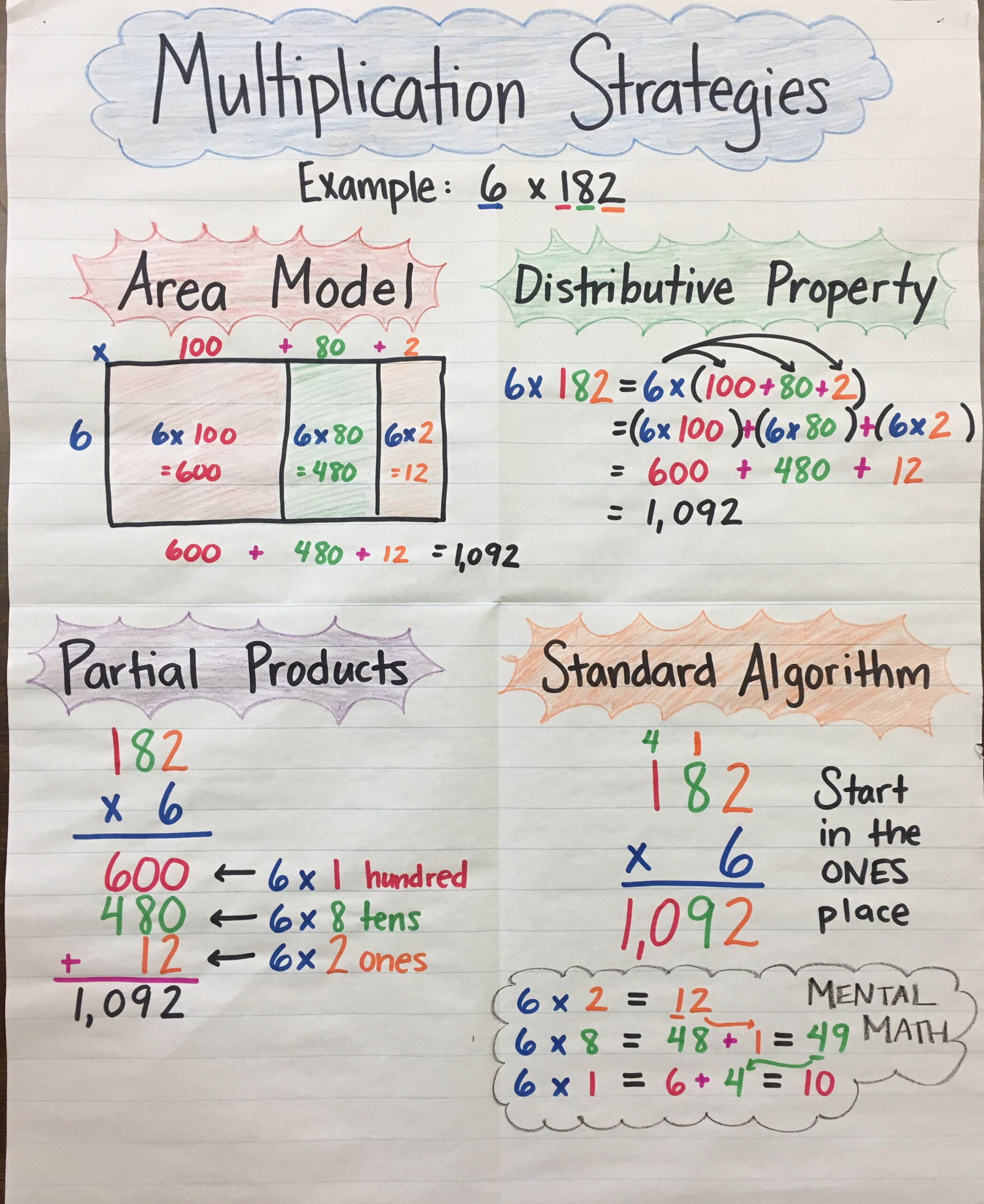
Multiplication Anchor Chart 3rd Grade Multiplication can be a daunting task for students of all ages. however, with the right multiplication strategies in place, it can become a fun and easy process. in this article, we will discuss 7 multiplication strategies that will help students understand the why behind multiplication before learning how to do it. In bridges and number corner, grades 3 and 4. originally developed by math interventionists laurie kilts and kim hornbeck, these posters have been updated to reflect the multiplication fact strategy names and models used in bridges 2nd edition. grade level suggestions grades 3 & 4 display each poster after you have introduced or reviewed the. 3.oa.a.3 use multiplication and division within 100 to solve word problems in situations involving equal groups, arrays, and measurement quantities. 3.oa.a.4 determine the unknown whole number in a multiplication or division. Multiplication facts are the basic facts of multiplying two single digit numbers, such as 2 x 3 = 6 or 9 x 9 = 81. these facts are also called the times tables because they show how many times a number is added to itself. for example, 4 x 5 = 20 means that 4 is added to itself 5 times: 4 4 4 4 4 = 20. multiplication facts are essential.
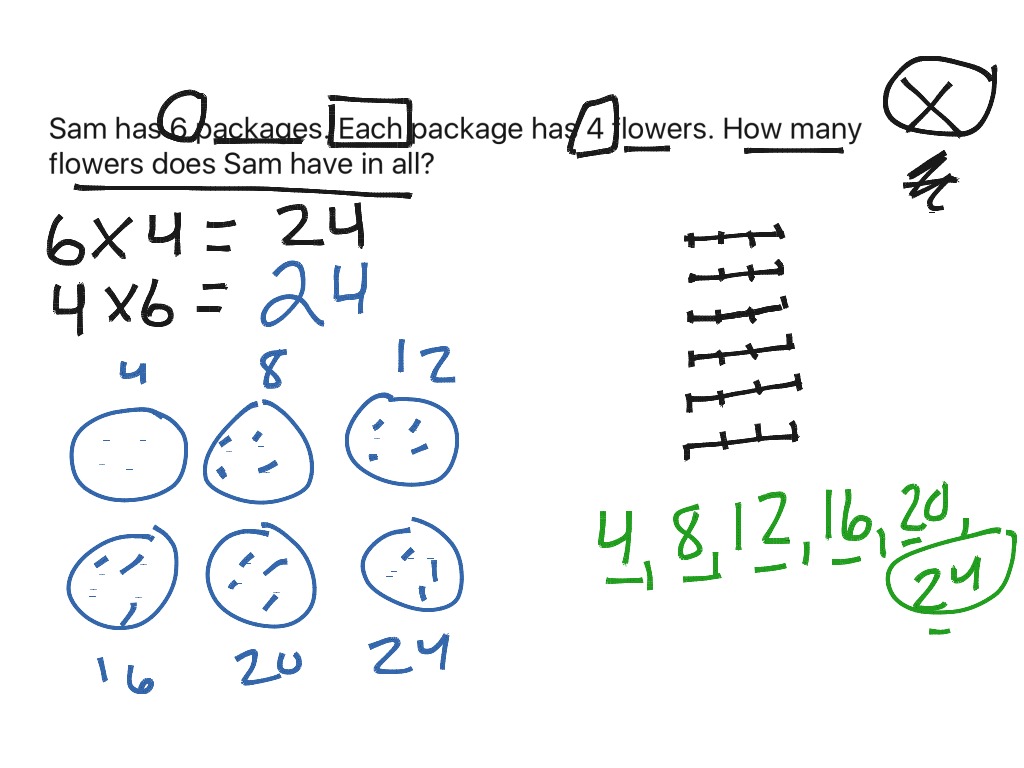
Multiplication Strategies Math Elementary Math 3rd Grade Showme 3.oa.a.3 use multiplication and division within 100 to solve word problems in situations involving equal groups, arrays, and measurement quantities. 3.oa.a.4 determine the unknown whole number in a multiplication or division. Multiplication facts are the basic facts of multiplying two single digit numbers, such as 2 x 3 = 6 or 9 x 9 = 81. these facts are also called the times tables because they show how many times a number is added to itself. for example, 4 x 5 = 20 means that 4 is added to itself 5 times: 4 4 4 4 4 = 20. multiplication facts are essential.

Comments are closed.