Monopoly Managerial Economics

What Is Monopoly вђ Eco Is Easy In economics, monopoly and competition signify certain complex relations among firms in an industry. a monopoly implies an exclusive possession of a market by a supplier of a product or a service for which there is no substitute. in this situation the supplier is able to determine the price of the product without fear of competition from other. A monopoly is a specific type of economic market structure. a monopoly exists when a specific person or enterprise is the only supplier of a particular good. as a result, monopolies are characterized by a lack of competition within the market producing a good or service. monopoly: the graph shows a monopoly and the price (p) and change in price.
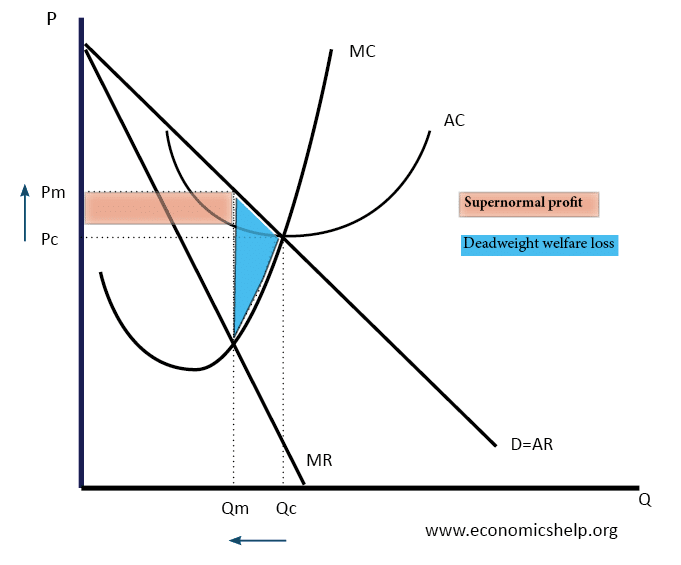
Diagram Of Monopoly Economics Help This page titled 7.2: monopoly is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by via that was edited to the style and standards of the libretexts platform. often, the main deterrent to a highly competitive market is market power possessed by sellers. in this section, we will consider the strongest form of seller market. Adam hayes, ph.d., cfa, is a financial writer with 15 years wall street experience as a derivatives trader. besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, adam is an expert in economics and. Monopoly is a market having single seller of a product which has no close substitutes. literally monopoly implies ‘mono’ means one and ‘poly’ means seller. thus monopoly means ‘one seller’ or ‘one producer’ exist in a market. there are three main important points regarding monopoly. i. Any price above marginal cost induces a net loss in social welfare. let us compare social welfare under monopoly (maximal market power) with that of perfect competition (zero market power): (fig. 1) perfect competition: total surplus = area opcs. monopoly: total surplus = area pmpctr area opmr.

Monopoly Managerial Economics Monopoly is a market having single seller of a product which has no close substitutes. literally monopoly implies ‘mono’ means one and ‘poly’ means seller. thus monopoly means ‘one seller’ or ‘one producer’ exist in a market. there are three main important points regarding monopoly. i. Any price above marginal cost induces a net loss in social welfare. let us compare social welfare under monopoly (maximal market power) with that of perfect competition (zero market power): (fig. 1) perfect competition: total surplus = area opcs. monopoly: total surplus = area pmpctr area opmr. Monopoly in economics explained. monopoly is derived from the words “monos” (single) and “polein” (to sell) of greek. monopoly was first depicted in the landlord’s game, which was invented by elizabeth magie phillips (or lizzie magie) in 1904. this game inspired the monopoly board game that is played by most students today. Chapter review. under monopoly, a manager maximizes profit by setting output at the point where marginal revenue equals marginal cost. it does not follow that managers in monopoly markets always earn significant profit. if the monopolist cannot cover its variable costs, it, like a perfectly competitive firm, will shut down, even in the short run.

Monopoly Managerial Economics Ppt Monopoly in economics explained. monopoly is derived from the words “monos” (single) and “polein” (to sell) of greek. monopoly was first depicted in the landlord’s game, which was invented by elizabeth magie phillips (or lizzie magie) in 1904. this game inspired the monopoly board game that is played by most students today. Chapter review. under monopoly, a manager maximizes profit by setting output at the point where marginal revenue equals marginal cost. it does not follow that managers in monopoly markets always earn significant profit. if the monopolist cannot cover its variable costs, it, like a perfectly competitive firm, will shut down, even in the short run.

Monopoly Definition Types Characteristics Examples Feedough

Comments are closed.