Module 33 Types Of Inflation Disinflation And Deflation
Ppt Module 33 Types Of Inflation Disinflation And Deflation So the government is forced to increase the money supply more rapidly, leading to an even higher rate of inflation, and so on. demand pull inflation. inflation (increase in price level) that is caused by an increase in aggregate demand. cost push inflation. a decrease in aggregate supply because of an increase in the price of an input. The reduction in the value of money held by the public caused by inflation cost push inflation inflation that is caused by a significant increase in the price of an input with economy wide importance.

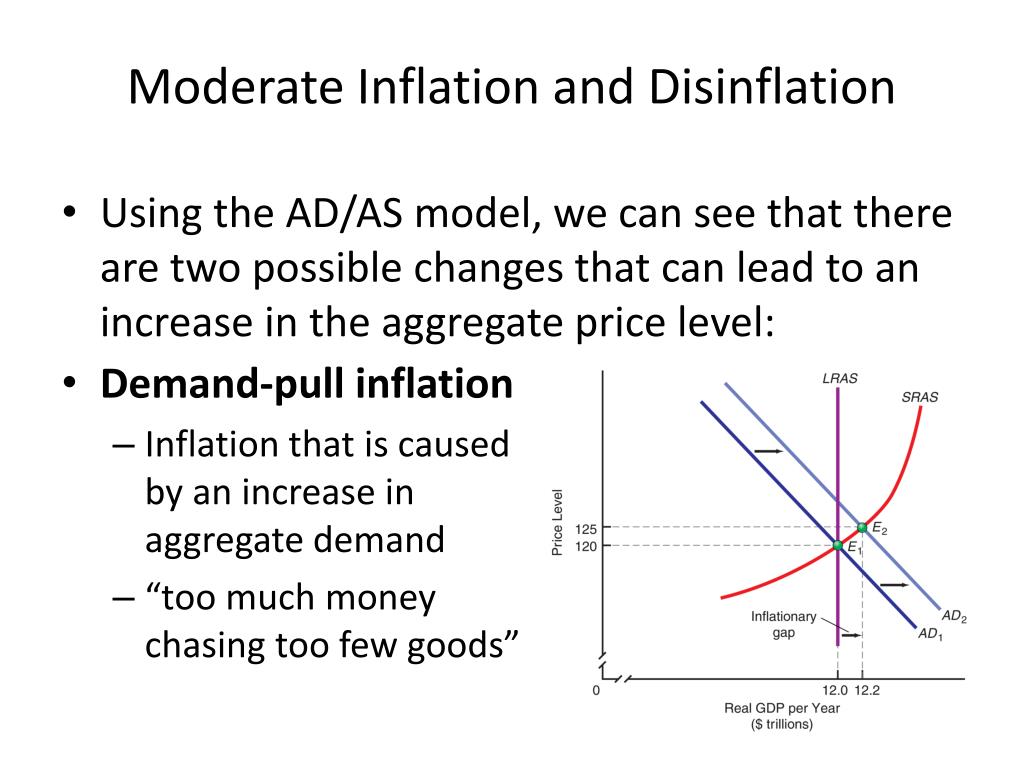
Module 33 Types Of Inflation Disinflation And Deflation Module 33: types of inflation, disinflation, and deflation the inflation tax: the inflation tax economists refer to the revenue generated by the government’s right to print money as seigniorage. ★ as we have seen, printing money to cover a budget deficit leads to inflation. Module 33: types of inflation, disinflation, and deflation study guide by davidgarcia1600 includes 23 questions covering vocabulary, terms and more. quizlet flashcards, activities and games help you improve your grades. Figure 33.1 reviews the effects of an increase in the money supply according to the a d– as model. the economy starts at e 1, a point of shor t run and lon g run macroeconomic equilibrium. it lies at the intersection of the aggregate demand curve, ad 1, and the shor t run aggregate supply curve, sras 1. it also lies on the lon. Figure 33.1 reviews the effects of an increase in the money supply according to the ad–as model. the economy starts at e1, a point of short run and long run macroeconomic equilibrium. it lies at the intersection of the aggregate demand curve, ad1, and the short run aggregate supply curve, sras1.

Module 33 Types Of Inflation Disinflation And Deflation Ap Macroeconomics Figure 33.1 reviews the effects of an increase in the money supply according to the a d– as model. the economy starts at e 1, a point of shor t run and lon g run macroeconomic equilibrium. it lies at the intersection of the aggregate demand curve, ad 1, and the shor t run aggregate supply curve, sras 1. it also lies on the lon. Figure 33.1 reviews the effects of an increase in the money supply according to the ad–as model. the economy starts at e1, a point of short run and long run macroeconomic equilibrium. it lies at the intersection of the aggregate demand curve, ad1, and the short run aggregate supply curve, sras1. Define the types of inflation: cos t push and deman d pull we have seen that monetary policy affects economic welfare in the shor t run. let’s take a closer look at two phenomena that involve monetary policy: inflation and deflation. Inflation that is caused by a significant increase in the price of an input with econom y wide importance is called cos t push inflation. for example, it is argued that the oil crisis in the 1970s led to an increase in energy prices in the united states, causing a leftward shift of the aggregate supply curve, increasing the aggregate price level.

Module33 Typesofinflation Disinflation Anddeflation Ppt Define the types of inflation: cos t push and deman d pull we have seen that monetary policy affects economic welfare in the shor t run. let’s take a closer look at two phenomena that involve monetary policy: inflation and deflation. Inflation that is caused by a significant increase in the price of an input with econom y wide importance is called cos t push inflation. for example, it is argued that the oil crisis in the 1970s led to an increase in energy prices in the united states, causing a leftward shift of the aggregate supply curve, increasing the aggregate price level.

Comments are closed.