Mig Welding Gas Explained At James Mendoza Blog
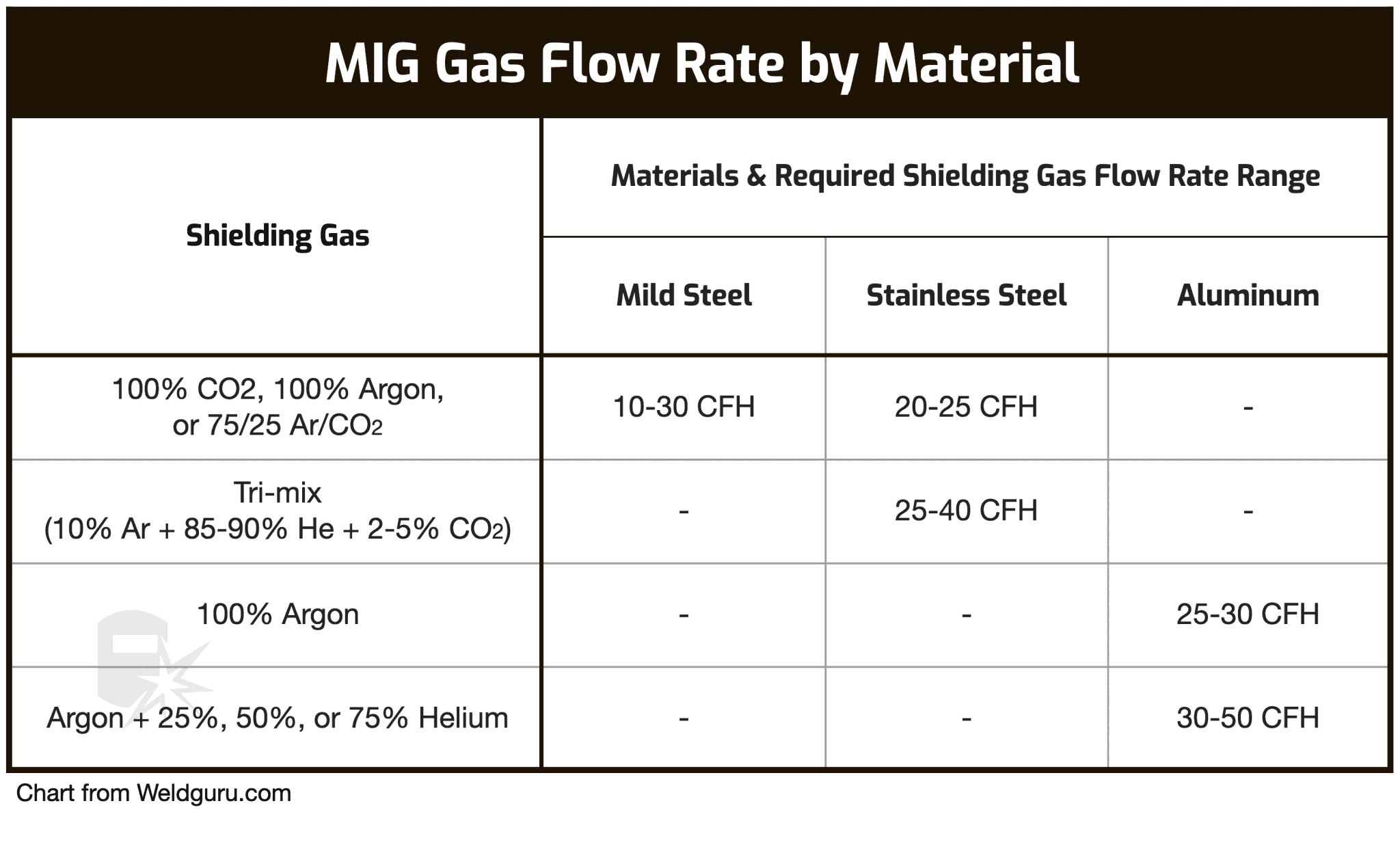
Mig Welding Gas Explained At James Mendoza Blog Mig welding, or gas metal arc welding (gmaw), is a welding process that employs an electric arc between a consumable wire electrode and the workpiece. the heat generated by the arc melts the wire electrode and the base metal, creating a molten weld pool. simultaneously, a shielding gas is fed through the welding gun to protect the weld pool. A 10% argon, 85% helium, and 5% carbon dioxide blend is the most popular tri mix gas and is used for various steel applications. a 75% argon and 25% helium blend is suitable for welding thick, non ferrous metals such as aluminum. increasing helium content will produce better welds for thick metals.
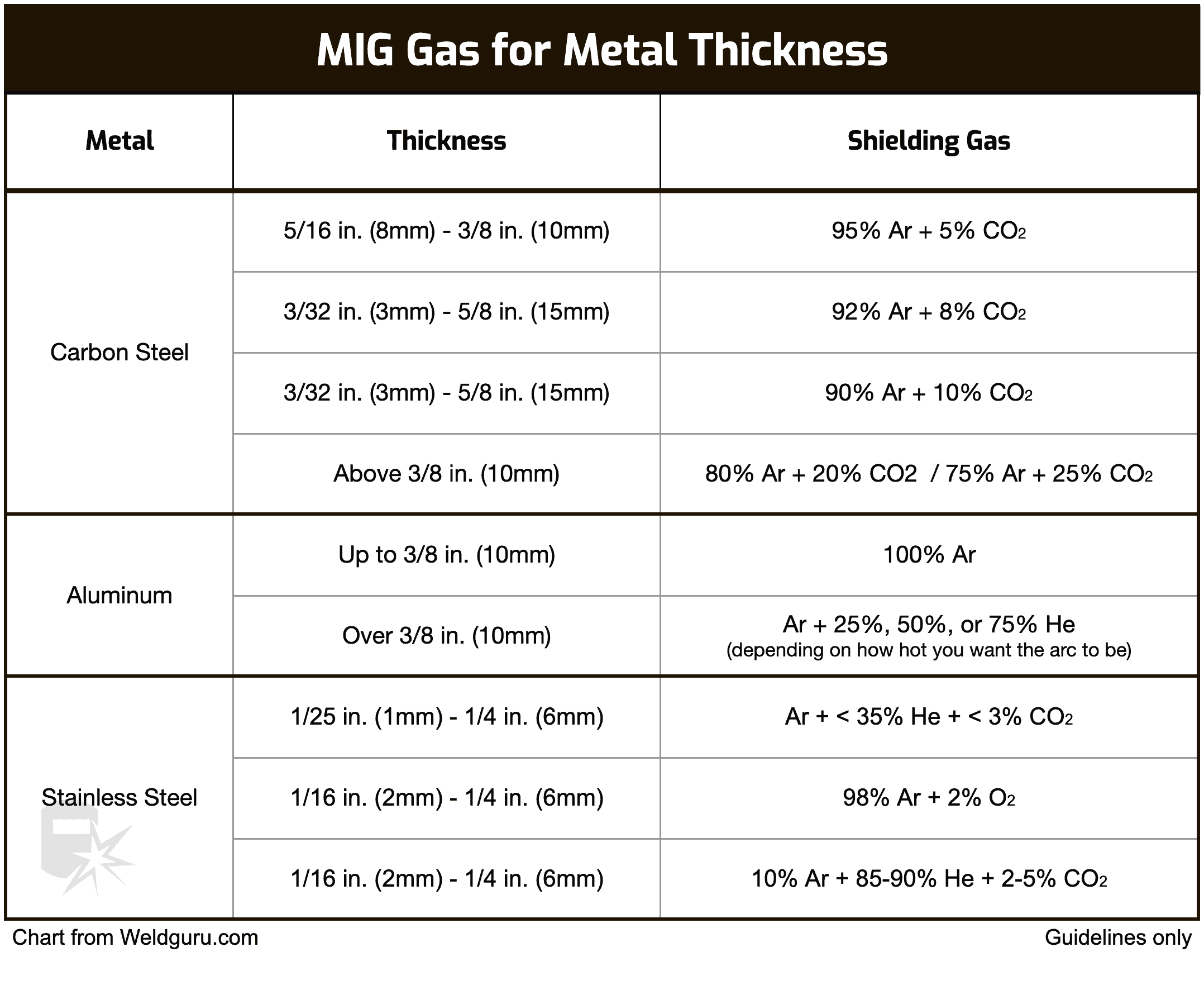
Mig Welding Gas Explained At James Mendoza Blog The most common gas used for mig welding is a 75% argon, 25% co2 mixture. but it is not the only gas you may need. a few other gases are also important. for example, you may see helium blends used to weld thick aluminum. your shielding gas choice significantly impacts the weld quality, arc behavior, productivity, and costs. May 03, 2024. mig (metal inert gas) welding is a cornerstone of modern fabrication, renowned for its efficiency and versatility. an essential part of mig welding success is the selection of welding gas. this comprehensive guide will explore the crucial role mig welding gas plays in welding. you should understand the intricacies of welding gas. Technically, when carbon dioxide or oxygen is used, it is no longer mig, or metal inert gas, welding. it is then mag, or metal active gas, welding. this is because neither carbon dioxide nor oxygen is an inert gas. mig welding utilizes inert shielding gases, such as helium or argon, whereas mag uses active gases instead. Metal inert gas (mig) welding, also known as gas metal arc welding (gmaw), is a popular welding process known for its versatility, speed, and relative ease of use. a critical aspect of mig welding is the choice of shielding gas, which protects the weld pool from atmospheric contamination. the right shielding gas can significantly affect the.
Mig Welding Gas Explained At James Mendoza Blog Technically, when carbon dioxide or oxygen is used, it is no longer mig, or metal inert gas, welding. it is then mag, or metal active gas, welding. this is because neither carbon dioxide nor oxygen is an inert gas. mig welding utilizes inert shielding gases, such as helium or argon, whereas mag uses active gases instead. Metal inert gas (mig) welding, also known as gas metal arc welding (gmaw), is a popular welding process known for its versatility, speed, and relative ease of use. a critical aspect of mig welding is the choice of shielding gas, which protects the weld pool from atmospheric contamination. the right shielding gas can significantly affect the. Metal inert gas (mig) welding, a popular method for joining metals, relies on a shielding gas to protect the weld pool from atmospheric contamination. this gas ensures a clean, strong weld by preventing oxidation during the welding process. the choice of gas can vary based on the materials being welded and the desired properties of the weld. 75% argon, 25% co2. this is one of the best and most commonly used two part blends in mig welding, and there is a reason. as an inert gas, argon provides excellent weld protection combined with fantastic arc stability. however, argon somewhat lacks penetration, and yeah, it is expensive.
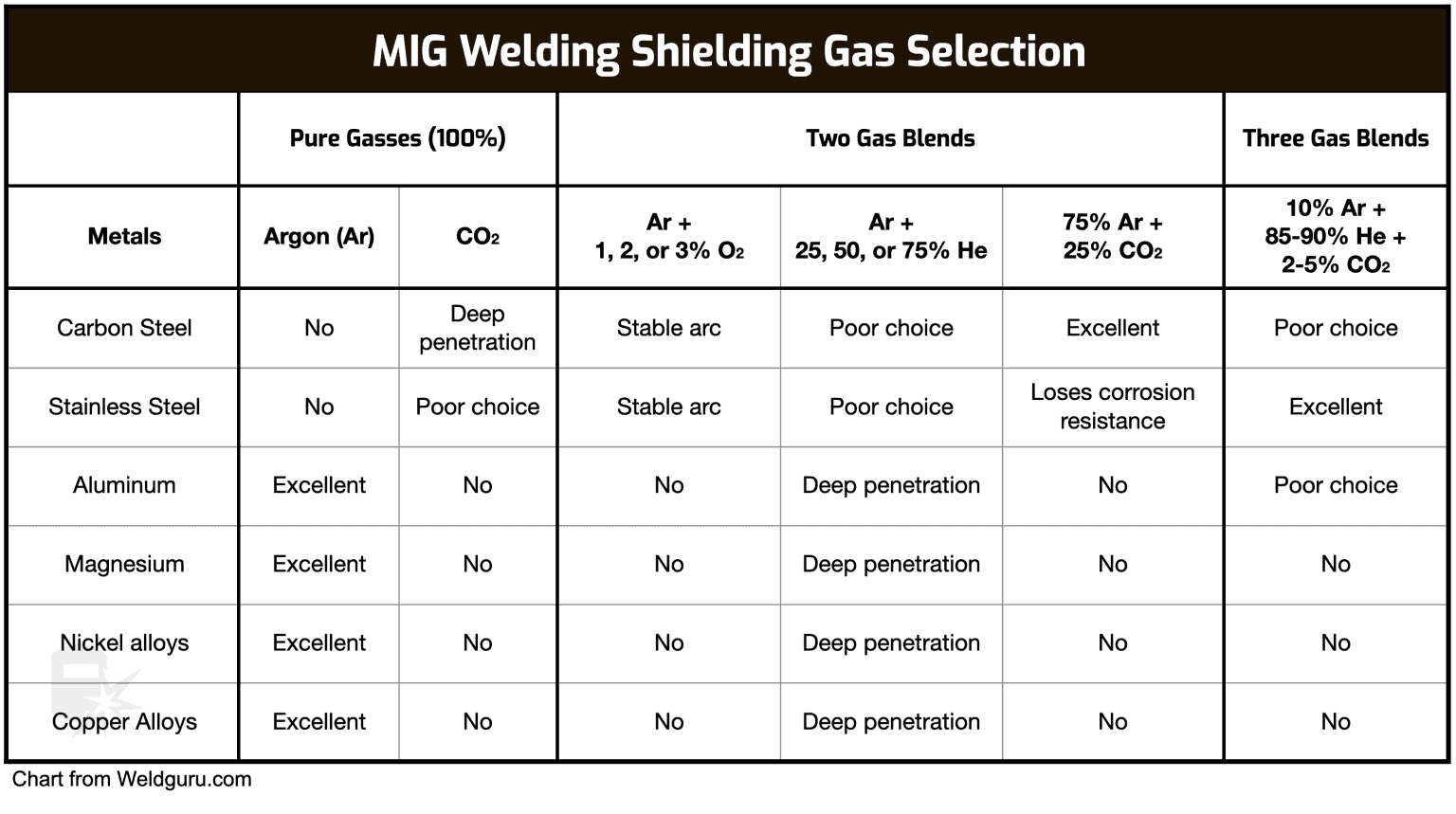
Mig Welding Gas Explained At James Mendoza Blog Metal inert gas (mig) welding, a popular method for joining metals, relies on a shielding gas to protect the weld pool from atmospheric contamination. this gas ensures a clean, strong weld by preventing oxidation during the welding process. the choice of gas can vary based on the materials being welded and the desired properties of the weld. 75% argon, 25% co2. this is one of the best and most commonly used two part blends in mig welding, and there is a reason. as an inert gas, argon provides excellent weld protection combined with fantastic arc stability. however, argon somewhat lacks penetration, and yeah, it is expensive.

Mig Welding Gas Explained At James Mendoza Blog

Comments are closed.