Melanoma Diagnosis Features Sentinel Node Staging
Melanoma Diagnosis Features Sentinel Node Staging Cutaneous melanoma is the fifth most common cancer diagnosis in the united states, and the incidence continues to increase with a projected 110000 new cases in the year 2030 compared to around 65000 new cases in 2011.[1] around 84% of the cases present with localized disease, 9% with involvement of regional lymph nodes, and 4% present with distant metastases at diagnosis.[2]. It includes a clinical and a pathological staging, both consisting of 5 stages (0–iv). the stage of a melanoma is determined by several factors, among which the breslow thickness, the pathological presence or absence of ulceration in the primary tumor, the presence and the number of tumor involved regional lymph nodes, the presence or absence.
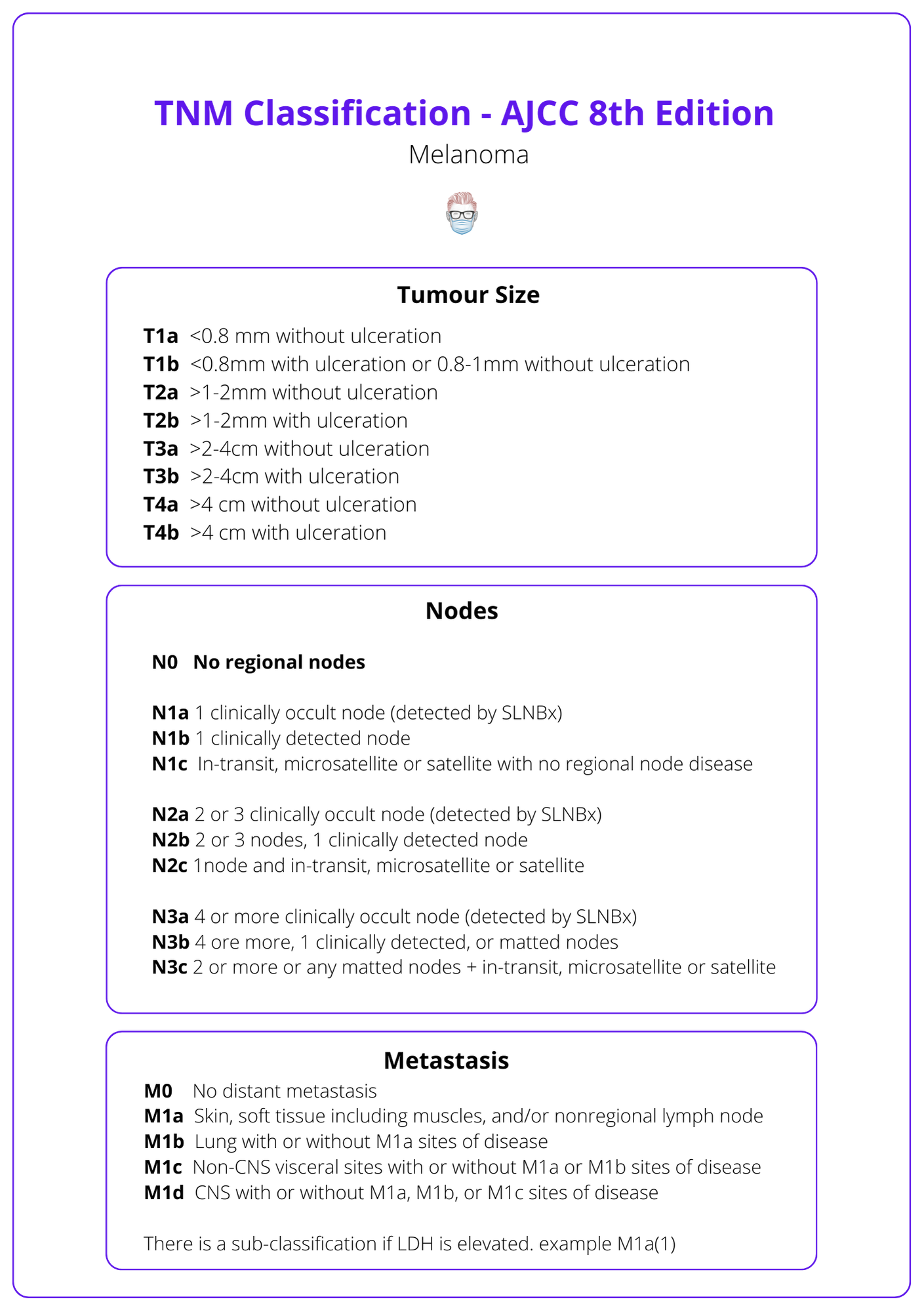
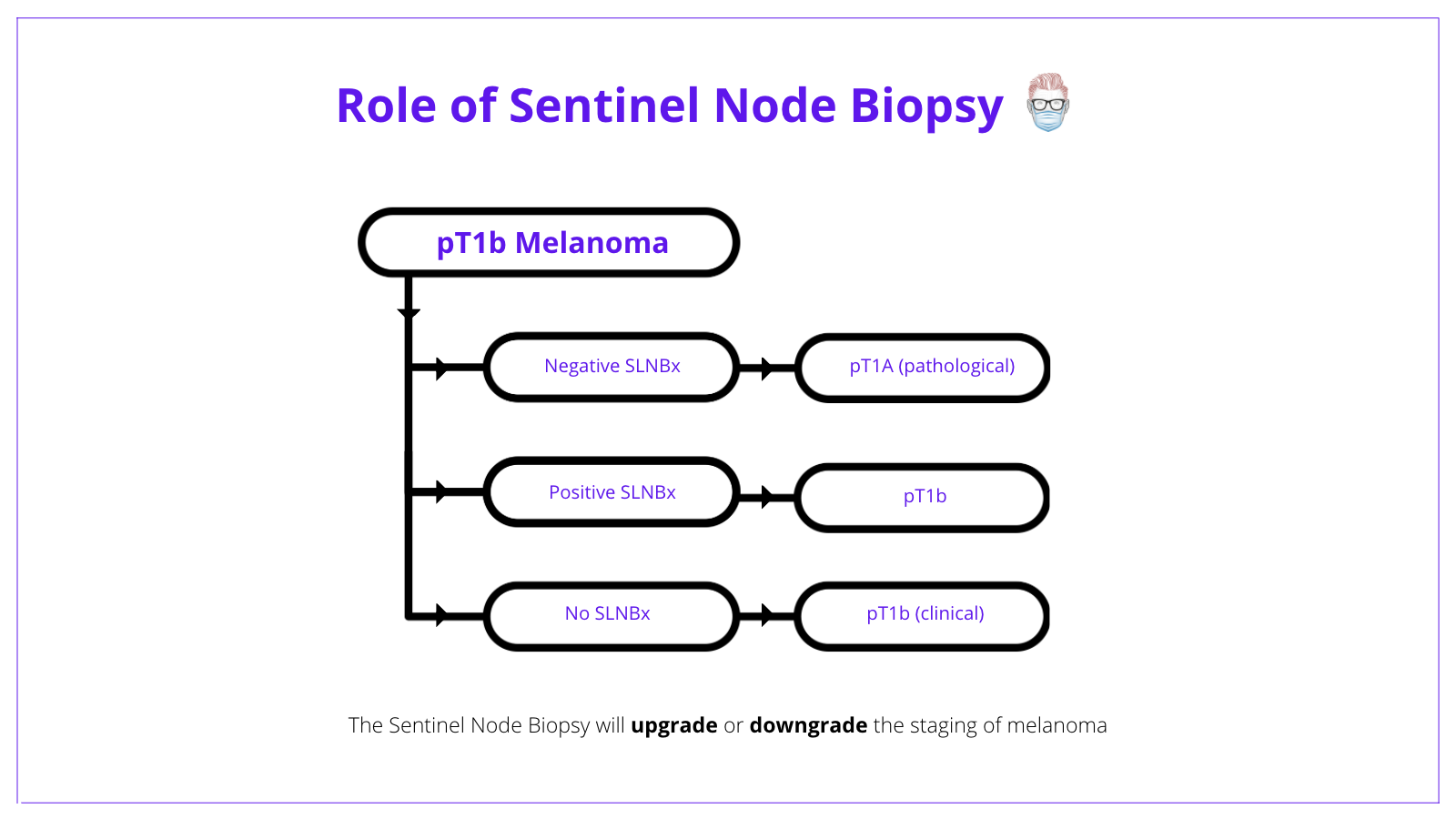
Melanoma Diagnosis Features Sentinel Node Staging Similarly, a melanoma measuring 1.04 mm thick would be recorded as 1.0 mm in the pathology report and designated as t1b for staging. data from a number of large independent data sets supported the. Satellite melanoma is stage 3 cancer that has spread less than 2 centimeters from the primary tumor. in transit melanoma is stage 3 cancer that has spread more than 2 centimeters from the primary melanoma. neither has reached lymph nodes. the treatment is the same for both types. stage 3 melanoma is also grouped into stages 3a, 3b, 3c, and 3d. Purpose the american society of clinical oncology (asco) and society of surgical oncology (sso) sought to provide an evidence based guideline on the use of lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymph node (sln) biopsy in staging patients with newly diagnosed melanoma. methods a comprehensive systematic review of the literature published from january 1990 through august 2011 was completed using. If melanoma cells are found in the sentinel node, the remaining lymph nodes in this area are typically removed and looked at as well. this is known as a lymph node dissection. (see surgery for melanoma skin cancer.) if a lymph node near a melanoma is abnormally large, a sentinel node biopsy probably won’t be needed.

Melanoma Diagnosis Features Sentinel Node Staging Purpose the american society of clinical oncology (asco) and society of surgical oncology (sso) sought to provide an evidence based guideline on the use of lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymph node (sln) biopsy in staging patients with newly diagnosed melanoma. methods a comprehensive systematic review of the literature published from january 1990 through august 2011 was completed using. If melanoma cells are found in the sentinel node, the remaining lymph nodes in this area are typically removed and looked at as well. this is known as a lymph node dissection. (see surgery for melanoma skin cancer.) if a lymph node near a melanoma is abnormally large, a sentinel node biopsy probably won’t be needed. In the evaluation of these cellular markers, care must be taken to ensure that ihc positive cells found within sentinel lymph nodes are correctly identified as metastatic melanoma cells. 83 to clarify a potential misconception, the ajcc eighth edition requires sentinel lymph node biopsy to be defined by abnormal cells that display both melana. Stage iv: the cancer has advanced to distant body areas, lymph nodes or organs, most often the lungs, liver, brain, bone and gastrointestinal tract. the two main ways to determine the degree of advancement in stage iv melanoma are the site of the distant tumors and the presence of elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase (ldh) levels.

Comments are closed.