Maximum Prices Definition Diagrams And Examples Economics Help
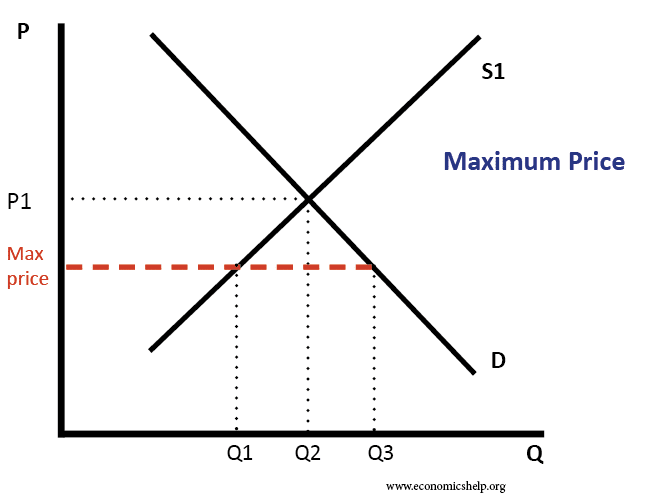
Maximum Prices Definition Diagrams And Examples Economics Help Definition – a maximum price occurs when a government sets a legal limit on the price of a good or service – with the aim of reducing prices below the market equilibrium price. for example, the government may set a maximum price of bread of £1 – or a maximum price of a weekly rent of £150. if the maximum price is set above the. A maximum price will also lead to a shortage – where demand will exceed supply; this leads to waiting lists. in housing it could lead to a rise in homelessness. a maximum price can lead to the emergence of black markets as people try to overcome the shortage of the good and pay well above the market price. examples of maximum prices. food.
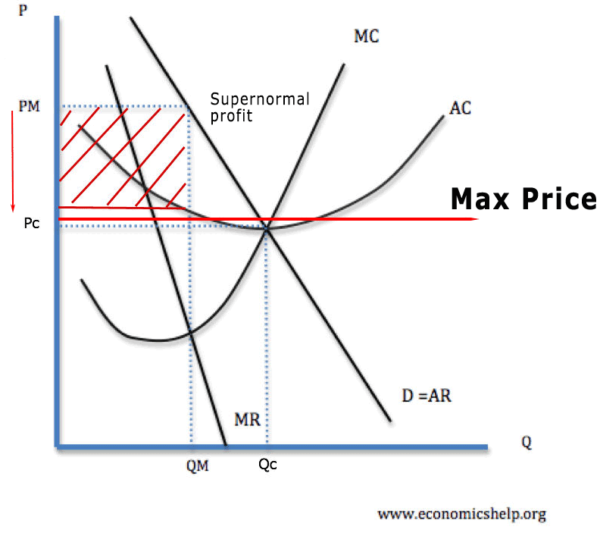
Maximum Prices Definition Diagrams And Examples Economics Help Maximum prices 2021 revision update. level: as, a level, ib. board: aqa, edexcel, ocr, ib, eduqas, wjec. last updated 2 feb 2021. share : in this revision resource we apply, analyse and evaluate the use of maximum prices in markets. in this revision update video we look at six examples of where maximum prices or price caps might or could be. In this video, you will cover the basics of maximum prices and consider the different types of market failure for which they could be used as an appropriate policy measure. maximum price video 1. activity 3: video diagrams for maximum prices. in this activity, we will practise adapting demand and supply diagrams following the introduction of. Price ceiling (maximum price) – the highest possible price that producers are allowed to charge consumers for the good service produced provided set by the government. it must be set below the equilibrium price to have any effect. governments will usually impose price ceilings when they believe that the equilibrium price in the market is too. Types of price controls. minimum prices – prices can’t be set lower (but can be set above) maximum price – limit to how much prices can be raised (e.g. market rent) buffer stocks – where government keep prices within a certain band. limiting price increases – in a privatised monopoly (e.g. electricity, gas, water – where there is no.
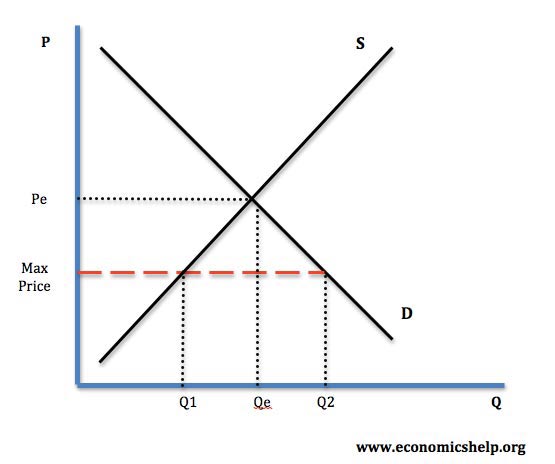
Maximum Prices вђ Definition Diagrams And Examples Economics Help Price ceiling (maximum price) – the highest possible price that producers are allowed to charge consumers for the good service produced provided set by the government. it must be set below the equilibrium price to have any effect. governments will usually impose price ceilings when they believe that the equilibrium price in the market is too. Types of price controls. minimum prices – prices can’t be set lower (but can be set above) maximum price – limit to how much prices can be raised (e.g. market rent) buffer stocks – where government keep prices within a certain band. limiting price increases – in a privatised monopoly (e.g. electricity, gas, water – where there is no. A maximum price is a limit or cap on a price set by a government or an organisation – it is the highest price that can be set by a producer, group of producers or a whole industry. a price below the maximum is acceptable, and no intervention would follow. a maximum price might be considered as providing a benefit to consumers, and while the. In this revision video we walk through the impact of a maximum price on consumer & producer surplus and the deadweight loss of welfare that results. key diagrams maximum prices and consumer welfare. maximum prices as a form of government intervention are becoming more common. a good example is the energy price cap in the uk.

Maximum Prices Definition Diagrams And Examples Economics Help A maximum price is a limit or cap on a price set by a government or an organisation – it is the highest price that can be set by a producer, group of producers or a whole industry. a price below the maximum is acceptable, and no intervention would follow. a maximum price might be considered as providing a benefit to consumers, and while the. In this revision video we walk through the impact of a maximum price on consumer & producer surplus and the deadweight loss of welfare that results. key diagrams maximum prices and consumer welfare. maximum prices as a form of government intervention are becoming more common. a good example is the energy price cap in the uk.
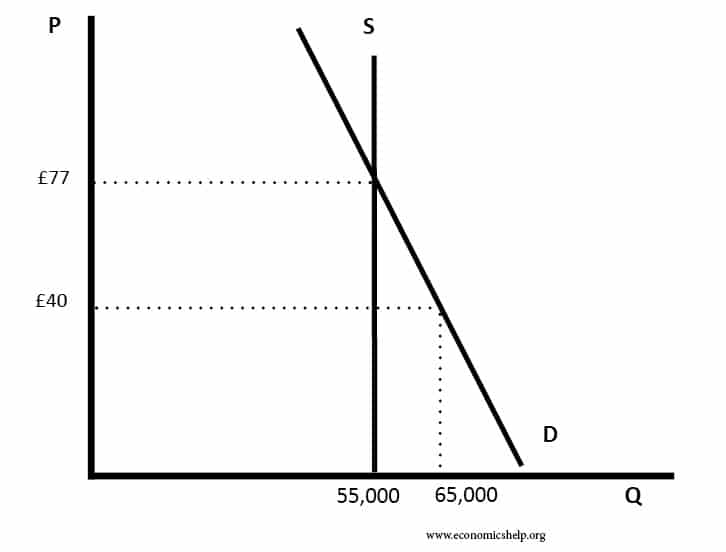
Maximum Prices Definition Diagrams And Examples Economics Help

Comments are closed.