Matrix Addition Subtraction And Laws

M2 Addition And Subtraction Of Matrices Learning Lab The main concept behind the addition or subtraction of two matrices is the addition or subtraction of corresponding terms of the given matrix. similarly, the given method can be generalized for the ‘n’ number of matrices to be added or subtracted. solved examples on matrix addition. example 1: addition of matrices with different order. let,. Rules on adding and subtracting matrices with the same size or dimension. both have two rows and two columns (2×2) with some arbitrary elements or entries. the “formulas” to add and subtract matrices are shown below. have the same “size” or “dimension” because their number of rows and columns are the same. both can be described as a.
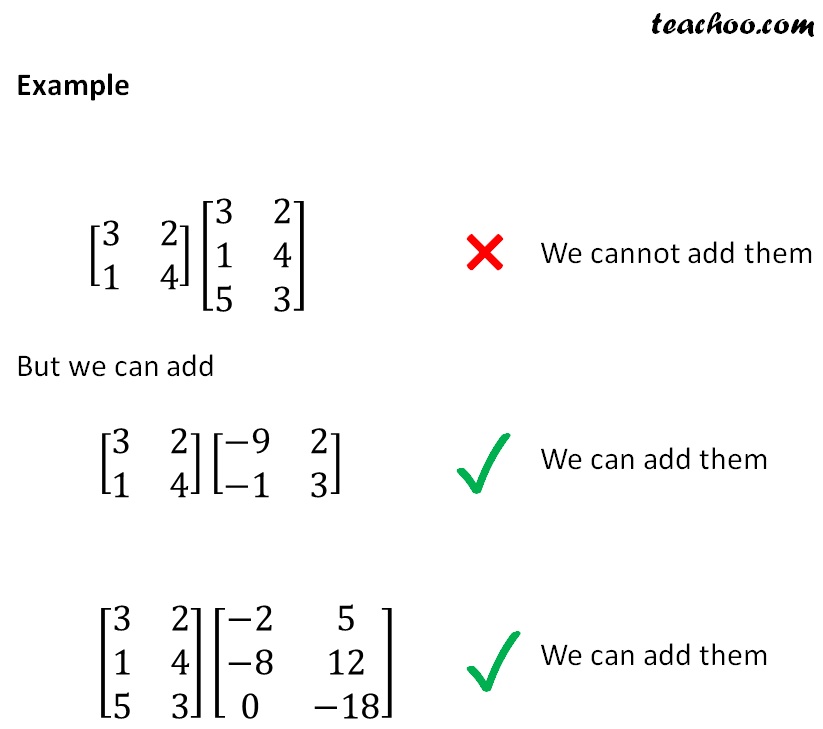
Addition Subtraction Of Matrices With Examples Teachoo The matrices for addition can be either a square matrix or a rectangular matrix, but the matrices should be of the same order. the addition of matrices follows similar properties of the addition of numbers: commutative law, associative law, additive inverse, additive identity, etc. the following properties help in the addition matrix operations. This short lesson covers only matrix addition and a few of its laws. this is the first of many tools we will use to manipulate matrices.timestamps00:00 | int. According to the additive identity property of matrix addition, for a given matrix a of order m*n, there exists an m×n matrix o such that: a o = a = o a. here, o is the m×n order zero matrix. example: let a be a 2×2 matrix, and let i be the 2×2 identity matrix. we want to show that a o = a = o a. Proposition 2.1.1: properties of matrix addition. let a, b and c be matrices. then, the following properties hold. commutative law of addition a b = b a. associative law of addition (a b) c = a (b c) existence of an additive identity there exists a zero matrix 0 such that a 0 = a.

Addition And Subtraction Of Matrices Lecture 3 Youtube According to the additive identity property of matrix addition, for a given matrix a of order m*n, there exists an m×n matrix o such that: a o = a = o a. here, o is the m×n order zero matrix. example: let a be a 2×2 matrix, and let i be the 2×2 identity matrix. we want to show that a o = a = o a. Proposition 2.1.1: properties of matrix addition. let a, b and c be matrices. then, the following properties hold. commutative law of addition a b = b a. associative law of addition (a b) c = a (b c) existence of an additive identity there exists a zero matrix 0 such that a 0 = a. Theorem 2.1.1 2.1. 1: properties of matrix addition and scalar multiplication. the following equalities hold for all m × n m × n matrices a a, b b and c c and scalars k k. be sure that this last property makes sense; it says that if we multiply any matrix by the number 0, the result is the zero matrix, or 0 0. In mathematics, matrix addition is the operation of adding two matrices by adding the corresponding entries together. for a vector, , adding two matrices would have the geometric effect of applying each matrix transformation separately onto , then adding the transformed vectors. however, there are other operations that could also be considered.

Comments are closed.