Material Acceleration
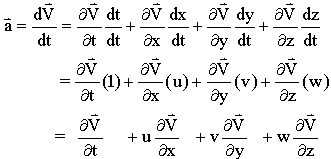
Material Acceleration Material acceleration. the material acceleration is defined as the acceleration following a fluid particle. since acceleration is the time derivative of velocity, the material acceleration can be derived from the definition of material derivative as follows: note that dt dt = 1 by definition, and since a fluid particle is being followed, dx dt. Definition. the material derivative is defined for any tensor field y that is macroscopic, with the sense that it depends only on position and time coordinates, y = y(x, t): where ∇y is the covariant derivative of the tensor, and u(x, t) is the flow velocity. generally the convective derivative of the field u·∇y, the one that contains the.
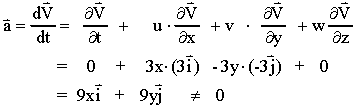
Material Acceleration The material derivative computes the time rate of change of any quantity such as temperature or velocity (which gives acceleration) for a portion of a material moving with a velocity, v v. if the material is a fluid, then the movement is simply the flow field. the sketch to the right shows a fluid flowing through a converging nozzle. 4.2 acceleration field and material derivative the acceleration of a fluid particle is the rate of change of its velocity. in the lagrangian approach the velocity of a fluid particle is a function of time only since we have described its motion in terms of its position vector. ( ) ( ̂ ) ̂ ( ) ̂ ̂ ̂ ̂. Lagrangian accelerations,du dt, and the eulerian acceleration,∂ui ∂t. the former is the acceleration of a particle fluid element within a flow, the rate of increase of the velocity as we travel with the fluid element. on the other hand, the latter is the rate of increase of the velocity at a particular, fixed point in the flow. < 1, there is no inflnite acceleration i.e. no inflnite forces , which is physically consistent. 1.4.1 consequences of continuous flow † material volume remains material. no segment of °uid can be joined or broken apart. † material surface remains material. the interface between two material volumes al ways exists. † material line.

Comments are closed.