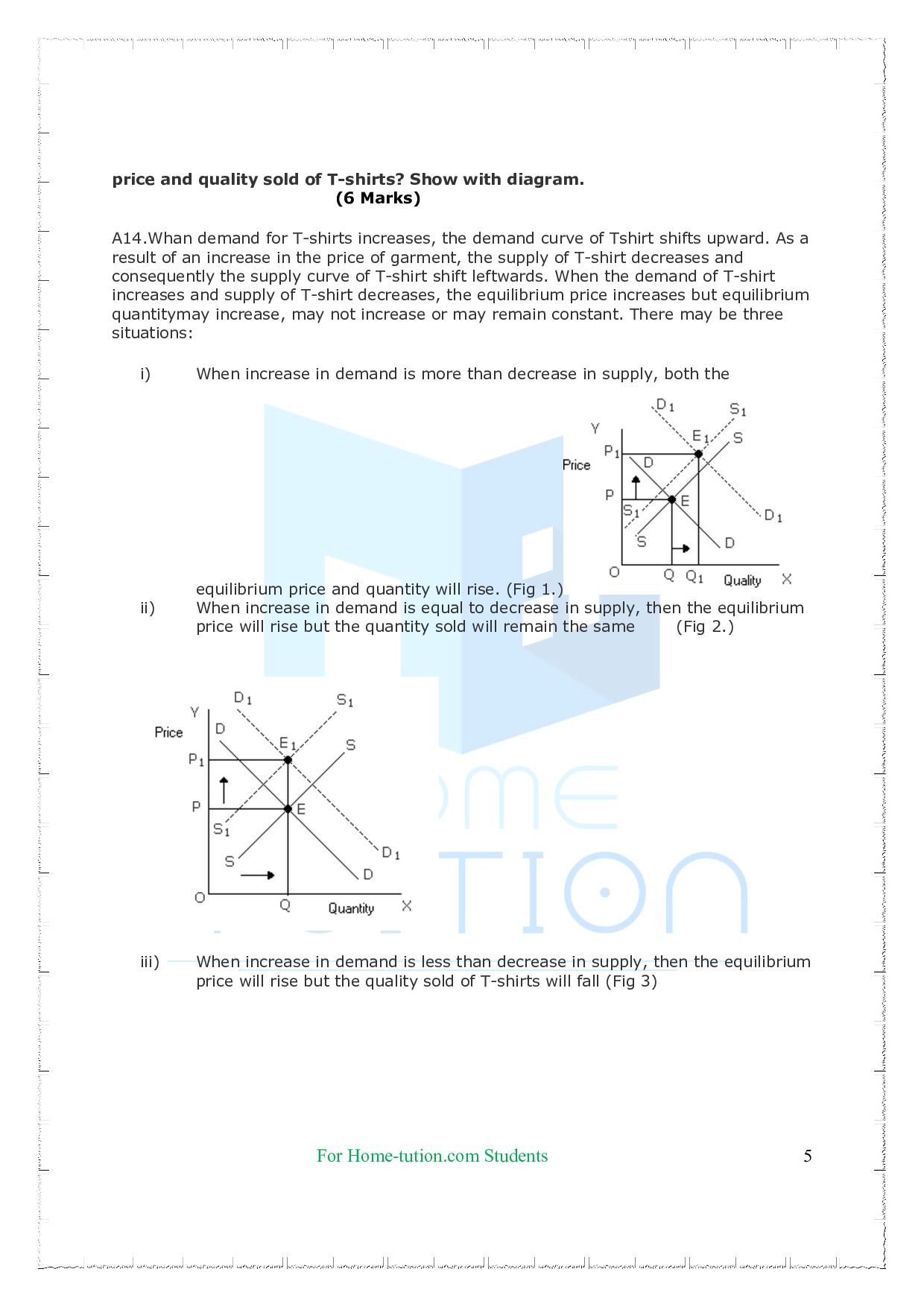
Market Equilibrium Chapter 5 Microeconomics

Ncert Solutions For Class 12 Economics Chapter 5 Market Equilibrium Market equilibrium in this diagram occurs at the intersection of supply and demand, or the intersection of mpc and msb (which is equivalent to mpb). this occurs at q 1. now we know that total private benefits at the market equilibrium are equal to a b c e f and we know that total private cost at the market equilibrium equals c f. Class 11 micro economics chapter 5 market equilibrium. price mechanism: the process of goods and services by demand and supply is called price mechanism. equilibrium: equilibrium means balance or equal. market equilibrium means a point where market demand and market supply are equal. the price at which demand and supply are equal is called.

Ncert Solutions For Class 12 Economics Chapter 5 Market Equilibrium Courses on khan academy are always 100% free. start practicing—and saving your progress—now: khanacademy.org economics finance domain ap macroec. O q'1 q'2 q* q. 2. q. 1 quantity. fig. 5.1market equilibrium with fixed number. of firms. equilibrium occurs at the intersection of the market demand curve dd and market supply. curve ss. the equilibrium quantity is q* and the equilibrium pr. ce is p*. at a price greater than p*, there will be excess supply, and at a price below p*, there will. Access answers to ncert class 12 microeconomics chapter 5. 1. explain market equilibrium. market equilibrium is referred to as that state in the market where supply is equal to demand. when a market is at equilibrium, the corresponding price will not change unless there is an external factor which is instrumental in changing the sup. Cbse class 12 micro economics revision notes. chapter 1 introduction to micro economics. chapter 2 theory of consumer behaviour. chapter 3 production and costs. chapter 4 the theory of the firm under perfect competition. chapter 5 market equilibrium. chapter 6 non competitive markets.

Ncert Solutions For Class 12 Economics Chapter 5 Market Equilibrium Access answers to ncert class 12 microeconomics chapter 5. 1. explain market equilibrium. market equilibrium is referred to as that state in the market where supply is equal to demand. when a market is at equilibrium, the corresponding price will not change unless there is an external factor which is instrumental in changing the sup. Cbse class 12 micro economics revision notes. chapter 1 introduction to micro economics. chapter 2 theory of consumer behaviour. chapter 3 production and costs. chapter 4 the theory of the firm under perfect competition. chapter 5 market equilibrium. chapter 6 non competitive markets. Market equilibrium is the point where the quantity supplied by producers and the quantity demanded by consumers are equal. when we put the demand and supply curves together, we can determine the equilibrium price: the price at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. in figure 10.1, the equilibrium price is shown as p ∗ p ∗. Ncert solutions for class 12 microeconomics chapter 5 market equilibrium. 1. explain market equilibrium. market equilibrium is referred to as that state in the market where supply is equal to demand. when a market is at equilibrium, the corresponding price will not change unless there is an external factor which is instrumental in changing the.
Important Questions For Class 12 Micro Economics Chapter 5 Market Market equilibrium is the point where the quantity supplied by producers and the quantity demanded by consumers are equal. when we put the demand and supply curves together, we can determine the equilibrium price: the price at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. in figure 10.1, the equilibrium price is shown as p ∗ p ∗. Ncert solutions for class 12 microeconomics chapter 5 market equilibrium. 1. explain market equilibrium. market equilibrium is referred to as that state in the market where supply is equal to demand. when a market is at equilibrium, the corresponding price will not change unless there is an external factor which is instrumental in changing the.

Ncert Solution For Class 12 Economics Chapter 5 Market Equilibrium

Comments are closed.