Marginal Utility Theory Economics Help
Marginal Utility Theory Economics Help J.r. hicks developed this theory of ordinal utility. satisfaction of wants. austrian school – von mises also argued it was harder to quantify utility.he proposed that the satisfaction of wants could be measured to some extent but after that it was difficult. related. law of diminishing marginal returns; expected utility theory; marginal analysis. It is the marginal utility of the good divided by its price. the utility gained by spending an additional dollar on good x, for example, is. m u x p x m u x p x. this additional utility is the marginal benefit of spending another $1 on the good. suppose that the marginal utility of good x is 4 and that its price is $2.

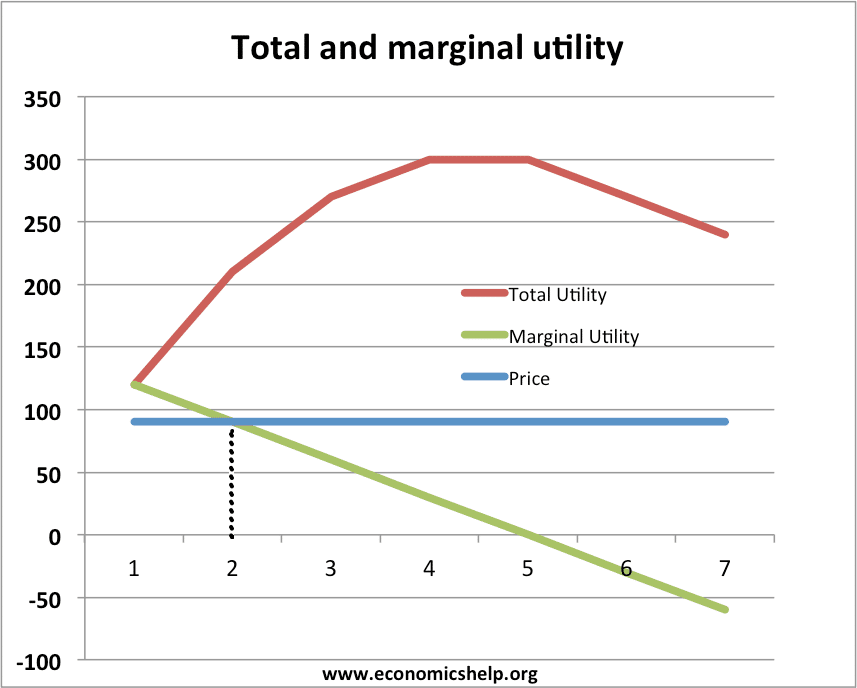
Marginal Utility Theory Economics Help The marginal utility is then zero. the concept of marginal utility grew out of attempts by 19th century economists to analyze and explain the fundamental economic reality of price. these economists believed that price was partly determined by a commodity’s utility—that is, the degree to which it satisfies a consumer’s needs and desires. Marginal utility is the added satisfaction that a consumer gets from having one more unit of a good or service. the concept of marginal utility is used by economists to determine how much of an. With ordinal utility, a person's preferences do not have a unique marginal utility, making the concept of diminishing marginal utility irrelevant. on the other hand, diminishing marginal utility is a significant concept in cardinal utility , which is used to analyse intertemporal choice , choice under uncertainty , and social welfare in modern economic theory. Gives people happiness. utility. • total utility: the total happiness one gets from consuming some amount of a good. • marginal utility: the extra utility derived from consuming one more unit of a good. diminishing marginal utility. • as a household consumes more of a good, the marginal utility of the good declines.

Comments are closed.