Management Of Infants Born To Mothers With Hiv Infection Aafp
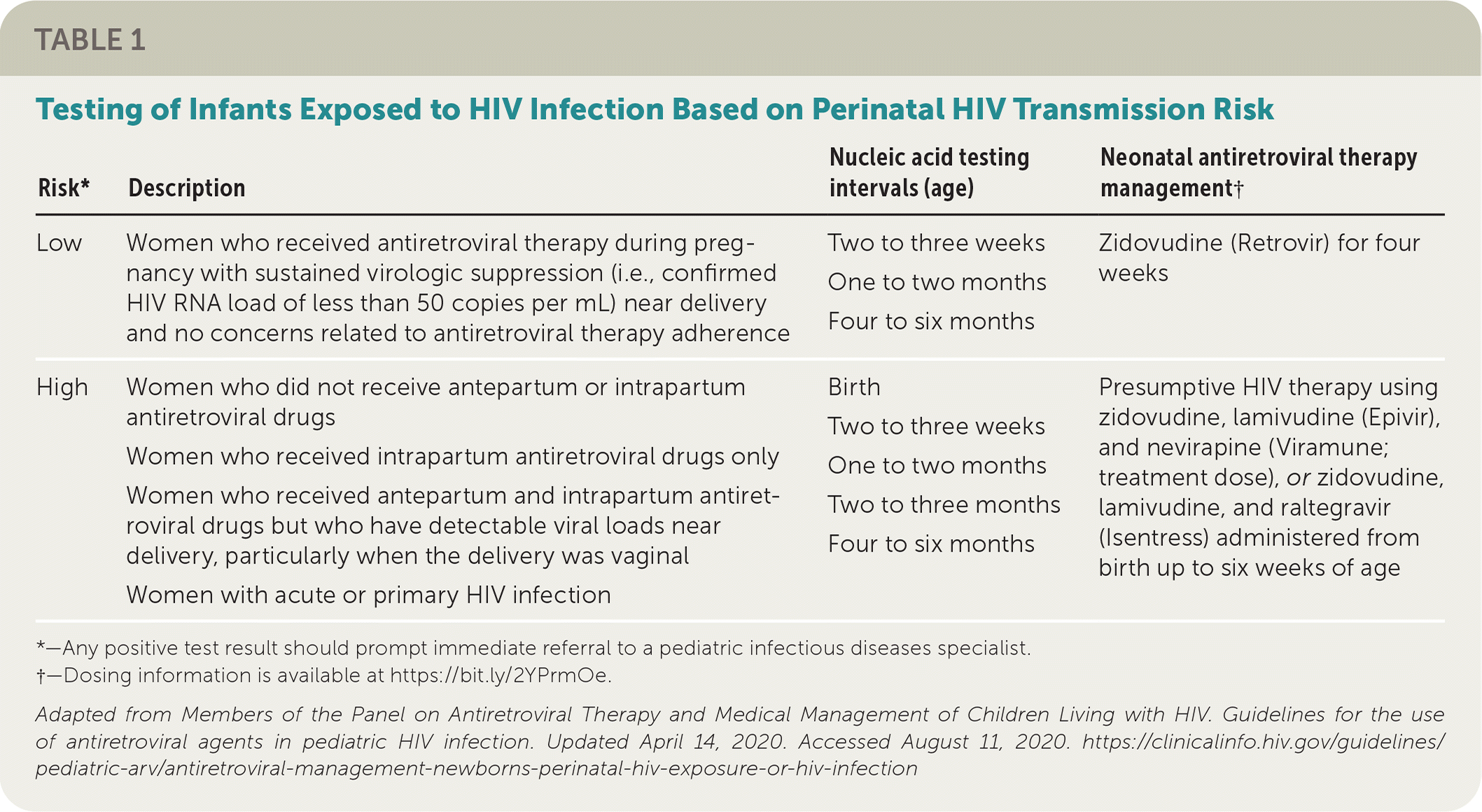
Management Of Infants Born To Mothers With Hiv Infection Aafp Strategies to prevent mother to child transmission include maternal and infant antiretroviral therapy and formula feeding instead of breastfeeding. all infants born to mothers with hiv infection. Elivery.12,14,16management of the infant after deliveryall infants born to mothers with hiv infec tion should receive antiretroviral postexposure prophylaxis a. soon as possible, ideally within.
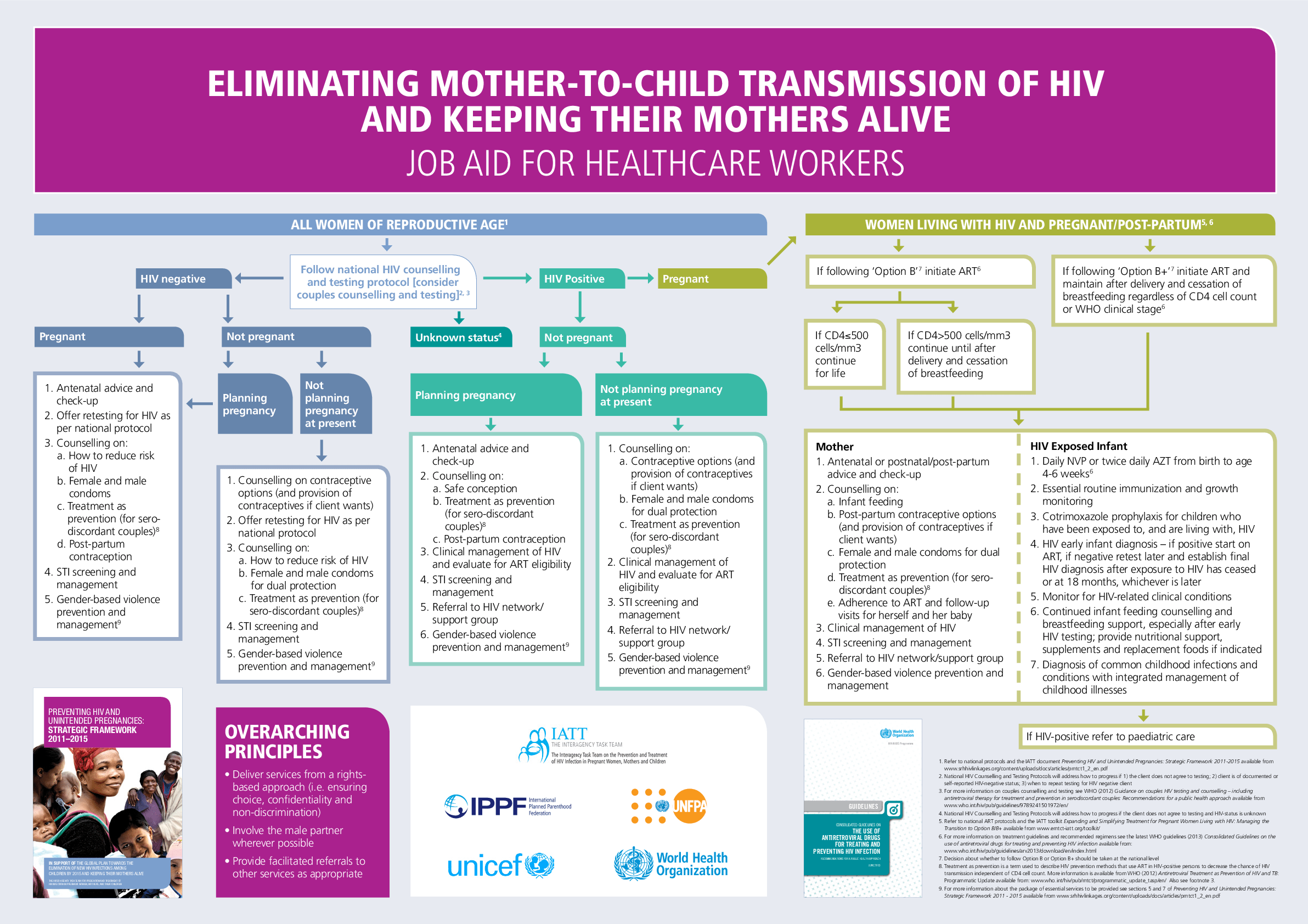
Eliminating Mother To Child Transmission Of Hiv And Keeping Their Infants born to hiv infected mothers should receive zidovu dine in a dosage of 2 mg per kg every six hours, beginning eight hours after birth and continuing for at least six weeks. Strategies to prevent mother to child transmission include maternal and infant antiretroviral therapy and formula feeding instead of breastfeeding. all infants born to mothers with hiv infection should receive antiretroviral postexposure prophylaxis as soon as possible, ideally within six hours after delivery. the type of prophylaxis depends on. Pediatricians play a crucial role in optimizing the prevention of perinatal transmission of hiv infection. pediatricians provide antiretroviral prophylaxis to infants born to women with hiv type 1 (hiv) infection during pregnancy and to those whose mother’s status was first identified during labor or delivery. infants whose mothers have an undetermined hiv status should be tested for hiv. Initial postnatal management of the neonate exposed to hiv. all newborns perinatally exposed to hiv should receive appropriate antiretroviral (arv) drugs as soon as possible, preferably within 6 hours, after delivery (see antiretroviral management of infants with perinatal hiv exposure or hiv infection) (ai). for infants in whom presumptive hiv.

Ambulatory Care Of Infants And Children Born To Hiv Infected Mothers Pediatricians play a crucial role in optimizing the prevention of perinatal transmission of hiv infection. pediatricians provide antiretroviral prophylaxis to infants born to women with hiv type 1 (hiv) infection during pregnancy and to those whose mother’s status was first identified during labor or delivery. infants whose mothers have an undetermined hiv status should be tested for hiv. Initial postnatal management of the neonate exposed to hiv. all newborns perinatally exposed to hiv should receive appropriate antiretroviral (arv) drugs as soon as possible, preferably within 6 hours, after delivery (see antiretroviral management of infants with perinatal hiv exposure or hiv infection) (ai). for infants in whom presumptive hiv. Although hiv 1 group m subtype b is the predominant viral subtype found in the united states, multiple subtypes and recombinant forms also are found in the united states. 62 data from the cdc national hiv surveillance system (nhss) showed that the number of non u.s. born children with hiv has exceeded the number of u.s. born children with hiv. Effective prevention strategies have reduced the risk of perinatal transmission of human immunodeficiency virus (hiv) infection to less than 1% to 2% in the united states, but failures to fully implement these strategies result in continued preventable infant hiv infections. in addition, the increasing number of sexually acquired hiv infections in adolescents underscores the important role of.

Initial Management Of Patients With Hiv Infection Aafp Although hiv 1 group m subtype b is the predominant viral subtype found in the united states, multiple subtypes and recombinant forms also are found in the united states. 62 data from the cdc national hiv surveillance system (nhss) showed that the number of non u.s. born children with hiv has exceeded the number of u.s. born children with hiv. Effective prevention strategies have reduced the risk of perinatal transmission of human immunodeficiency virus (hiv) infection to less than 1% to 2% in the united states, but failures to fully implement these strategies result in continued preventable infant hiv infections. in addition, the increasing number of sexually acquired hiv infections in adolescents underscores the important role of.

Comments are closed.