Lipid Profiles Of Neurons Glia Cells Lipidomic Profiles Of Neural
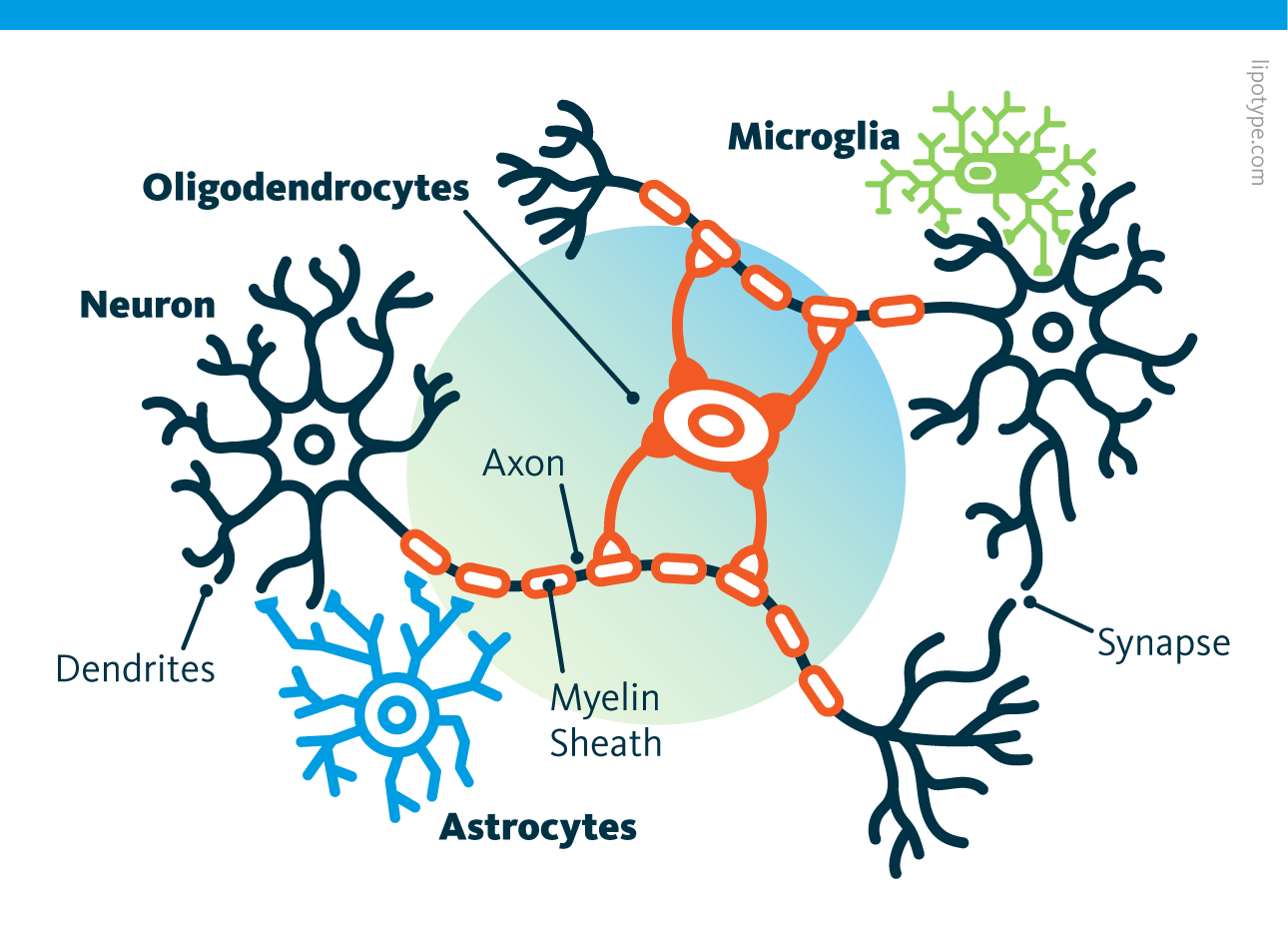
Lipid Profiles Of Neurons Glia Cells Lipidomic Profiles Of Neural Summary. • lipids account for over 50% of human brain dry weight. • a cell type resolved molecular assessment of neural cells. • lipidomics revealed specific lipid profiles for neurons and glia cell types. about 75% of all mammalian lipid species are exclusively found in neural tissues. in their variety, lipids contribute to the. Lipid shuttling between neurons and glia contributes to the development, function, and stress responses of the nervous system. to understand how a neuron acquires its lipid supply from specific.
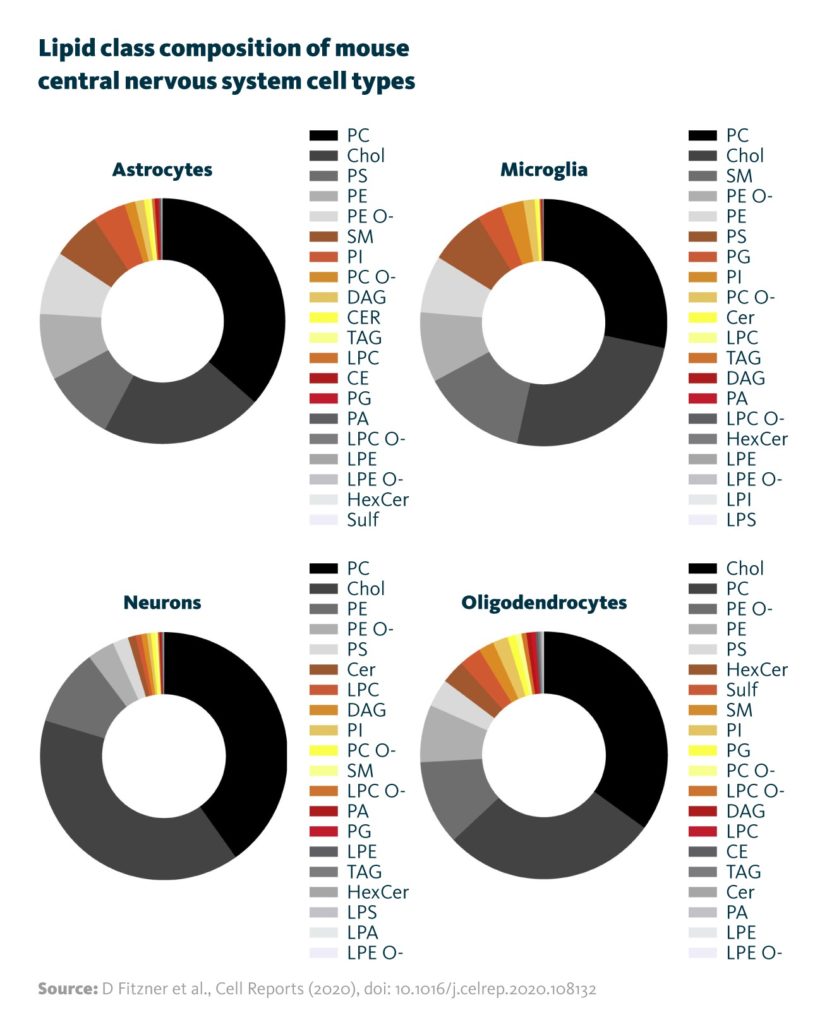
Lipid Profiles Of Neurons Glia Cells Lipidomic Profiles Of Neural We quantified around 700 lipid species and evaluated lipid features such as fatty acyl chain length, hydroxylation, and number of acyl chain double bonds (dbs) to obtain a detailed cell type and brain region resolved profile of cns lipid composition. we correlated the lipidomic dataset obtained with proteomic data. For lipidomic profiling, 100,000 neurons, 100,000 ap1 neg glia and 35,000 ap1 glia were collected per replicate, with 5–6 replicates per cell type. cells were immediately frozen at −80 °c. Lipid molecules are key components of the brain's complex structure and function, with lipids comprising around 50% of the brain's dry weight. the lipid composition of neuronal and glial cell membranes has been shown to affect cell function and neurotransmission (o'brien and sampson, 1965; puchkov and haucke, 2013). The goal of neural lipidomics is to understand how large scale changes in lipid profiles affect neuronal and glial cell function. membrane lipids adopt characteristic molecular shapes — conical.
Lipid Profiles Of Neurons Glia Cells Lipidomic Profiles Of Neural Lipid molecules are key components of the brain's complex structure and function, with lipids comprising around 50% of the brain's dry weight. the lipid composition of neuronal and glial cell membranes has been shown to affect cell function and neurotransmission (o'brien and sampson, 1965; puchkov and haucke, 2013). The goal of neural lipidomics is to understand how large scale changes in lipid profiles affect neuronal and glial cell function. membrane lipids adopt characteristic molecular shapes — conical. Using lipidomics coupled with immunostaining, litvinchuk et al. demonstrate that apoe promotes changes in cholesterol metabolism and lipid accumulation in glia of 9.5 month old p301s mice. lxr agonist gw3965 diet and abca1 overexpression markedly decrease tauopathy, neurodegeneration, synapse loss and behavioral deficits, neuroinflammation, and glial lipid accumulation in 9.5 month old p301s. The ability of glial cells to protect neurons by internalizing toxic lipids released by neurons may be a common feature of neurodegeneration that includes motor neuron disease. further studies are required to understand how these hsp associated proteins regulate lipid droplet turnover and how this contributes to motor neuron degeneration.
Lipid Profiles Of Neurons Glia Cells Lipidomic Profiles Of Neural Using lipidomics coupled with immunostaining, litvinchuk et al. demonstrate that apoe promotes changes in cholesterol metabolism and lipid accumulation in glia of 9.5 month old p301s mice. lxr agonist gw3965 diet and abca1 overexpression markedly decrease tauopathy, neurodegeneration, synapse loss and behavioral deficits, neuroinflammation, and glial lipid accumulation in 9.5 month old p301s. The ability of glial cells to protect neurons by internalizing toxic lipids released by neurons may be a common feature of neurodegeneration that includes motor neuron disease. further studies are required to understand how these hsp associated proteins regulate lipid droplet turnover and how this contributes to motor neuron degeneration.

Comments are closed.