Line Integral From Vector Calculus Over A Closed Curve

Engineering Math Sharetechnote Vector line integrals are integrals of a vector field over a curve in a plane or in space. let’s look at scalar line integrals first. a scalar line integral is defined just as a single variable integral is defined, except that for a scalar line integral, the integrand is a function of more than one variable and the domain of integration is a. 2. this is just a little question. suppose you want to evaluate an integral around a closed path formed by a curve c(t) (only one curve), i suspect that the result would be 0, because you will do an integral from the point p to the same point. so for example if p = c(a), then your integral is ∫cf = ∫a af(c(t)) ⋅ c ′ (t)dt = 0.

Closed Curve Line Integrals Of Conservative Vector Fields Line integrals of vector fields over closed curves (relevant section from stewart, calculus, early transcendentals, sixth edition: 16.3) recall the basic idea of the generalized fundamental theorem of calculus: if f is a gradient or conservative vector field – here, we’ll simply use the fact that it is a gradient field, i.e., f = ~∇ f for. Free ebook tinyurl engmathyti present an example where i calculate the line integral of a given vector function over a closed curve in particul. Section 16.4 : line integrals of vector fields. in the previous two sections we looked at line integrals of functions. in this section we are going to evaluate line integrals of vector fields. we’ll start with the vector field, →f (x,y,z) =p (x,y,z)→i q(x,y,z)→j r(x,y,z)→k f → (x, y, z) = p (x, y, z) i → q (x, y, z) j → r. 6.2.1 calculate a scalar line integral along a curve. 6.2.2 calculate a vector line integral along an oriented curve in space. 6.2.3 use a line integral to compute the work done in moving an object along a curve in a vector field. 6.2.4 describe the flux and circulation of a vector field.

Multivariable Calculus Closed Curve Line Integral Over Conservat Section 16.4 : line integrals of vector fields. in the previous two sections we looked at line integrals of functions. in this section we are going to evaluate line integrals of vector fields. we’ll start with the vector field, →f (x,y,z) =p (x,y,z)→i q(x,y,z)→j r(x,y,z)→k f → (x, y, z) = p (x, y, z) i → q (x, y, z) j → r. 6.2.1 calculate a scalar line integral along a curve. 6.2.2 calculate a vector line integral along an oriented curve in space. 6.2.3 use a line integral to compute the work done in moving an object along a curve in a vector field. 6.2.4 describe the flux and circulation of a vector field. Out of the four fundamental theorems of vector calculus, three of them involve line integrals of vector fields. green's theorem and stokes' theorem relate line integrals around closed curves to double integrals or surface integrals. if you have a conservative vector field, you can relate the line integral over a curve to quantities just at the. In qualitative terms, a line integral in vector calculus can be thought of as a measure of the total effect of a given tensor field along a given curve. for example, the line integral over a scalar field (rank 0 tensor) can be interpreted as the area under the field carved out by a particular curve. this can be visualized as the surface created.

Line Integral From Vector Calculus Over A Closed Curve Youtube Out of the four fundamental theorems of vector calculus, three of them involve line integrals of vector fields. green's theorem and stokes' theorem relate line integrals around closed curves to double integrals or surface integrals. if you have a conservative vector field, you can relate the line integral over a curve to quantities just at the. In qualitative terms, a line integral in vector calculus can be thought of as a measure of the total effect of a given tensor field along a given curve. for example, the line integral over a scalar field (rank 0 tensor) can be interpreted as the area under the field carved out by a particular curve. this can be visualized as the surface created.
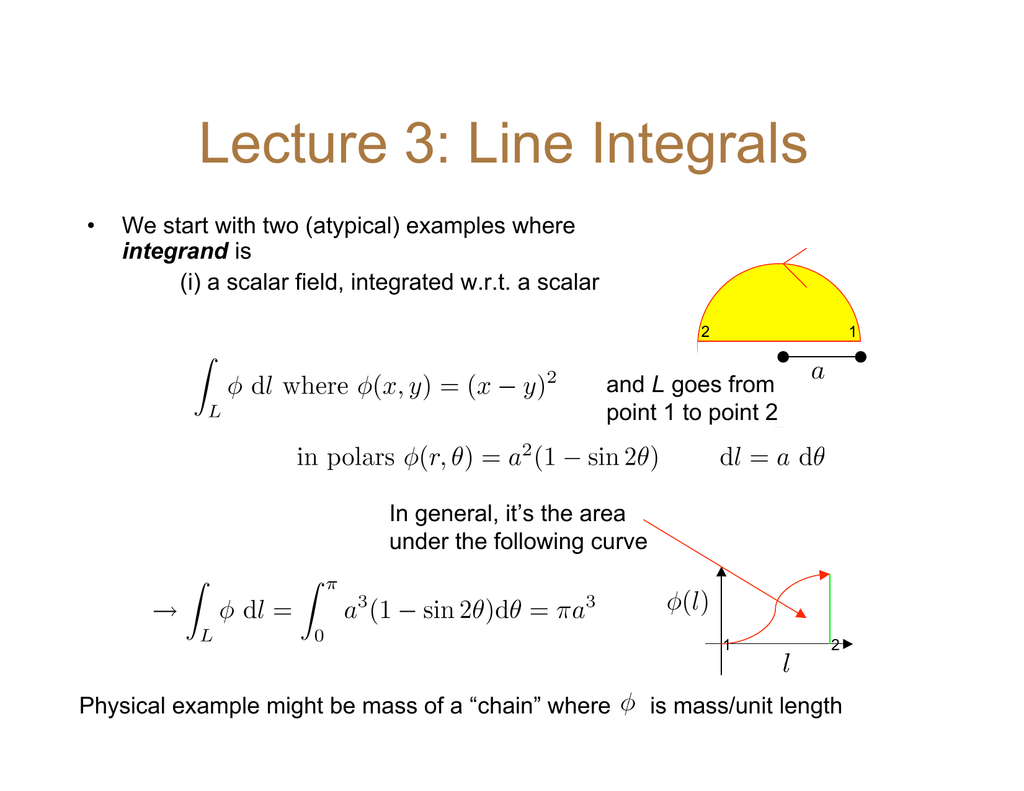
Lecture 3 Line Integrals

Comments are closed.