Learn The Six Plant Growth Stages
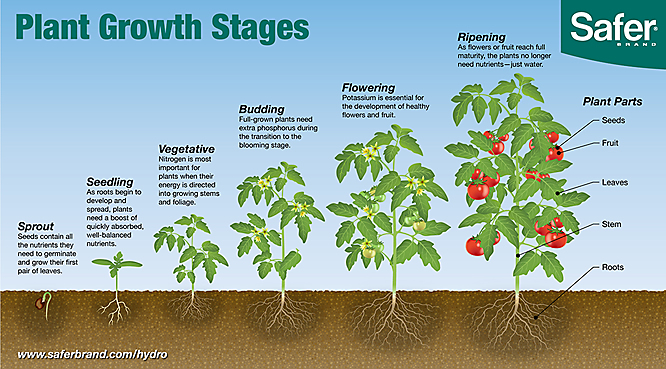
Learn The Six Plant Growth Stages Plant growth stages. 1 sprout. seeds contain all the nutrients they need to germinate and grow their first pair of leaves. 2 seeding. as roots begin to develop and spread, plants need a bost of quickly absorbed, well balanced nutrients. 3 vegetative. nitrogen is most important for plants when their energy is directed into growing stems and foliage. Key takeaways. – plants go through different stages of growth from seed to seed, which are called the plant life cycle. – the main stages of a plant’s life cycle are seed, germination, seedling, adult plant, pollination, and seed dispersal. – different types of plants have different life cycles, depending on their shape, size, lifespan.
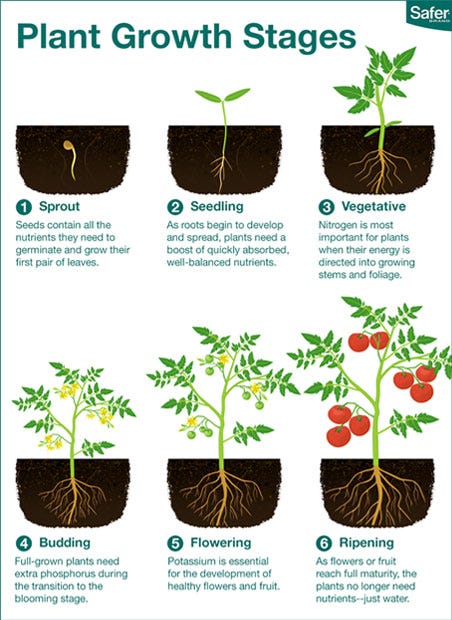
Learn The Six Plant Growth Stages In this case, they might only use 5 stages: 5 stages of plant growth: germination; leafy growth; budding; flower; harvest; and along these same lines – some crops also have very delicate needs in the early stages of their development, so food producers might include an extra seedling stage, leaving us with 6 stages: 6 stages of plant growth. 5. ripening. after pollination, the plant’s flowers start to produce fruit. the fruits contain the plant’s seeds. this is the final stage in the plant’s life cycle and marks the beginning of a new generation of plants. in the vegetable and fruit gardens, this is the most productive of all the plant growth stages. 2. seedling. during this period, sprouts grow into a baby plant producing roots and true leaves that are smaller versions of the leaves found in mature plants. a supply of well balanced nutrients helps the seedling to grow fast. 3. vegetative. plants in this stage develop sturdy stems and green leafy growth. The plant life cycle describes the stages that the plant goes through from its birth until its death. they are found in all types of plants; flowering or non flowering and vascular or nonvascular. in flowering plants, the process starts with seed formation, which then germinates to give rise to a new plant. the young plant gradually matures to.
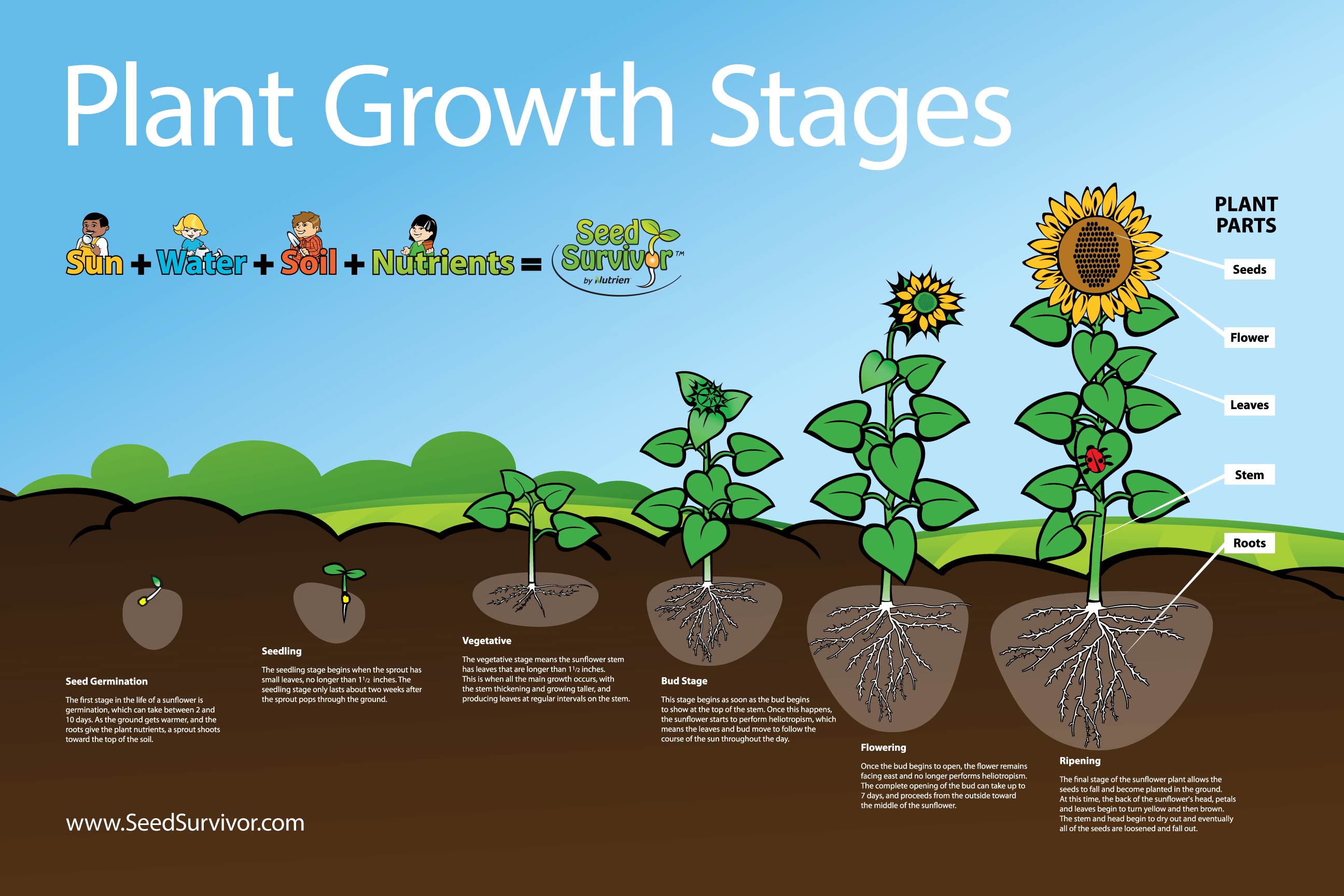
Posters Seed Survivor 2. seedling. during this period, sprouts grow into a baby plant producing roots and true leaves that are smaller versions of the leaves found in mature plants. a supply of well balanced nutrients helps the seedling to grow fast. 3. vegetative. plants in this stage develop sturdy stems and green leafy growth. The plant life cycle describes the stages that the plant goes through from its birth until its death. they are found in all types of plants; flowering or non flowering and vascular or nonvascular. in flowering plants, the process starts with seed formation, which then germinates to give rise to a new plant. the young plant gradually matures to. 3. vegetative stage: growth and development. next in the stages of plant growth is the vegetative stage. plants invest energy in root development to maintain and expand their root system. as the roots grow and branch out, they explore a larger soil volume, seeking essential elements for healthy growth. Fertilization process in plant growth. after pollination, a pollen tube grows in the plant’s ovary. the sperm of the male gamete cells then move along the pollen tube toward the ovary to fertilize the female gamete cell. once the cell is fertilized, a zygote is formed, which develops into an embryo.

Learn The Six Plant Growth Stages 3. vegetative stage: growth and development. next in the stages of plant growth is the vegetative stage. plants invest energy in root development to maintain and expand their root system. as the roots grow and branch out, they explore a larger soil volume, seeking essential elements for healthy growth. Fertilization process in plant growth. after pollination, a pollen tube grows in the plant’s ovary. the sperm of the male gamete cells then move along the pollen tube toward the ovary to fertilize the female gamete cell. once the cell is fertilized, a zygote is formed, which develops into an embryo.

Comments are closed.