Kirchhoffs Voltage Law Kvl Circuits Loop Rule Ohms Law Series Circuits Physics

Kirchhoff S Voltage Law Kvl Circuits Loop Rule Ohm S Kirchhoff’s voltage law states that the algebraic sum of the potential differences in any loop must be equal to zero as: Σv = 0. since the two resistors, r1 and r2 are wired together in a series connection, they are both part of the same loop so the same current must flow through each resistor. thus the voltage drop across resistor, r 1 = i. Consider this absurd example, tracing “loop” 2 3 6 3 2 in the same parallel resistor circuit: using kirchhoff’s voltage law in a complex circuit. kvl can be used to determine an unknown voltage in a complex circuit, where all other voltages around a particular “loop” are known.

Kirchhoff S Voltage Law Kvl Explained This physics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into kirchoff's voltage law which states that the sum of all the voltages in a loop must add to zer. The sum of all currents entering a junction must equal the sum of all currents leaving the junction: ∑iin = ∑iout. ∑ i i n = ∑ i o u t. (10.4.1) kirchhoff’s second rule—the loop rule. the algebraic sum of changes in potential around any closed circuit path (loop) must be zero: ∑v = 0. ∑ v = 0. (10.4.2). Example 20.3.1 20.3. 1: illustrates the changes in potential in a simple series circuit loop. kirchhoff’s second rule requires emf−ir−ir 1 −ir 2 =0. rearranged, this is emf=ir ir 1 ir 2, meaning that the emf equals the sum of the ir (voltage) drops in the loop. Lecture 5 6: circuit analysis kvl, loop analysis. define kirchhoff's voltage law (kvl) compute currents in simple circuits using kvl and ohm's law. use loop analysis method to compute loop currents. derive voltage division formula and analyze the limitations of of voltage divider. in practice we can encounter circuits that may have several.
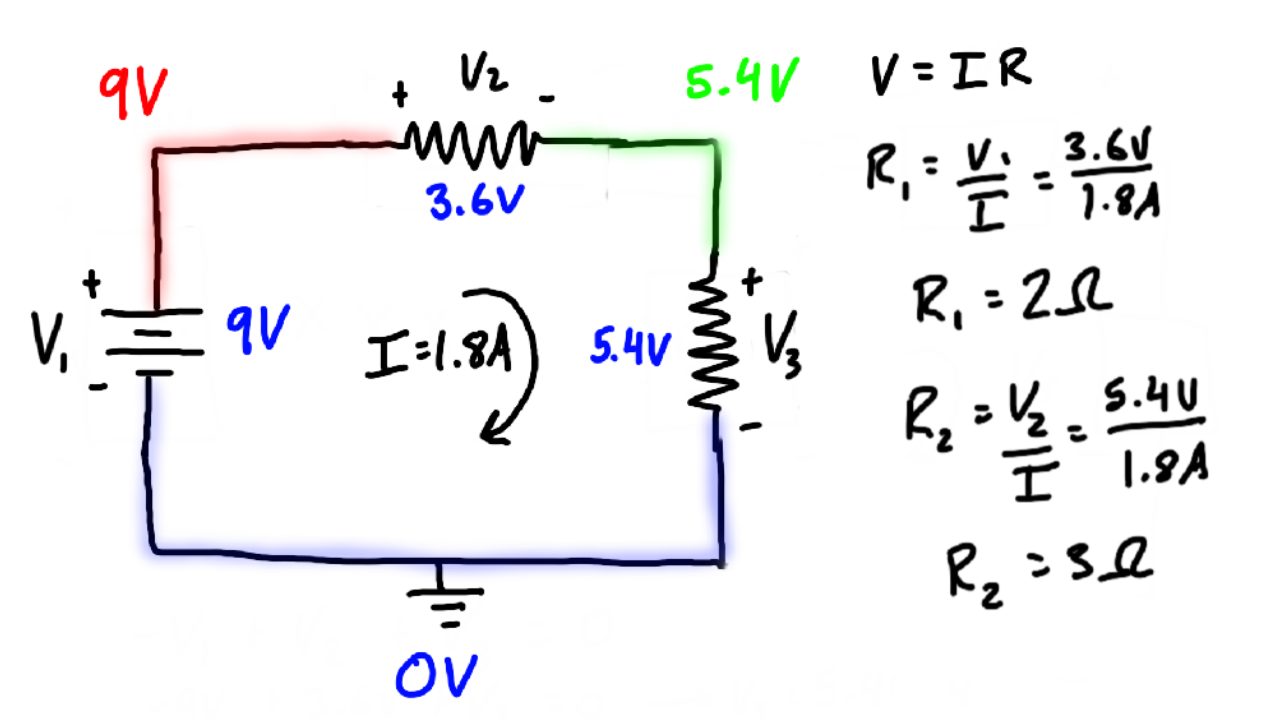
Kirchhoff S Voltage Law Kvl Engineer4free The 1 Source For Free Example 20.3.1 20.3. 1: illustrates the changes in potential in a simple series circuit loop. kirchhoff’s second rule requires emf−ir−ir 1 −ir 2 =0. rearranged, this is emf=ir ir 1 ir 2, meaning that the emf equals the sum of the ir (voltage) drops in the loop. Lecture 5 6: circuit analysis kvl, loop analysis. define kirchhoff's voltage law (kvl) compute currents in simple circuits using kvl and ohm's law. use loop analysis method to compute loop currents. derive voltage division formula and analyze the limitations of of voltage divider. in practice we can encounter circuits that may have several. Kirchhoff's circuit laws are two equalities that deal with the current and potential difference (commonly known as voltage) in the lumped element model of electrical circuits. they were first described in 1845 by german physicist gustav kirchhoff. [1] this generalized the work of georg ohm and preceded the work of james clerk maxwell. The voltage divider rule (vdr) along with ohm's law, the key law governing series circuits is kirchhoff's voltage law, or kvl. named after nineteenth century german physicist gustav kirchhoff, this law states that the sum of voltage rises and voltage drops around a series loop must equal zero (the rises and drops having opposite polarities).

юааkirchhoffтащsюаб юааvoltageюаб юааlawюаб юааkvlюаб Electrical Academia Kirchhoff's circuit laws are two equalities that deal with the current and potential difference (commonly known as voltage) in the lumped element model of electrical circuits. they were first described in 1845 by german physicist gustav kirchhoff. [1] this generalized the work of georg ohm and preceded the work of james clerk maxwell. The voltage divider rule (vdr) along with ohm's law, the key law governing series circuits is kirchhoff's voltage law, or kvl. named after nineteenth century german physicist gustav kirchhoff, this law states that the sum of voltage rises and voltage drops around a series loop must equal zero (the rises and drops having opposite polarities).

Kirchhoff S Voltage Law Kvl Example Electrical Circuit Diagram Basic

Comments are closed.