Key Skill Calculate Probabilities Using A Venn Diagram

Key Skill Calculate Probabilities Using A Venn Diagram Youtube "calculate probabilities using a venn diagram.". Example 6: organizing data using venn diagrams to find probabilities. in a sample of 100 students enrolling in a university, a questionnaire indicated that 45 of them studied english, 40 studied french, 35 studied german, 20 studied both english and french, 23 studied both english and german, 19 studied both french and german, and 12 studied all three languages.

Calculating Probability Using A Venn Diagram Statistics And How to calculate probabilities from a venn diagram. in order to calculate probabilities from a venn diagram: determine the parts of the venn diagram that are in the subset. calculate the frequency of the subset. calculate the total frequency of the larger set. write the probability as a fraction, and simplify. Slide 1 of 9, example one.an image of a venn diagram with two intersecting circles. the circle on the left, is labelled, north pole. the circle on the right, is labelled, south pole. Key learning points. in this lesson, we will learn how to calculate probabilities from venn diagrams with 2 or more sets, including using the correct notation for union, intersect and complement. it is useful to have a knowledge of how to draw venn diagrams prior to this lesson but this skill is revised. licence. The set c, shown using a circle and labelled c (three set venn diagram). set a and set b (and set c) overlap, showing the items which are in set a and in set b. this is called the intersection. to analyse data using venn diagrams, all of the values within each set must be correctly allocated into the correct part of the venn diagram.

Calculating Probability Using Venn Diagrams Youtube Key learning points. in this lesson, we will learn how to calculate probabilities from venn diagrams with 2 or more sets, including using the correct notation for union, intersect and complement. it is useful to have a knowledge of how to draw venn diagrams prior to this lesson but this skill is revised. licence. The set c, shown using a circle and labelled c (three set venn diagram). set a and set b (and set c) overlap, showing the items which are in set a and in set b. this is called the intersection. to analyse data using venn diagrams, all of the values within each set must be correctly allocated into the correct part of the venn diagram. In #3 we will continue to explore the concept of a conditional probability and how to use a venn diagram to solve these problems as well as the formula for conditional probability. let's use the venn diagram below to find the following probabilities. notice that the sum of all the values in the diagram is 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 = 1. We recall that in any venn diagram, the probabilities must sum to one. 0.3 plus 0.2 plus 0.4 plus 0.1 is equal to one. the first part of our question asks us to calculate the probability of 𝐴. this is equal to the sum of all the probabilities inside circle 𝐴. we need to add 0.3 and 0.2. this is equal to 0.5.
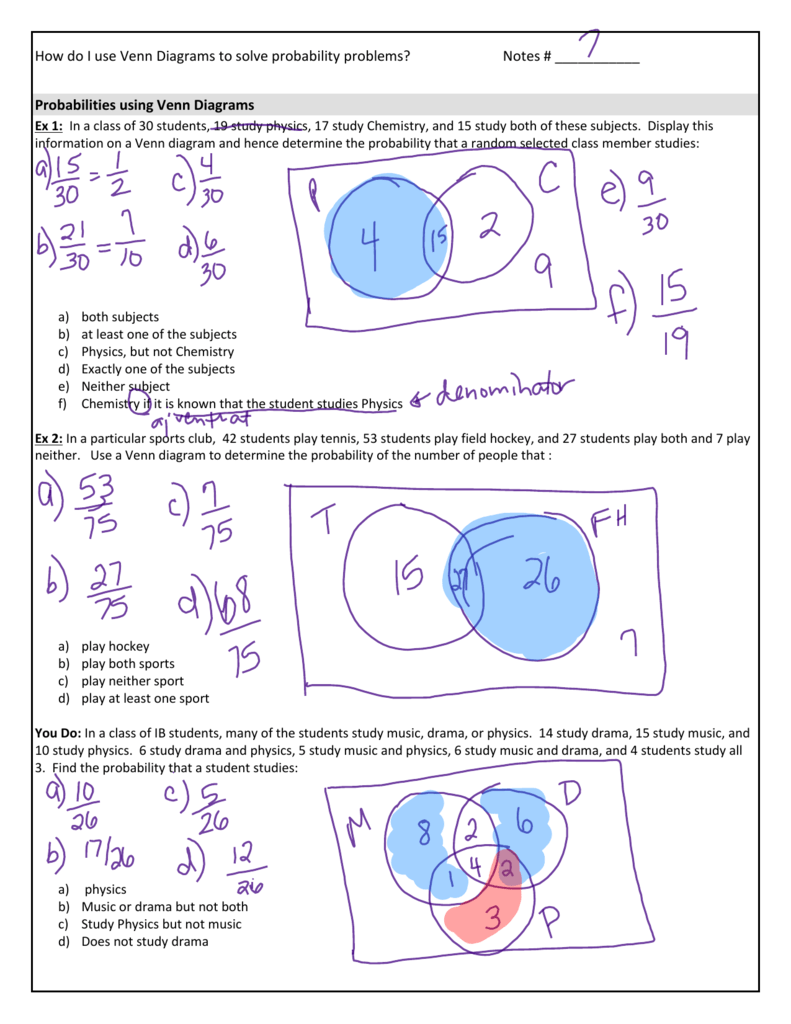
Probabilities Using Venn Diagrams In #3 we will continue to explore the concept of a conditional probability and how to use a venn diagram to solve these problems as well as the formula for conditional probability. let's use the venn diagram below to find the following probabilities. notice that the sum of all the values in the diagram is 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 = 1. We recall that in any venn diagram, the probabilities must sum to one. 0.3 plus 0.2 plus 0.4 plus 0.1 is equal to one. the first part of our question asks us to calculate the probability of 𝐴. this is equal to the sum of all the probabilities inside circle 𝐴. we need to add 0.3 and 0.2. this is equal to 0.5.

Comments are closed.