Introduction To The Hematologic System
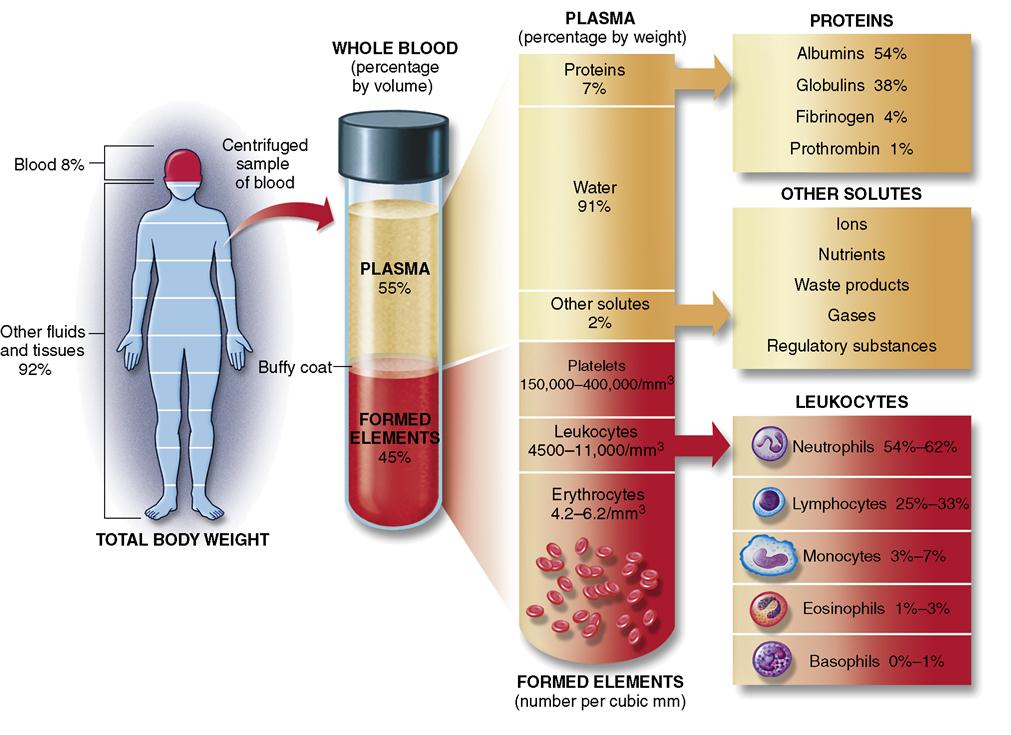
16 The Hematologic System Nurse Key Discussion of the physiology of blood, including the major components of blood, and the function of the hemotologic system. Plasma is a pale, straw colored fluid that constitutes 55% of a blood sample. plasma is mostly water with dissolved proteins, including albumin, immunoglobulins, and clotting factors. it also contains nutrients, electrolytes, and cellular wastes. plasma suspends rbcs, wbcs, and platelets, enabling them to circulate throughout the body within.
16 The Hematologic System Nurse Key The hematology system consists of the blood and the bone marrow that create the cellular elements of the blood, as well as accessory organs, including the spleen and the liver. blood the formed elements include erythrocytes (ĕr Ĭ thrō sītz), leukocytes (loo kō sītz), and thrombocytes (thrŌm bō sītz), all suspended in a liquid called. Haematology is the clinical specialty relating to all aspects of blood and its associated structures, specifically lymphoid tissue. in summary, it is concerned with how it forms, its function and pathologies associated with it. as there is no specific organ for haematology, diseases pertaining to haematology will occur either in the bone marrow. Introduction ; 23.1 overview of the digestive system ; 23.2 digestive system processes and regulation ; 23.3 the mouth, pharynx, and esophagus ; 23.4 the stomach ; 23.5 the small and large intestines ; 23.6 accessory organs in digestion: the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder ; 23.7 chemical digestion and absorption: a closer look ; key terms. During hemostasis, a protein called fibrin (fĪ brin) is produced to form a blood clot. fibrinolysis (fī brĭ nŌl ĭ sĭs) is the process in which a clot is degraded in a healing vessel. an anticoagulant (an tī kō ag yū lănt) is a substance or medication that prevents coagulation. examples of commonly prescribed anticoagulant medications.
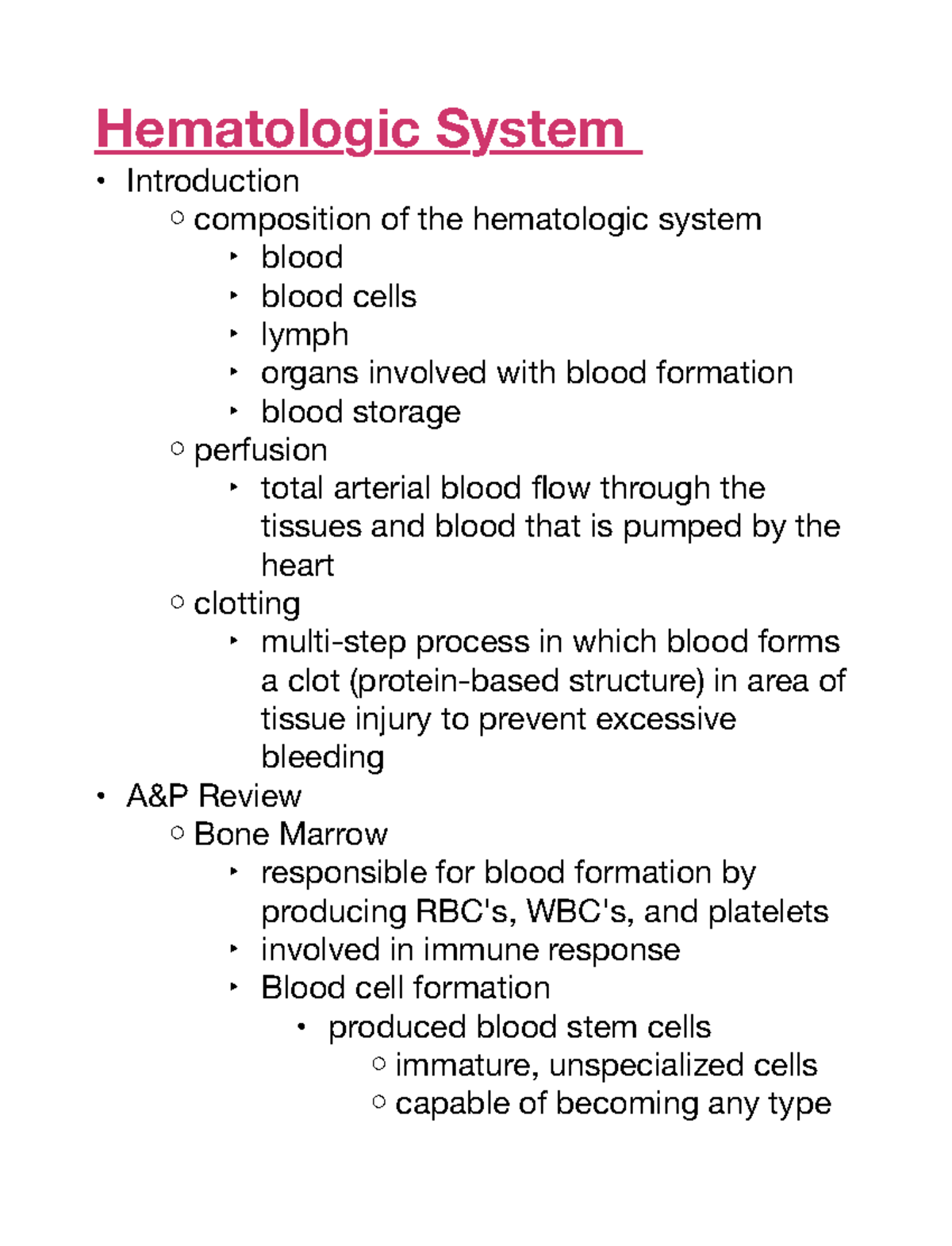
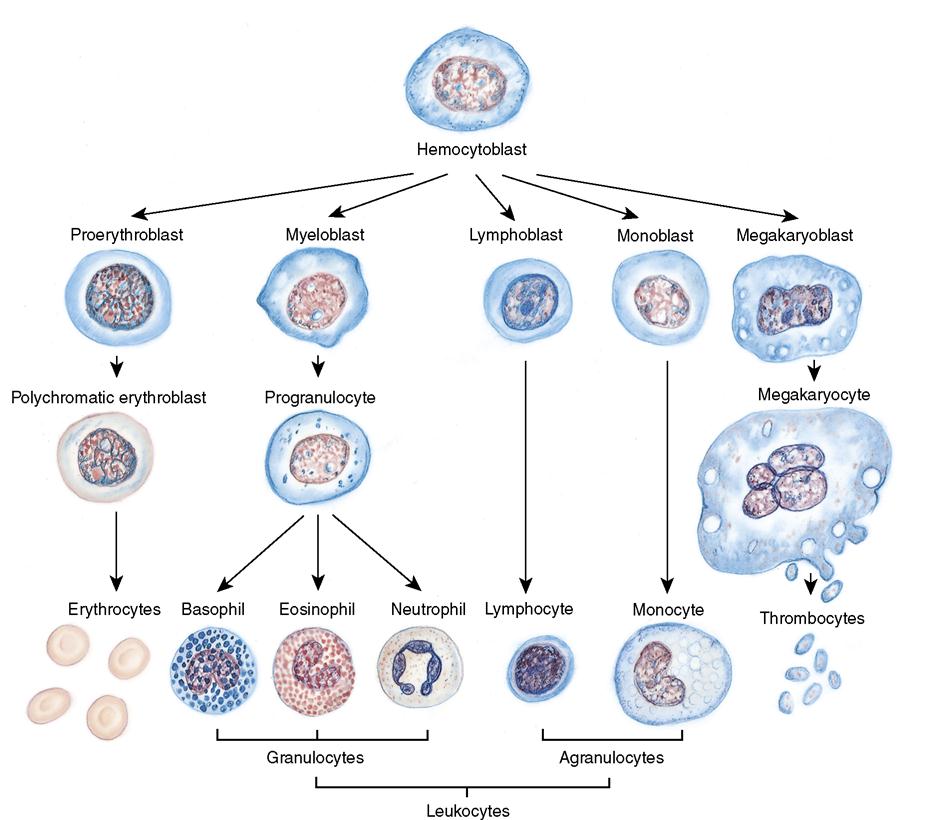
Hematologic System Hematologic System Introduction Composition Of The Introduction ; 23.1 overview of the digestive system ; 23.2 digestive system processes and regulation ; 23.3 the mouth, pharynx, and esophagus ; 23.4 the stomach ; 23.5 the small and large intestines ; 23.6 accessory organs in digestion: the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder ; 23.7 chemical digestion and absorption: a closer look ; key terms. During hemostasis, a protein called fibrin (fĪ brin) is produced to form a blood clot. fibrinolysis (fī brĭ nŌl ĭ sĭs) is the process in which a clot is degraded in a healing vessel. an anticoagulant (an tī kō ag yū lănt) is a substance or medication that prevents coagulation. examples of commonly prescribed anticoagulant medications. Blood helps maintain homeostasis by stabilizing ph, temperature, osmotic pressure, and by eliminating excess heat. blood supports growth by distributing nutrients and hormones, and by removing waste. red blood cells contain hemoglobin, which binds oxygen. these cells deliver oxygen to the cells and remove carbon dioxide. Discover the origins of blood cells in the bone marrow and the role of the pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell in creating all 10 types of blood cells. explore the myeloid and lymphoid lineages, and learn how these precursor cells contribute to our immune system and overall health. uncover the surprising connections between different types of blood cells.

Anatomy Of The Hematologic System Nursing Anatomy Youtube Blood helps maintain homeostasis by stabilizing ph, temperature, osmotic pressure, and by eliminating excess heat. blood supports growth by distributing nutrients and hormones, and by removing waste. red blood cells contain hemoglobin, which binds oxygen. these cells deliver oxygen to the cells and remove carbon dioxide. Discover the origins of blood cells in the bone marrow and the role of the pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell in creating all 10 types of blood cells. explore the myeloid and lymphoid lineages, and learn how these precursor cells contribute to our immune system and overall health. uncover the surprising connections between different types of blood cells.
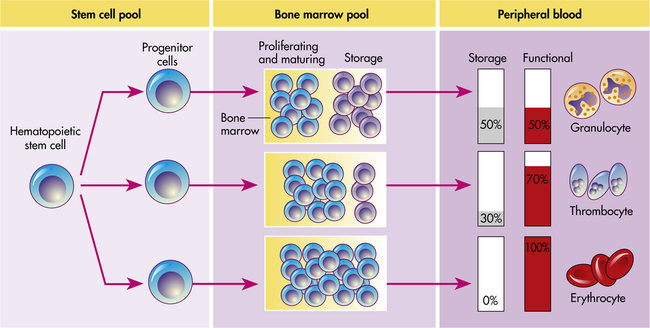
Structure And Function Of The Hematologic System Basicmedical Key

Comments are closed.