Inode Numbers Explained

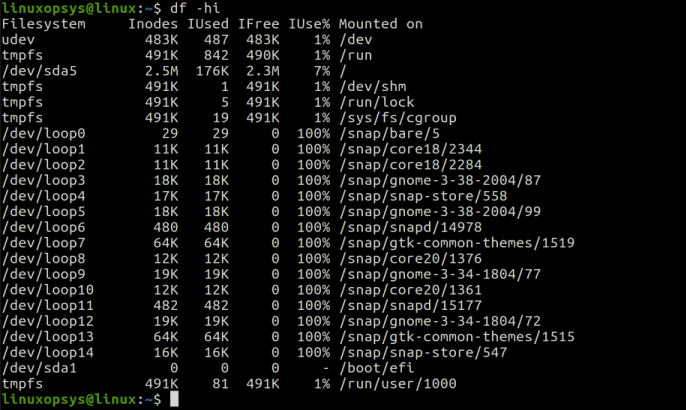
Inodes Explained When a new file is created, it is assigned an inode number and a file name. an inode number is a unique number within that file system. both name and inode number are stored as entries in a directory. when i ran the ls command “ ls li ” the file name and inodes number are what was stored in the directory . The i (inodes) option of the. df. command instructs it to display its output in numbers of inodes. we're going to look at the file system on the first partition on the first hard drive, so we type the following: df i dev sda1. the output gives us: file system: the file system being reported on.

Cs 111 Lecture 12 Scribe Notes Spring 14 Inode. the inode (index node) is a data structure in a unix style file system that describes a file system object such as a file or a directory. each inode stores the attributes and disk block locations of the object's data. [1] file system object attributes may include metadata (times of last change, [2] access, modification), as well as owner. To summarize inode usage for an entire directory subtree, use du with i parameter: $ du ih var . 369218 var. this reveals the total inodes consumed under var for thorough tracking. as we can see, linux offers extensive visibility into inode consumption from high level overviews to file specific numbers. In linux, whenever a new file is created, it is given a file name and an inode number. this number works as the unique identifier for that file. as a user, you will use the file name to access the file but linux will first map that filename with an inode number in a database to access the file. in basic words, an inode number is just like an. There are many inodes on every system, and there are a couple of numbers to be aware of. first up, and less important, the theoretical maximum number of inodes is equal to 2^32 (approximately 4.3 billion inodes). second, and far more important, is the number of inodes on your system. generally, the ratio of inodes is 1:16kb of system capacity.
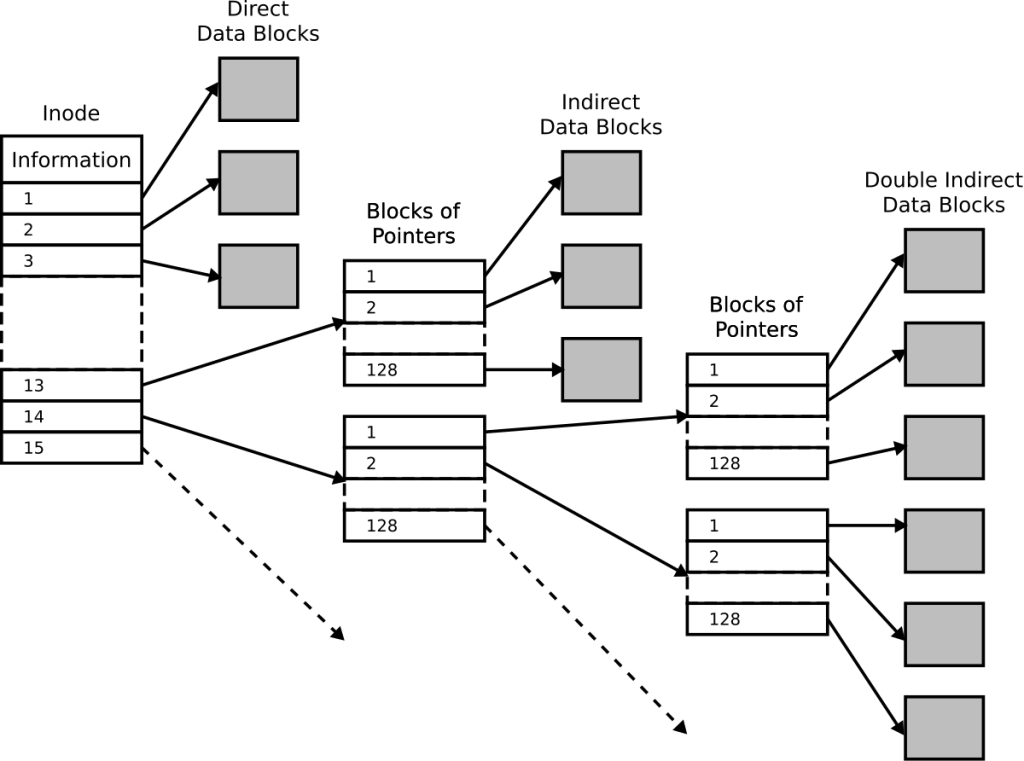
What Are Inodes In A Linux Dedicated Server Prolimehost In linux, whenever a new file is created, it is given a file name and an inode number. this number works as the unique identifier for that file. as a user, you will use the file name to access the file but linux will first map that filename with an inode number in a database to access the file. in basic words, an inode number is just like an. There are many inodes on every system, and there are a couple of numbers to be aware of. first up, and less important, the theoretical maximum number of inodes is equal to 2^32 (approximately 4.3 billion inodes). second, and far more important, is the number of inodes on your system. generally, the ratio of inodes is 1:16kb of system capacity. Inode number: creating, copying and modifying files. as explained above, each inode is identified by an inode number. therefore, when creating or copying a file, linux assigns a different inode number to the new file. however, when moving a file, the inode number will only change if the file is moved to a different filesystem. Inodes are usually located near the beginning of a partition. they store all the information associated with a file except the file name and the actual data. all files in any linux directory have a filename and an inode number. users can retrieve the metadata for a file by referencing the inode number. file names and inode numbers are stored in.
Inodes In Linux Explained Inode number: creating, copying and modifying files. as explained above, each inode is identified by an inode number. therefore, when creating or copying a file, linux assigns a different inode number to the new file. however, when moving a file, the inode number will only change if the file is moved to a different filesystem. Inodes are usually located near the beginning of a partition. they store all the information associated with a file except the file name and the actual data. all files in any linux directory have a filename and an inode number. users can retrieve the metadata for a file by referencing the inode number. file names and inode numbers are stored in.

What Is Inode Number In Linux вђ Tecadmin

Comments are closed.