Inferior Vena Cava Ivc External Anatomy Of The Heart Thorax
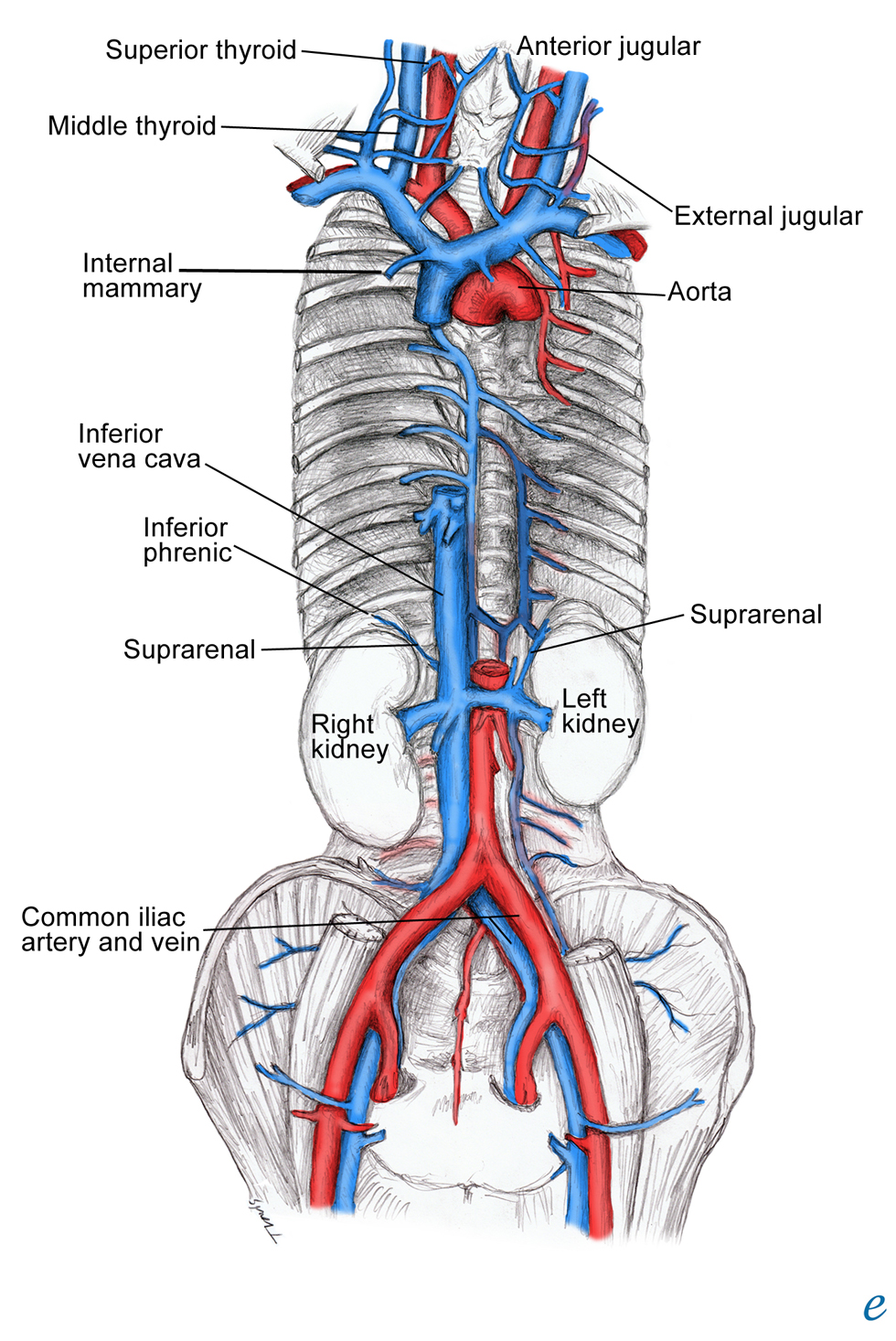
Veia Cava Inferior Anatomia Modisedu The inferior vena cava (ivc) is another great vessel responsible for returning deoxygenated blood to the heart. in fact, it is the largest vein in the human body. the ivc does not have any valves, and it is a retroperitoneal vein located in the abdominal cavity. The inferior vena cava (ivc) is the largest vein of the human body. it is located at the posterior abdominal wall on the right side of the aorta. the ivc’s function is to carry the venous blood from the lower limbs and abdominopelvic region to the heart. the inferior vena cava anatomy is essential due to the vein’s great drainage area.

The Inferior Vena Cava Anatomy Of The Inferior Vena Cava о The inferior vena cava (ivc) is a large retroperitoneal vessel formed by the confluence of the right and left common iliac veins. anatomically this usually occurs at the l5 vertebral level. the ivc lies along the right anterolateral aspect of the vertebral column and passes through the central tendon of the diaphragm around the t8 vertebral level. the ivc is a large blood vessel responsible. Function. clinical significance. the inferior vena cava (also known as ivc or the posterior vena cava) is a large vein that carries blood from the torso and lower body to the right side of the heart. from there the blood is pumped to the lungs to get oxygen before going to the left side of the heart to be pumped back out to the body. Santise g, d’ancona g, baglini r et al; hybrid treatment of inferior vena cava obstruction after orthotopic heart transplantation, interactive cardiovascular and thoracic surgery 2010;11:817 819 interact cardiovasc thorac surg 2010;11:817 819; sinnatamby cs. l ast’s anatomy, 12th edition. published in 2011; snell rs. The inferior vena cava is formed by the union of the right and left common iliac veins, at a point that lies anterior to the l5 vertebra and inferior to the bifurcation of the aorta. course from its origin, the inferior vena cava travels superiorly along the right side of the anterior aspect of the lower lumbar vertebrae, their associated intervertebral discs and the anterior longitudinal.

Comments are closed.