Ib Biology 2 5 Enzymes Interactive Lecture

Ib Biology 2 5 Enzymes Interactive Lecture Youtube About press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. Ib biology hl 2.5 enzymes. state the relationship between enzyme substrate and enzyme product. an enzyme is a globular protein which acts as a biological catalyst by speeding up the rate of a chemical reaction. enzymes are not changed or consumed by the reactions they catalyse and thus can be reused. enzymes are typically named after the.

Ib Biology 2 5 Slides Enzymes How does an enzyme catalyst occur? 1. substrate binds to active site. 2. substrates change into different chemical substances (products) 3. products separate from active site, leaving it vacant for next reaction. what is a collision? the coming together of a substrate molecule and active site. Ib biology: 2.5 enzymes. term. 1 12. enzymes. click the card to flip 👆. definition. 1 12. proteins which speed up chemical reactions without being altered themselves. click the card to flip 👆. Browse thousands of questions, flashcards, and study notes. metabolism, cell respiration and photosynthesis (hl). Understanding, application, skills. 2.5.u1 enzymes have an active site to which specific substrates bind. 2.5.u2 enzyme catalysis involves molecular motion and the collision of substrates with the active site. 2.5.u3 temperature, ph and substrate concentration affect the rate of activity of enzymes.
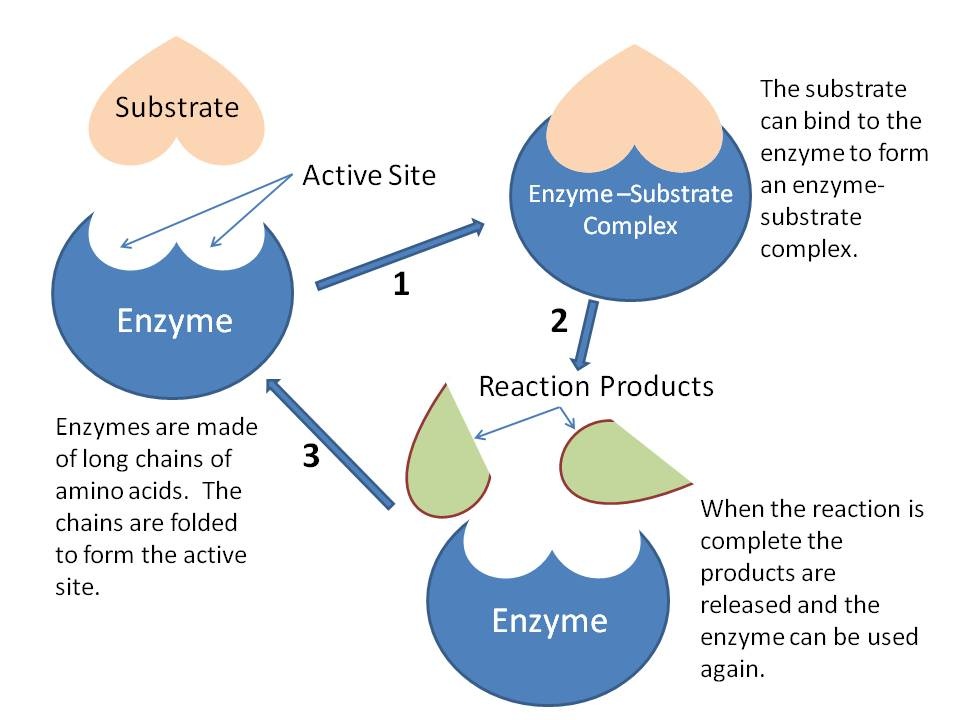
2 5 Enzymes Biology4ibdp Browse thousands of questions, flashcards, and study notes. metabolism, cell respiration and photosynthesis (hl). Understanding, application, skills. 2.5.u1 enzymes have an active site to which specific substrates bind. 2.5.u2 enzyme catalysis involves molecular motion and the collision of substrates with the active site. 2.5.u3 temperature, ph and substrate concentration affect the rate of activity of enzymes. Enzymes are globular proteins that speed up reactions. they convert substrates to ** products**. all substrates bind to the active site of its enzymes, the shape of the active site and the substrate are complementary. the shape of the active site is determined by the arrangement and bonding between amino acids that make up the enzyme. Ib biology 2.5 slides: enzymes. this document discusses enzymes and how they control metabolism in cells. it provides details on how enzymes have an active site that binds to specific substrates, and how enzyme catalysis involves molecular motion and substrate collision with the active site. it describes how temperature, ph, and substrate.

Comments are closed.