Hypocalcemia Clinical Presentation Ddx Lesson Part 1 Sketchy

Hypocalcemia Clinical Presentation Ddx Lesson Part 1 Sketchy Ready to tackle your clerkships? check out free clerkship guides!psychiatry: info.sketchy guide psychiatry clerkship?utm medium=organic social&ut. Watch a free lesson about hypocalcemia (clinical presentation & ddx) from our electrolytes & acid base unit. sketchy medical helps you learn faster and score higher on the usmle step 1 and step 2 exams.

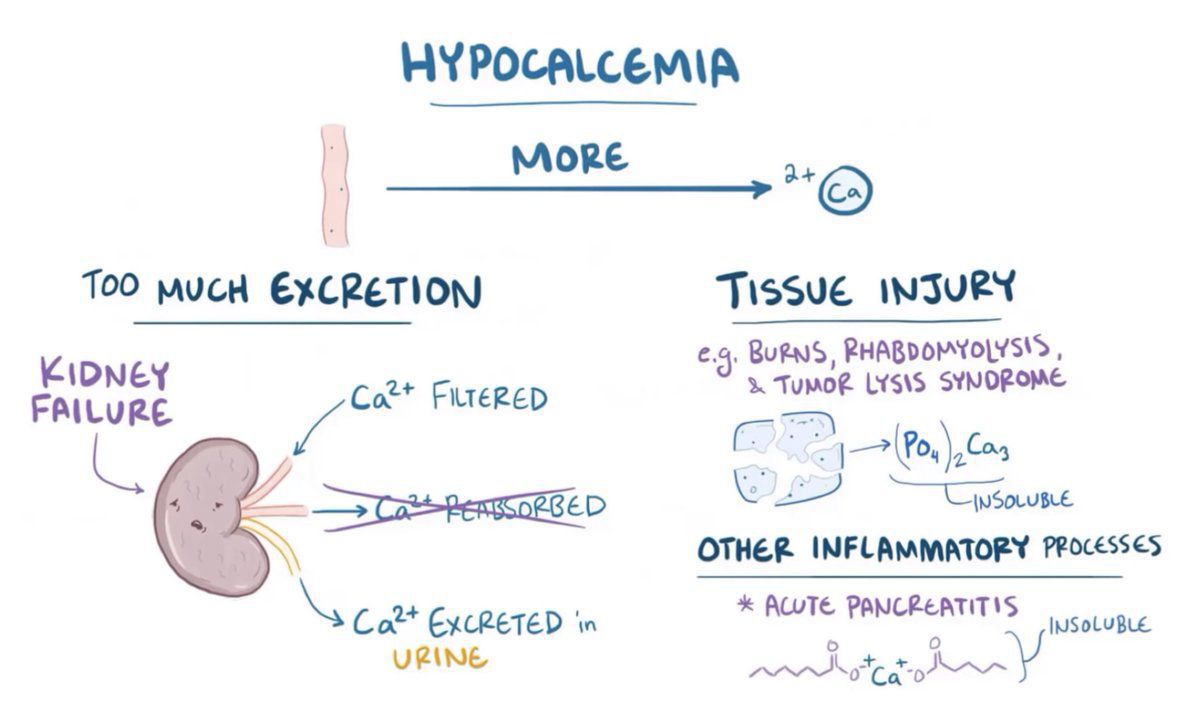
Hypokalemia Clinical Presentation Ddx Internal Medicine Sketchy Among the symptoms of hypocalcemia, tetany, papilledema, and seizures may occur in patients who develop hypocalcemia acutely. by comparison, ectodermal and dental changes, cataracts, basal ganglia calcification, and extrapyramidal disorders are features of chronic hypocalcemia. these last findings are most common in patients with. The diagnostic approach to hypocalcemia involves confirming, by repeat measurement, the presence of hypocalcemia and distinguishing among the potential etiologies. the diagnosis may be obvious from the patient's history; examples include chronic kidney disease and postsurgical hypoparathyroidism. when the cause is not obvious or a suspected. 1 background. 1.1 serum levels; 1.2 fraction [5] 1.3 causes; 2 clinical features. 2.1 symptoms of hypocalcemia; 3 differential diagnosis. 3.1 movement disorders and other abnormal contractions; 3.2 jaw spasms; 4 evaluation. 4.1 ecg; 4.2 trousseau's sign; 4.3 chvostek sign; 4.4 labs; 5 management; 6 disposition; 7 see also; 8 references. Hypocalcemia is an electrolyte derangement commonly encountered on surgical and medical services. this derangement can result from a vast spectrum of disorders. the condition may be transient, reversing with addressing the underlying cause expeditiously, or chronic and even lifelong, when due to a genetic disorder or the result of irreversible damage to the parathyroid glands after surgery or.
Hypocalcemia Medizzy 1 background. 1.1 serum levels; 1.2 fraction [5] 1.3 causes; 2 clinical features. 2.1 symptoms of hypocalcemia; 3 differential diagnosis. 3.1 movement disorders and other abnormal contractions; 3.2 jaw spasms; 4 evaluation. 4.1 ecg; 4.2 trousseau's sign; 4.3 chvostek sign; 4.4 labs; 5 management; 6 disposition; 7 see also; 8 references. Hypocalcemia is an electrolyte derangement commonly encountered on surgical and medical services. this derangement can result from a vast spectrum of disorders. the condition may be transient, reversing with addressing the underlying cause expeditiously, or chronic and even lifelong, when due to a genetic disorder or the result of irreversible damage to the parathyroid glands after surgery or. Signs and symptoms. hypocalcemia varies from a mild asymptomatic biochemical abnormality to a life threatening disorder. acute hypocalcemia can lead to paresthesia, tetany, and seizures (characteristic physical signs may be observed, including chvostek sign, which is poorly sensitive and specific of hypocalcemia, and trousseau sign). The aim of this clinical narrative review is to summarize and critically appraise the literature on the differential diagnosis of hypocalcemia and to provide its correct management. calcium is essential for muscle contraction and neurotransmitter release, but clinical manifestations of hypocalcaemia (serum calcium level <8 mg dl; 2.12 mmol l) may involve almost any organ and system and may.

Hypocalcemia Ppt Signs and symptoms. hypocalcemia varies from a mild asymptomatic biochemical abnormality to a life threatening disorder. acute hypocalcemia can lead to paresthesia, tetany, and seizures (characteristic physical signs may be observed, including chvostek sign, which is poorly sensitive and specific of hypocalcemia, and trousseau sign). The aim of this clinical narrative review is to summarize and critically appraise the literature on the differential diagnosis of hypocalcemia and to provide its correct management. calcium is essential for muscle contraction and neurotransmitter release, but clinical manifestations of hypocalcaemia (serum calcium level <8 mg dl; 2.12 mmol l) may involve almost any organ and system and may.

Comments are closed.