Human Digestive System And Digestion Of Carbohydrates Proteins And
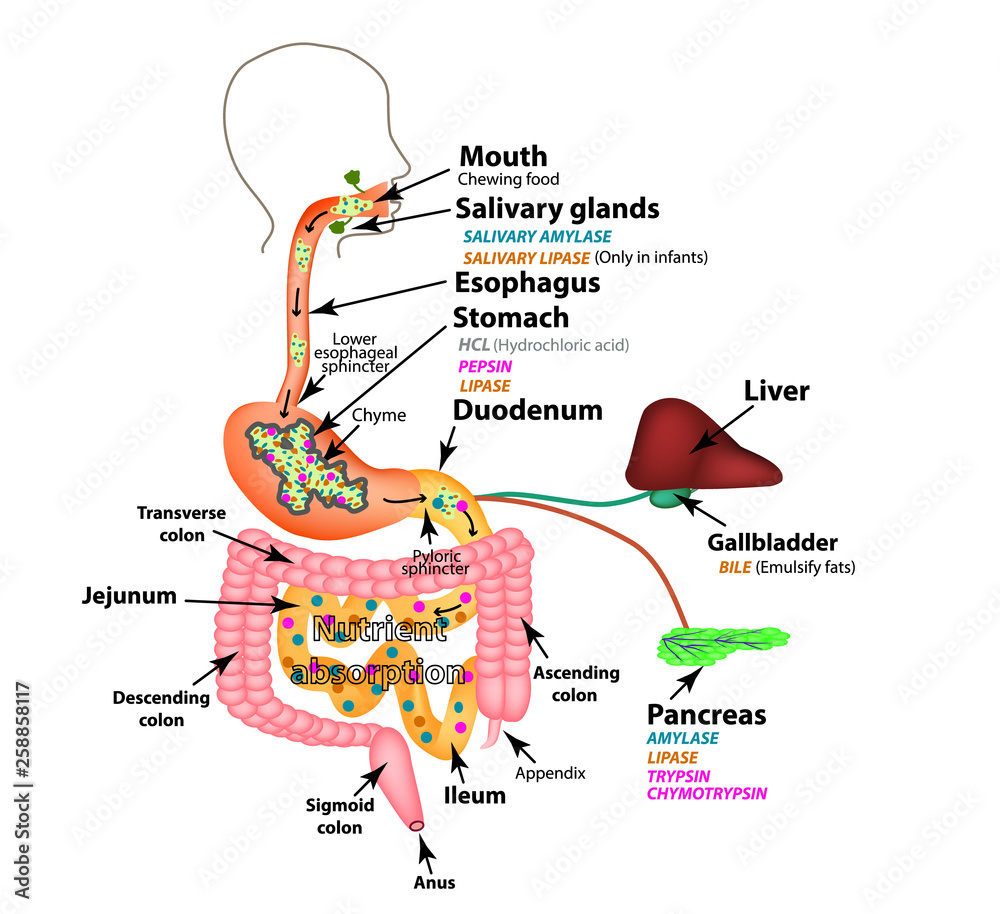
The Human Digestive System Anatomical Structure Digestion Of Carbohydrate digestion: a diagram of the action of the oligosaccharide cleaving enzymes in the small intestine. lipid digestion: lipid digestion involves the formation of micelles in the presence of bile salts, and the passage of micelles and fatty acids through the unstirred layer. the diagram depicts dietary fat at the top, with pancreatic. All the food you eat goes through your digestive system so it can be broken down and used by the body. carbohydrates take a journey starting with the intake at the mouth and ending with.

Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates вђ Human Nutrition Human digestive system proteins, enzymes, absorption: the digestion of protein entails breaking the complex molecule first into peptides, each having a number of amino acids, and second into individual amino acids. the pepsins are enzymes secreted by the stomach in the presence of acid that breaks down proteins (proteolysis). the pepsins account for about 10 to 15 percent of protein. The amino acids are absorbed into the bloodstream through the small intestine. figure 34.10.1 34.10. 1: protein digestion and absorption: protein digestion is a multistep process that begins in the stomach and continues through the intestines. proteins are absorbed into the blood stream by the small intestine. Digestion of food is a form of catabolism, in which the food is broken down into small molecules that the body can absorb and use for energy, growth, and repair. digestion occurs when food is moved through the digestive system. it begins in the mouth and ends in the small intestine. the final products of digestion are absorbed from the. The digestive process starts when you put food in your mouth. mouth. food starts to move through your gi tract when you eat. when you swallow, your tongue pushes the food into your throat. a small flap of tissue, called the epiglottis, folds over your windpipe to prevent choking and the food passes into your esophagus.
Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates Digestion of food is a form of catabolism, in which the food is broken down into small molecules that the body can absorb and use for energy, growth, and repair. digestion occurs when food is moved through the digestive system. it begins in the mouth and ends in the small intestine. the final products of digestion are absorbed from the. The digestive process starts when you put food in your mouth. mouth. food starts to move through your gi tract when you eat. when you swallow, your tongue pushes the food into your throat. a small flap of tissue, called the epiglottis, folds over your windpipe to prevent choking and the food passes into your esophagus. Your digestive system is a network of organs that help you digest and absorb nutrition from your food. it includes your gastrointestinal (gi) tract and your biliary system. your gi tract is a series of hollow organs that are all connected to each other, leading from your mouth to your anus. your biliary system is a network of three organs that. Gastrointestinal tract. human digestive system, system used in the human body for the process of digestion. the human digestive system consists primarily of the digestive tract, or the series of structures and organs through which food and liquids pass during their processing into forms that can be absorbed into the bloodstream.

Comments are closed.