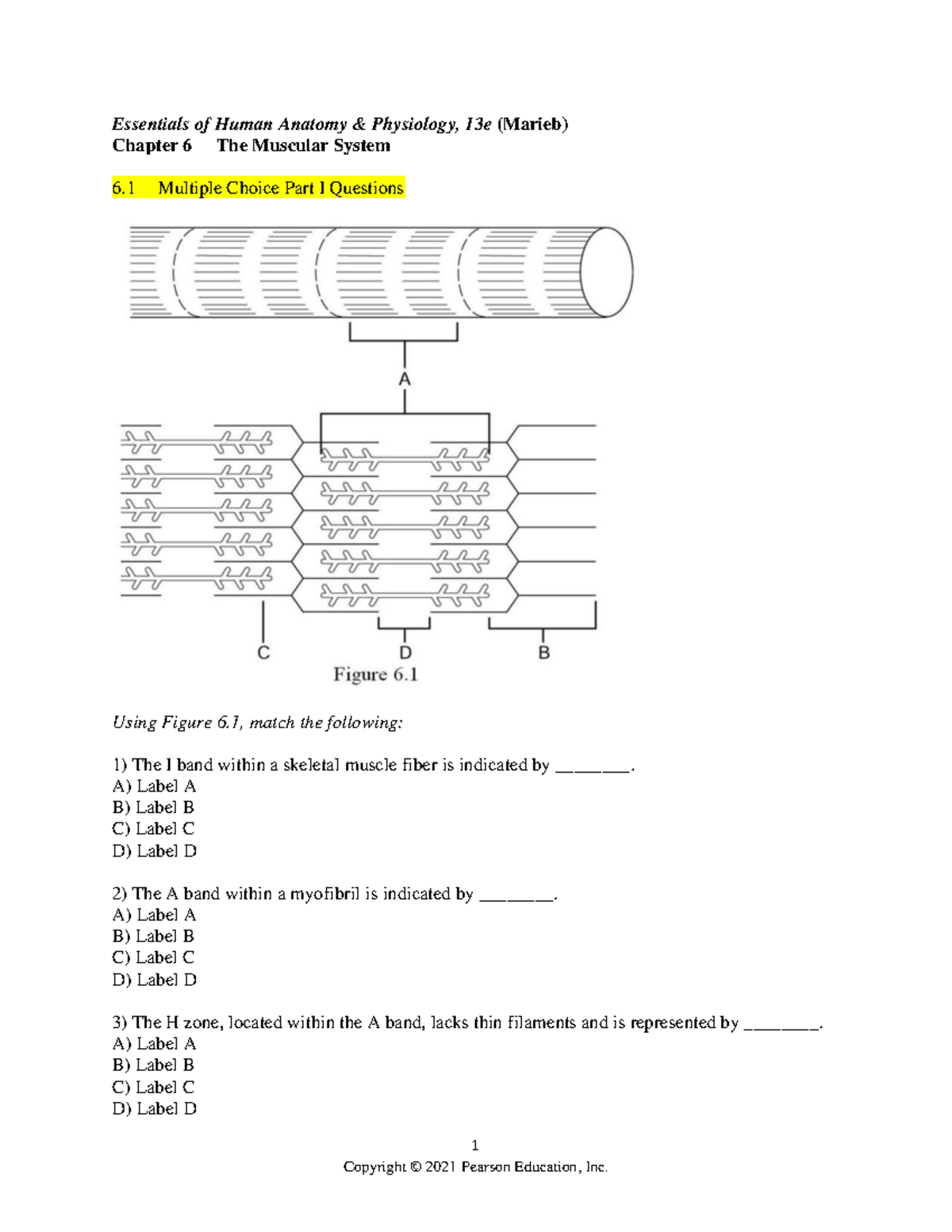
Human Biology Chapter 13 Muscular System

Biol 130 Ch 13 Muscular System Part 1 1 Youtube Allow for movement by attaching to the skeleton. 3. allows facial expression. 4. help maintain a constant body temperature. 5. to stabilize joints. structure of skeletal muscles. classified according to shape and orientation of fascicles (bundles of muscle fiber). and shape and orientation determine the strength and direction of muscle's pull. Functions of skeletal muscles. support: allows us to remain upright. movement of bones and other body structures. maintaining a constant body temperature. movement of fluids in the cvs and lymphatic systems. protection of the internal organs and the stabilization of joints. what is the basic structure of a skeletal muscle? contains.

Muscular System Voluntary Muscles Human biology chapter 13: muscular system. term. 1 11. muscular system. click the card to flip 👆. definition. 1 11. system of muscles that produces movement, both within the body and of its limbs; principal components are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. Notes from dr. simmon's lecture on chapter 13 of the book human biology by sylvia mader 13.1 overview of the muscular system muscular system functions in:. The muscular system consists of all the muscles of the body. the largest percentage of muscles in the muscular system consists of skeletal muscles, which are attached to bones and enable voluntary body movements. there are almost 650 skeletal muscles in the human body, many of them shown in figure 7.2. besides skeletal muscles, the muscular. Muscular system structures and functions. differentiate between skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle in terms of structure, location, and function. connected to bones by tendons, a type of dense regular connective tissue that joins muscles to bone. the abdominal muscles are also held with broad tendon sheaths termed.
Muscular System Revision Q A 1 Essentials Of Human Anatomy The muscular system consists of all the muscles of the body. the largest percentage of muscles in the muscular system consists of skeletal muscles, which are attached to bones and enable voluntary body movements. there are almost 650 skeletal muscles in the human body, many of them shown in figure 7.2. besides skeletal muscles, the muscular. Muscular system structures and functions. differentiate between skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle in terms of structure, location, and function. connected to bones by tendons, a type of dense regular connective tissue that joins muscles to bone. the abdominal muscles are also held with broad tendon sheaths termed. The muscular system is the biological system of humans that produces movement. the muscular system, in vertebrates, is controlled through the nervous system, although some muscles, like cardiac muscle, can be completely autonomous. muscle is contractile tissue and is derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells. Besides skeletal muscles, the muscular system also includes cardiac muscle, which makes up the walls of the heart, and smooth muscles, which control movement in other internal organs and structures. figure 12.2.2 many of the skeletal muscles in the human muscular system are shown in this drawing of the human body. muscle structure and function.
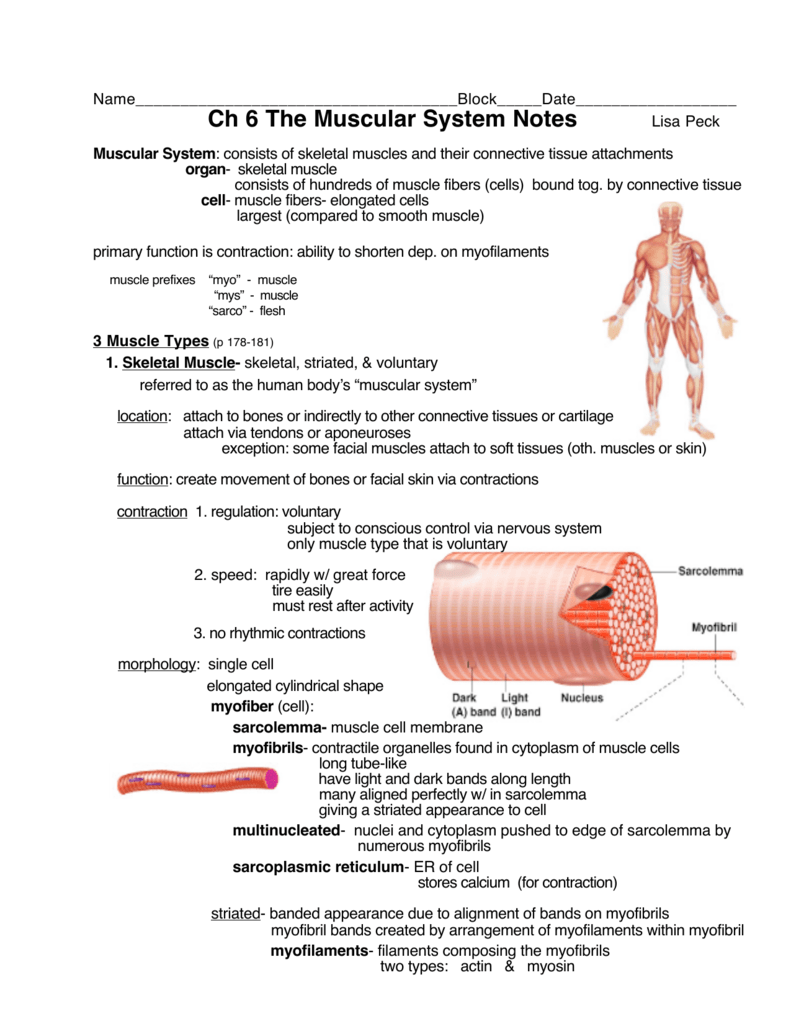
Ch 6 The Muscular System Notes The muscular system is the biological system of humans that produces movement. the muscular system, in vertebrates, is controlled through the nervous system, although some muscles, like cardiac muscle, can be completely autonomous. muscle is contractile tissue and is derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells. Besides skeletal muscles, the muscular system also includes cardiac muscle, which makes up the walls of the heart, and smooth muscles, which control movement in other internal organs and structures. figure 12.2.2 many of the skeletal muscles in the human muscular system are shown in this drawing of the human body. muscle structure and function.

Comments are closed.