How To Read A Cooling Curve Youtube
How To Read A Cooling Curve Youtube This is a chemistry tutorial video that goes through how to read and interpret heating curves or cooling curves. there are several examples of different ques. This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the heating curve of water and the cooling curve of water. as heat is added to water, the t.

How To Read And Interpret A Heating Curve Or Cooling Curve Youtube In this video, you will learn what heating curves and cooling curves are. there also be tips and tricks on how to solve them as well as sample problems. lear. By removing the time axis from the curves and replacing it with composition, the cooling curves indicate the temperatures of the solidus and liquidus for a given composition. this allows the solidus and liquidus to be plotted to produce the phase diagram: this page titled 12.5: interpretation of cooling curves is shared under a cc by nc sa. Figure 13.18.1 13.18. 1: in the heating curve of water, the temperature is shown as heat is continually added. changes of state occur during plateaus, because the temperature is constant. the change of state behavior of all substances can be represented with a heating curve of this type. A cooling curve of a substance is a graph of the variation of the temperature with time as it is allowed to cool. the gradient of the cooling curve is related to the heat capacity, the thermal conductivity of the substance, and the external temperature. the more heat is required to change the temperature of the substance, the slower it cools.

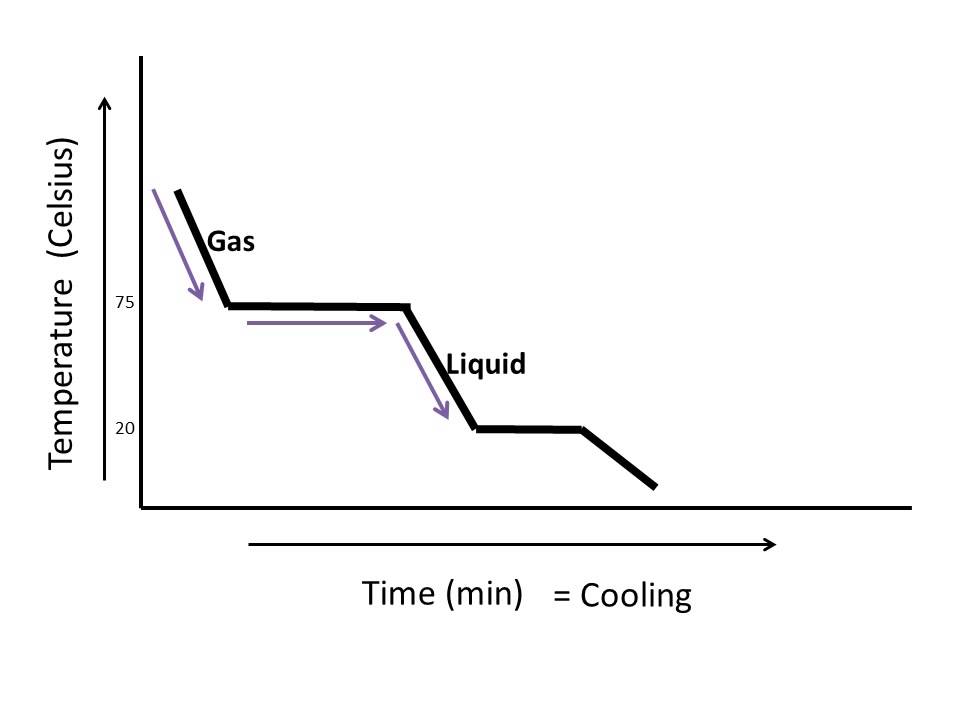
How To Read And Interpret Heating Cooling Curve Youtube Figure 13.18.1 13.18. 1: in the heating curve of water, the temperature is shown as heat is continually added. changes of state occur during plateaus, because the temperature is constant. the change of state behavior of all substances can be represented with a heating curve of this type. A cooling curve of a substance is a graph of the variation of the temperature with time as it is allowed to cool. the gradient of the cooling curve is related to the heat capacity, the thermal conductivity of the substance, and the external temperature. the more heat is required to change the temperature of the substance, the slower it cools. The cooling curve, a plot of temperature versus cooling time, in figure \(\pageindex{4}\) plots temperature versus time as a 75 g sample of steam, initially at 1 atm and 200°c, is cooled. although we might expect the cooling curve to be the mirror image of the heating curve in figure \(\pageindex{3}\), the cooling curve is not an identical. A quick note about cooling curves. let's say we wanted to go from steam to ice. we would use a cooling curve. the cooling curve is a mirror image of the heating curve. so, it will start at a high temperature and have downward diagonals. the diagonals alternate with plateaus. the flat lines are the enthalpy of condensation and freezing. remember.

Comments are closed.