How To Find Protons Electrons For Cu And Cu2 Copper Ii And Iii

How To Find Protons Electrons For Cu And Cu2 Copper Ii And Ii In this video we’ll use the periodic table and a few simple rules to find the number of protons and electrons for the copper i (cu ) and copper ii (cu2 ) ion. Video: cu, cu , and cu2 electron configuration notation. in writing the electron configuration for copper the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for copper go in the 2s orbital. the next six electrons will go in the 2p orbital. the p orbital can hold up to six electrons.
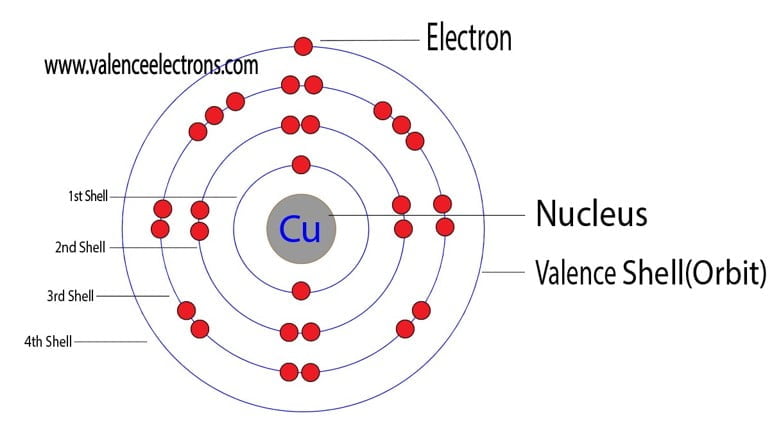
Electron Configuration For Copper Cu Cu Cu2 Atomic number, atomic weight and charge of copper ion. cu – 2e – → cu 2 . the electron configuration of copper ions (cu 2 ) is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 9. copper atoms exhibit 1 and 2 oxidation states. the oxidation state of the element changes depending on the bond formation. First, to find the number of protons, we need to realize that the neutral atom had 53 electrons because it is the additional one electron that makes it a 1 anion. now, because the atom has 53 electrons, it must also have 53 protons, and to find the number of neutrons we subtract this from the mass number. # n = a – # p = 127 – 53 = 74. In this video we’ll use the periodic table and a few simple rules to find the protons, electrons, and neutrons for the element copper (cu). and neutrons for the element copper (cu). from the. Make sure that you round the atomic mass to the nearest whole number. for example, the atomic mass of boron is 10.811, but you can just round the atomic mass up to 11. 6. subtract the atomic number from the atomic mass. to find the number of neutrons, you will need to subtract the atomic number from the atomic mass.

How To Find The Number Of Protons Electrons Neutrons For Copper Cu In this video we’ll use the periodic table and a few simple rules to find the protons, electrons, and neutrons for the element copper (cu). and neutrons for the element copper (cu). from the. Make sure that you round the atomic mass to the nearest whole number. for example, the atomic mass of boron is 10.811, but you can just round the atomic mass up to 11. 6. subtract the atomic number from the atomic mass. to find the number of neutrons, you will need to subtract the atomic number from the atomic mass. The copper anode dissolves forming blue copper(ii) ions cu 2 . these positive ions are attracted to the negative cathode and become copper atoms. the mass of copper dissolving at the anode exactly equals the mass of copper deposited on the cathode. the concentration of the copper(ii) sulfate remains constant. A proton is one of the subatomic particles that make up matter. in the universe, protons are abundant, making up about half of all visible matter.it has a positive electric charge ( 1e) and a rest mass equal to 1.67262 × 10 −27 kg (938.272 mev c 2)— marginally lighter than that of the neutron but nearly 1836 times greater than that of the electron.
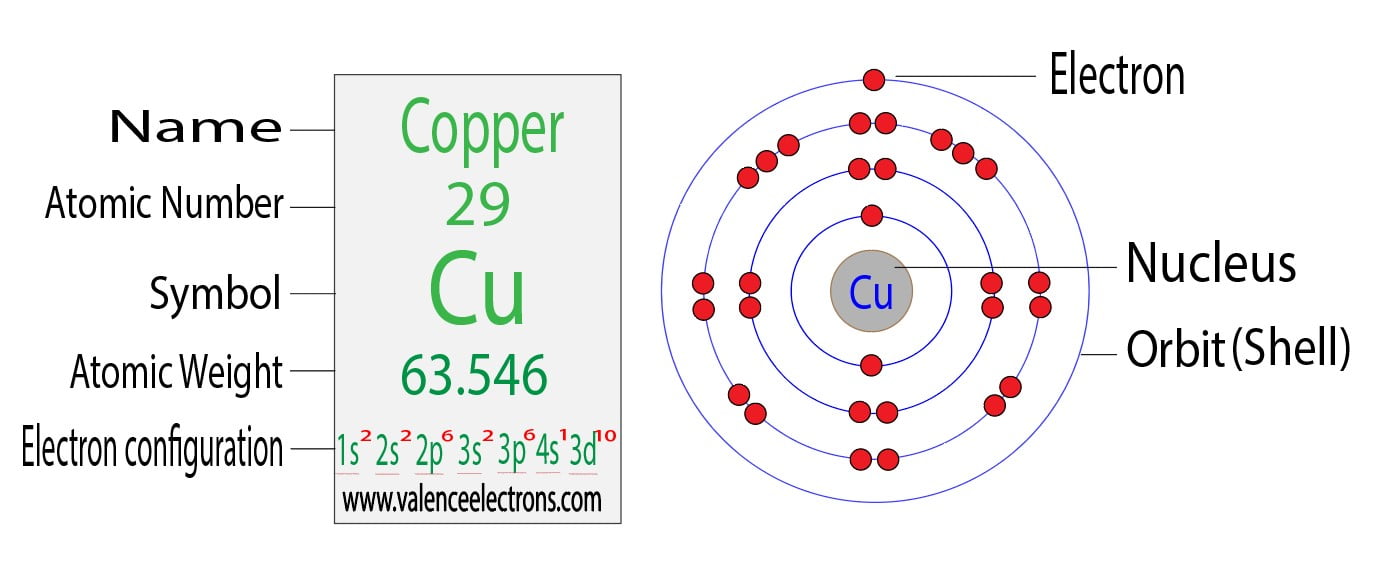
Electron Configuration For Copper Cu Cu Cu2 The copper anode dissolves forming blue copper(ii) ions cu 2 . these positive ions are attracted to the negative cathode and become copper atoms. the mass of copper dissolving at the anode exactly equals the mass of copper deposited on the cathode. the concentration of the copper(ii) sulfate remains constant. A proton is one of the subatomic particles that make up matter. in the universe, protons are abundant, making up about half of all visible matter.it has a positive electric charge ( 1e) and a rest mass equal to 1.67262 × 10 −27 kg (938.272 mev c 2)— marginally lighter than that of the neutron but nearly 1836 times greater than that of the electron.

How To Find The Valence Electrons For Copper Cu Youtube

Comments are closed.