How Enzymes Work

Enzymes Definition Classification Functions Enzymes are proteins or rna molecules that catalyze chemical reactions in cells. they help with digestion, metabolism, dna replication, and more. learn about their function, definition, examples, and types. Learn how enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up specific chemical reactions in cells. find out how enzymes interact with substrates and produce new molecules in the lock and key or induced fit models.
/what-is-enzyme-structure-and-function-375555_v4-6f22f82931824e76b1c31401230deac8.png)
Structure And Function Of An Enzyme Enzymes are substances that act as catalysts in living organisms, regulating the rate of chemical reactions without being altered. learn about the chemical nature, nomenclature, and mechanism of enzyme action, as well as their applications and examples. Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. learn about the etymology, history, classification and examples of enzymes, as well as their structure, function and regulation. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions by lowering the activation energy. learn how enzymes bind to substrates, regulate their activity, and participate in metabolic pathways. Digestive enzymes secreted in the acidic environment (low ph) of the stomach help break down proteins into smaller molecules. the main digestive enzyme in the stomach is pepsin, which works best at a ph of about 1.5. these enzymes would not work optimally at other phs. trypsin is another enzyme in the digestive system, which breaks protein.

Enzymes Mim Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions by lowering the activation energy. learn how enzymes bind to substrates, regulate their activity, and participate in metabolic pathways. Digestive enzymes secreted in the acidic environment (low ph) of the stomach help break down proteins into smaller molecules. the main digestive enzyme in the stomach is pepsin, which works best at a ph of about 1.5. these enzymes would not work optimally at other phs. trypsin is another enzyme in the digestive system, which breaks protein. Explore how enzymes work and how they shape the active site to catalyze biochemical reactions . khan academy offers a free, world class education for anyone, anywhere. Learn how enzymes use chemical and physical strategies to speed up reactions by stabilizing transition states. explore examples of acid base, metal ion, and electrostatic catalysis, and how enzymes employ these mechanisms.
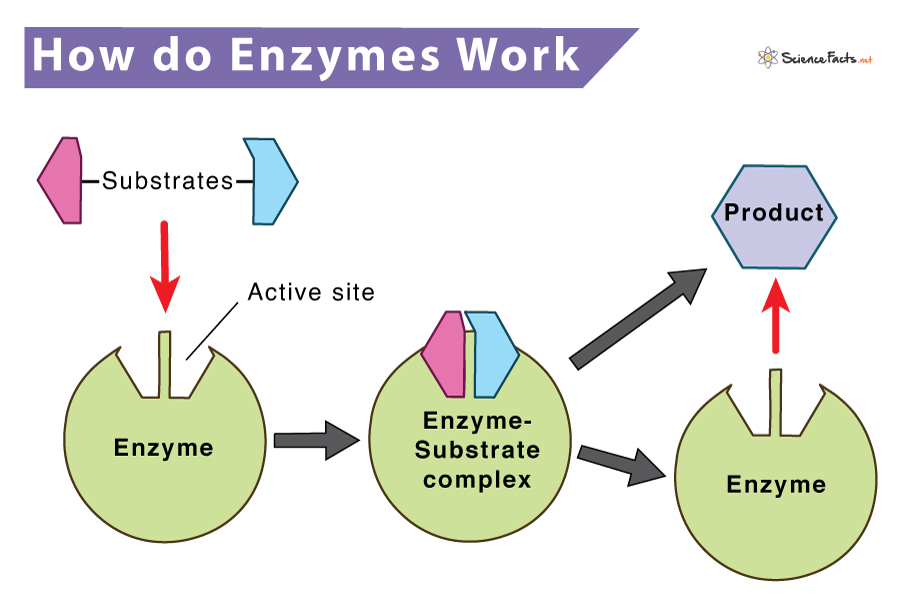
Enzyme Definition Types Structure Functions Diagram Explore how enzymes work and how they shape the active site to catalyze biochemical reactions . khan academy offers a free, world class education for anyone, anywhere. Learn how enzymes use chemical and physical strategies to speed up reactions by stabilizing transition states. explore examples of acid base, metal ion, and electrostatic catalysis, and how enzymes employ these mechanisms.
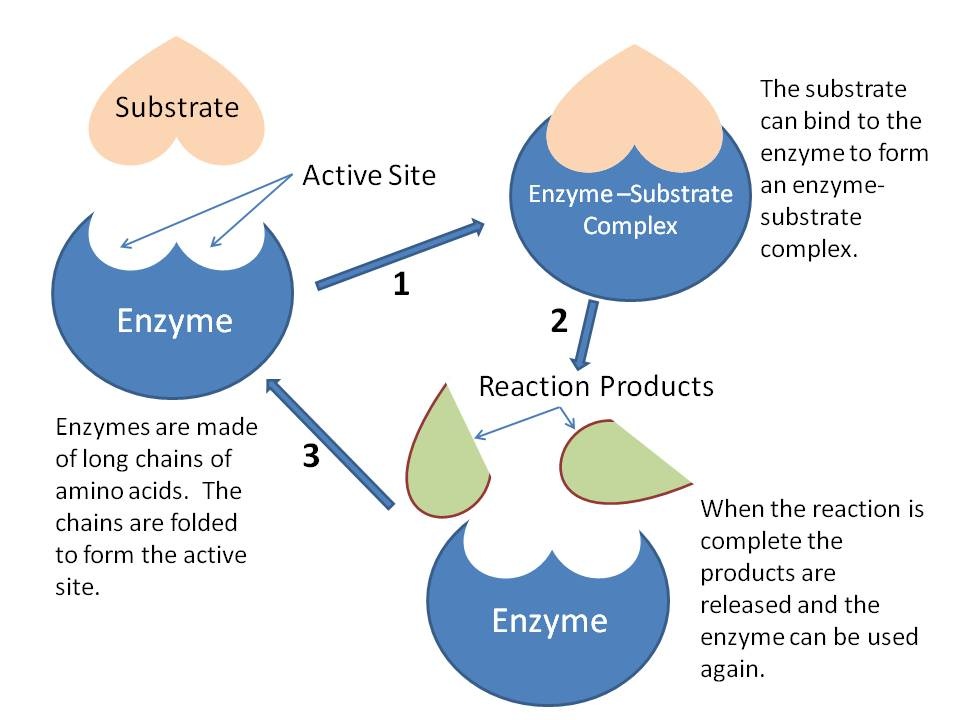
2 5 Enzymes Biology4ibdp

Comments are closed.