Histone Methylation And Acetylation

Histones In addition to relationship between dna methylation and acetylation, it was found that histone acetylation can induce dna demethylation. the model described above, according to which dna methylation can induce histone deacetylation, can explain gene inactivation, but is insufficient to explain the demethylation of the gene upon its activation. Some histone modifications, such as lysine acetylation, were long thought to be highly dynamic, whereas others, such as lysine methylation, were considered to be fairly stable 8. nowadays, we.
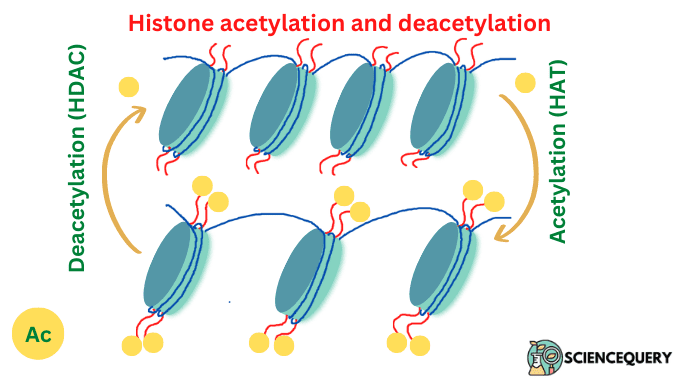
What Is Histone Acetylation Sciencequery Histone methylation mainly occurs on the side chains of lysines and arginines. unlike acetylation and phosphorylation, however, histone methylation does not alter the charge of the histone protein. The best studied histone post‐translational modifications (ptm) are currently acetylation (kuo & allis, 1998), methylation (kouzarides, 2002), and phosphorylation (oki et al, 2007). it has been suggested that these ptms could form a so‐called histone code (strahl & allis, 2000 ). In addition to histone acetylation and methylation, other histone modifications including ubiquitination, phosphorylation, and lactylation are associated with ad. bmi1, a component of prc1 that. Post synthetic modification of histone proteins in chromatin architecture plays a central role in the epigenetic regulation of transcription. histone acetylation and methylation are the two major modifications that function as a specific transcription regulator in response to various cellular signals. albeit the mechanism of action of these.

Role Of Histone Methylation In The Transcriptional Regulation Of In addition to histone acetylation and methylation, other histone modifications including ubiquitination, phosphorylation, and lactylation are associated with ad. bmi1, a component of prc1 that. Post synthetic modification of histone proteins in chromatin architecture plays a central role in the epigenetic regulation of transcription. histone acetylation and methylation are the two major modifications that function as a specific transcription regulator in response to various cellular signals. albeit the mechanism of action of these. Unlike acetylation and methylation, histone phosphorylation establishes interactions between other histone ptms and acts as a platform that causes downstream cascading events. 86 similar to other ptm, histone phosphorylation is also reversible. 87 with the deepening of research on histone phosphorylation, more and more discoveries have been. Histone h4 is one of the core histones that is also very important for chromatin function. there are diverse identified h4 modifications, including lysine acylation at h4k5, h4k8, h4k12, h4k16, h4k20, and h4k31; lysine methylation at h4k20 and h4k31; arginine methylation at h4r3, h4r17, h4r19, and h4r23; and serine phosphorylation at h4s1 (figure 1a). 5, 6 the function of h4 lysine acetylation.

Pdf Histone Methylation Versus Histone Acetylation New Insights Into Unlike acetylation and methylation, histone phosphorylation establishes interactions between other histone ptms and acts as a platform that causes downstream cascading events. 86 similar to other ptm, histone phosphorylation is also reversible. 87 with the deepening of research on histone phosphorylation, more and more discoveries have been. Histone h4 is one of the core histones that is also very important for chromatin function. there are diverse identified h4 modifications, including lysine acylation at h4k5, h4k8, h4k12, h4k16, h4k20, and h4k31; lysine methylation at h4k20 and h4k31; arginine methylation at h4r3, h4r17, h4r19, and h4r23; and serine phosphorylation at h4s1 (figure 1a). 5, 6 the function of h4 lysine acetylation.

Comments are closed.