Hip Spica Adduction Abduction

Hip Spica Adduction Abduction Youtube Safe zone is the range of hip movements between two points: 1. point of maximum adduction: point of dislocation beyond which if adducted the hip will dislocate 2. point of maximum safe abduction: maximum possible abduction beyond which chances of avn are high. a narrow safe zone less than 50 indicates unstable reduction and needs action. Limited hip range of motion is typically defined as abduction of less than 75° or adduction exceeding 30° past midline. asymmetrical gait (ie, trendelenburg gait) due to abductor insufficiency, lumbar lordosis, toe walking, leg length discrepancies, and early hip osteoarthritis may also suggest hip dysplasia.
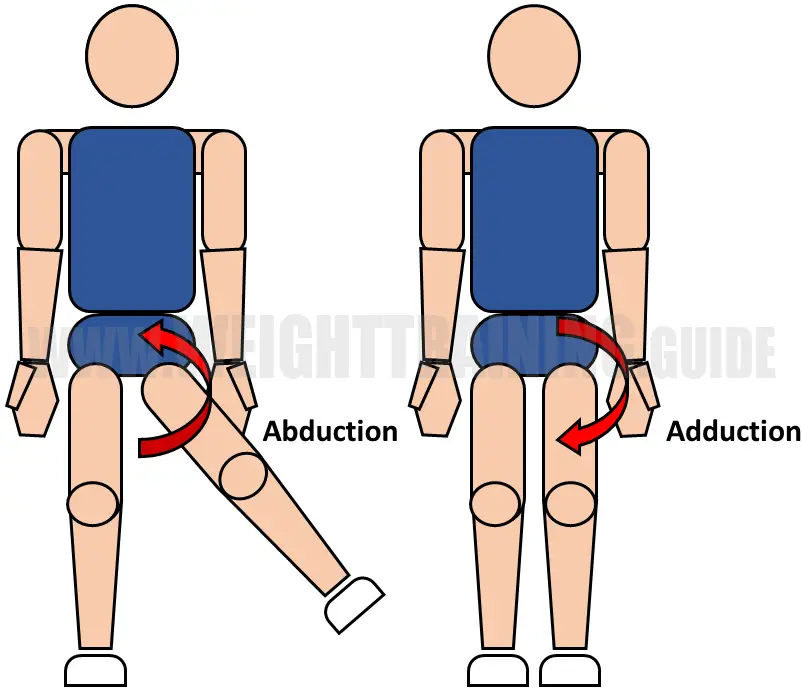
Joint Articulations And The Three Planes Of Motion Muscle Activation Human position (salter position): hip joint in 95° flexion and 40 45° abduction (best for maintaining hip stability and minimizing the risk of osteonecrosis) “safe zone” of ramsey: between maximum adduction before re dislocation and excessive abduction, which increases risk of osteonecrosis. technique of hip spica application. Introduction. avascular necrosis (avn) is one of the most serious complications of open or closed reduction of the hip in the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip (ddh), with reported rates in the range of 6% to 48%. 1 early studies suggested that excessive post operative hip abduction in spica is an important risk factor for developing osteone crosis. 2 4 further, it has been. Developmental dysplasia of the hip (ddh) is a disorder of abnormal development resulting in dysplasia, subluxation, and possible dislocation of the hip secondary to capsular laxity and mechanical factors. treatment varies from pavlik bracing to surgical reduction and osteotomies depending on the age of the patient and degree of dysplasia. Hip spica is a plaster cast that extends from the torso down to the feet and is applied in theatre under a general anaesthetic. the objective of the hip spica is to immobilise the hip, pelvis and or femur fractures, or post reduction for developmental dysplasia of the hip (ddh). hip spicas are generally used for children from 6 months to 6.
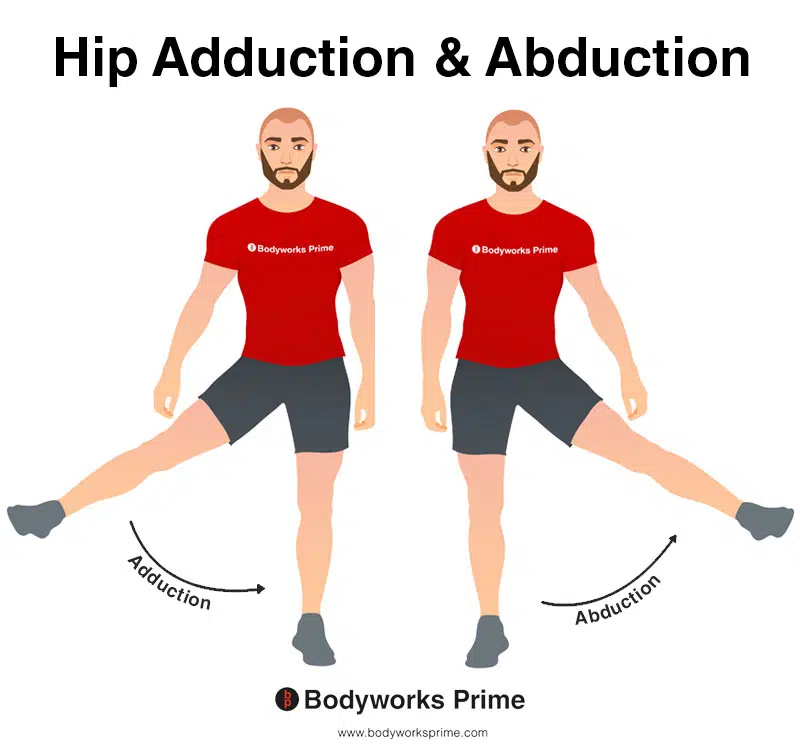
Iliotibial Tract Itb Anatomy Bodyworks Prime Developmental dysplasia of the hip (ddh) is a disorder of abnormal development resulting in dysplasia, subluxation, and possible dislocation of the hip secondary to capsular laxity and mechanical factors. treatment varies from pavlik bracing to surgical reduction and osteotomies depending on the age of the patient and degree of dysplasia. Hip spica is a plaster cast that extends from the torso down to the feet and is applied in theatre under a general anaesthetic. the objective of the hip spica is to immobilise the hip, pelvis and or femur fractures, or post reduction for developmental dysplasia of the hip (ddh). hip spicas are generally used for children from 6 months to 6. Spica cast application following a medial open reduction: a spica cast will be applied with the hips in 100° to 110° of flexion and 45° of abduction (<60° of abduction is highly recommended). excessive internal rotation should be avoided; however, slight internal rotation may increase the stability of the hip. The purpose of the spica cast is to maintain the hip in 100° of flexion and 40–50° of abduction, which is commonly referred to as the “human position” of the hip (fig. 9). the spica cast is technically demanding, but close attention to detail can ensure hip positioning and maintenance of the reduction.

Comments are closed.