Heredity Definition 3 Theories And Importance

Heredity Definition 3 Theories And Importance Heredity definition, 3 theories, and importance. inheritance, often known as heredity, is the process of passing on traits from one generation to the next, either through gametes, sperm, and ova in sexual reproduction or by asexual reproductive bodies in asexual reproduction. heredity is the cause of similarities between individuals, while. Heredity, the sum of all biological processes by which particular characteristics are transmitted from parents to their offspring. the concept of heredity encompasses two seemingly paradoxical observations about organisms: the constancy of a species from generation to generation and the variation among individuals within a species. constancy.
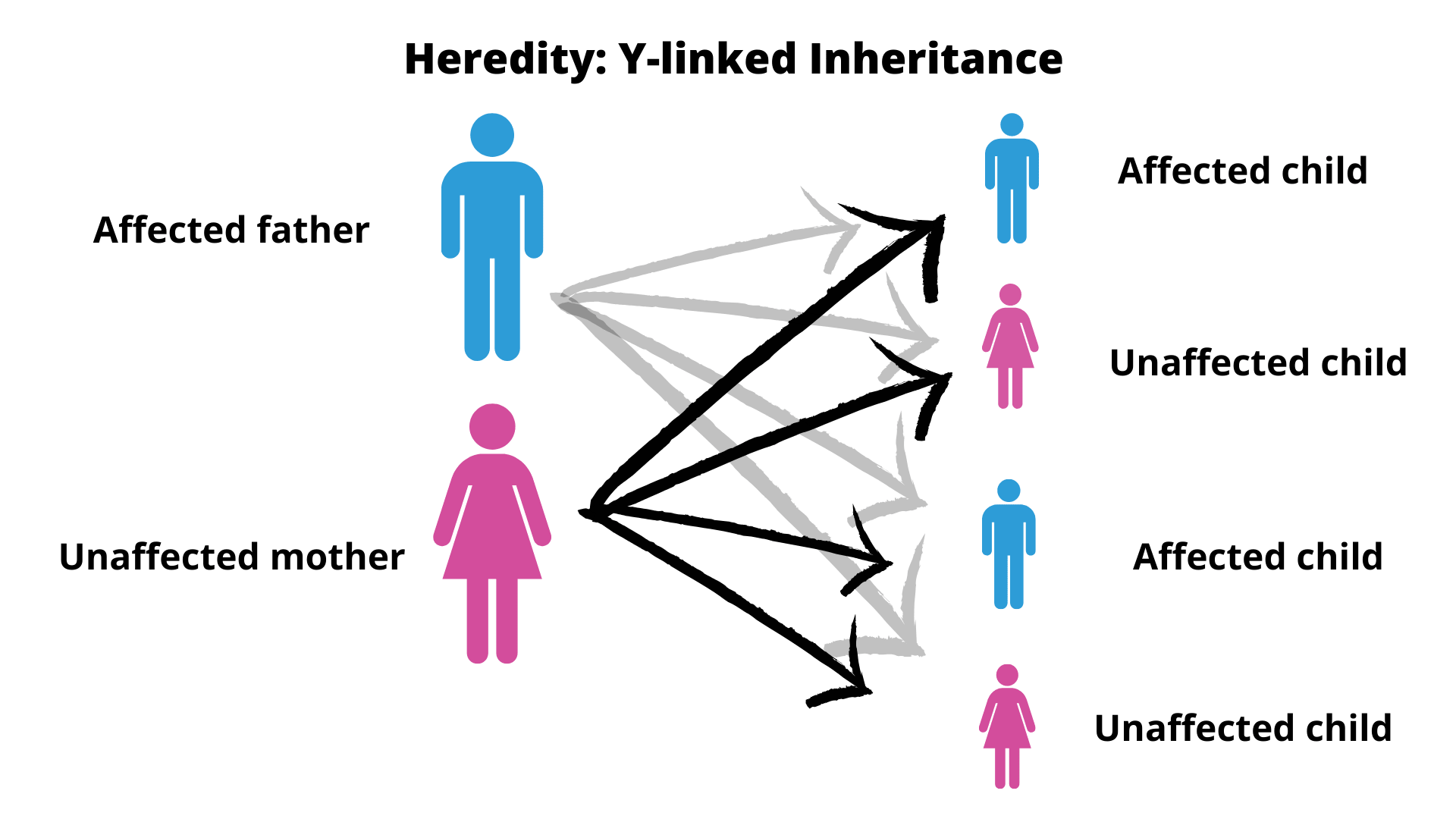
Heredity Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary Heredity definition in biology. heredity is the study of how parents pass down their traits to their offspring through genetics. many theories about heredity have existed, and the general concepts of heredity appeared before people understood cells completely. however, modern day heredity and genetics are newer fields. Notes definition, theories, and importance inheritance, often known as heredity, is the process of passing on traits from one generation to the next, either. Heredity definition. heredity is the passing of traits from parent to offspring. molecules of dna carry information that codes for various proteins. these proteins interact with the environment, causing observable patterns of life. the complex mechanisms that replicate and reproduce dna and the organisms it creates can be recombined and mutated. Heredity, transmission of traits from parents to offspring through genes, the functional units of heritable material that are found within all living cell s. from his studies in the mid 19th century, gregor mendel derived certain basic concepts of heredity, which eventually became the foundation for the modern science of genetics.
Main Principles Of Heredity And Mendel S Experiments Science Online Heredity definition. heredity is the passing of traits from parent to offspring. molecules of dna carry information that codes for various proteins. these proteins interact with the environment, causing observable patterns of life. the complex mechanisms that replicate and reproduce dna and the organisms it creates can be recombined and mutated. Heredity, transmission of traits from parents to offspring through genes, the functional units of heritable material that are found within all living cell s. from his studies in the mid 19th century, gregor mendel derived certain basic concepts of heredity, which eventually became the foundation for the modern science of genetics. Examples of heredity. heredity is the means by which the offspring acquire characteristics from the parent. the passing of traits may be through sexual reproduction or asexual reproduction. in sexual reproduction, male and female gametes are involved. the male gamete fertilizes the female gamete. their union results in a single cell containing. Heredity, genes, and dna. perhaps the most fundamental property of all living things is the ability to reproduce. all organisms inherit the genetic information specifying their structure and function from their parents. likewise, all cells arise from preexisting cells, so the genetic material must be replicated and passed from parent to progeny.

Comments are closed.