Graphing Piecewise Functions Domain Range Limits Continuity Absolute Value

Graphing Piecewise Functions Domain Range Limits Continuityођ This math video tutorial focuses on graphing piecewise functions as well determining points of discontinuity, limits, domain and range. introduction to func. Free piecewise functions calculator explore piecewise function domain, range, intercepts, extreme points and asymptotes step by step.
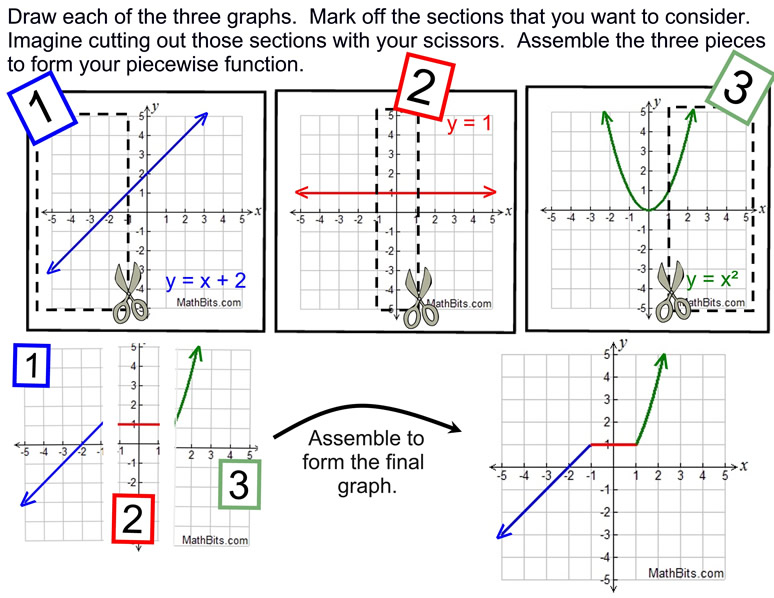
Piecewise Absolute Value And Step Functions Mathbitsnotebook A1 Finding domain and range from graphs. another way to identify the domain and range of functions is by using graphs. because the domain refers to the set of possible input values, the domain of a graph consists of all the input values shown on the x axis. the range is the set of possible output values, which are shown on the y axis. Piecewise function examples. example 1: graph the piecewise function f (x) = {−2x, −1≤ x <0 x2, 0 ≤ x <2 f (x) = {− 2 x, − 1 ≤ x <0 x 2, 0 ≤ x <2. solution: let us make tables for each of the given intervals using their respective definitions of the function. let us just plot them and join them by curves. Here are a few examples of piecewise functions: the absolute value function: f(x) = |x| is a piecewise function because it has different rules for different parts of its domain. specifically, f(x) = x if x is greater than or equal to 0, and f(x) = x if x is less than 0. This calculus review video tutorial explains how to evaluate limits using piecewise functions and how to make a piecewise function continuous by finding the.
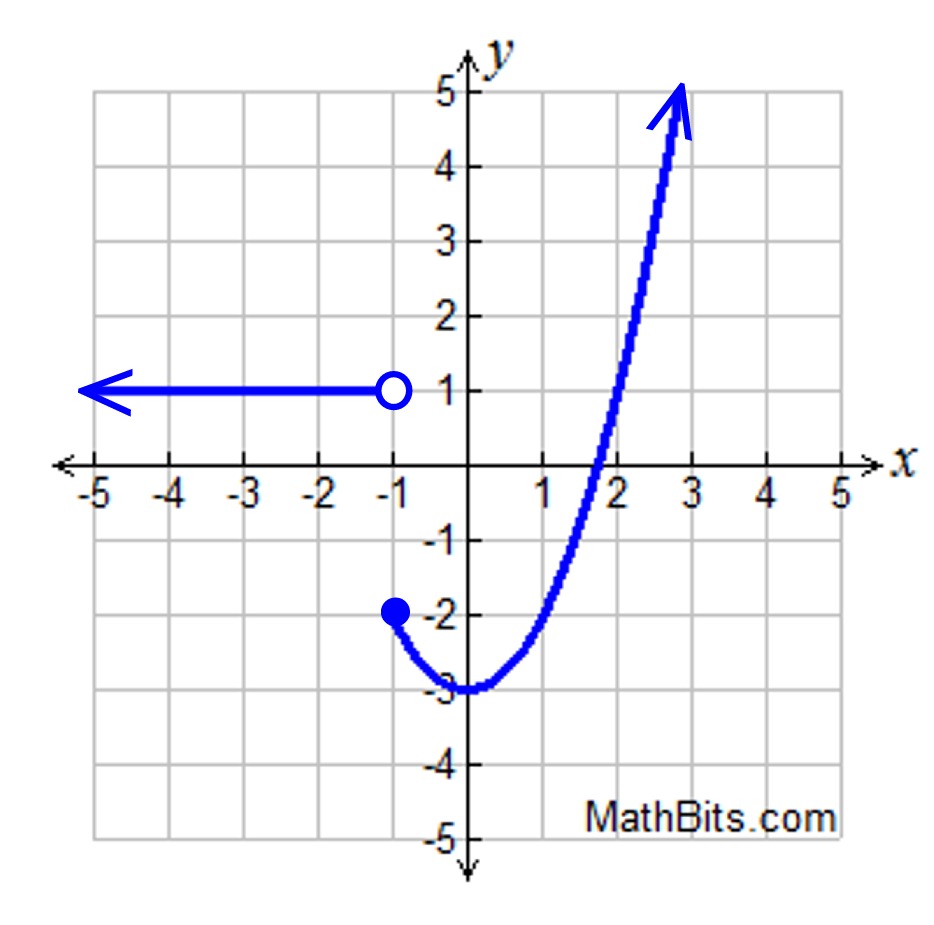
Piecewise Absolute Value And Step Functions Practice Here are a few examples of piecewise functions: the absolute value function: f(x) = |x| is a piecewise function because it has different rules for different parts of its domain. specifically, f(x) = x if x is greater than or equal to 0, and f(x) = x if x is less than 0. This calculus review video tutorial explains how to evaluate limits using piecewise functions and how to make a piecewise function continuous by finding the. A piecewise function is a function in which more than one formula is used to define the output. each formula has its own domain, and the domain of the function is the union of all these smaller domains. we notate this idea like this: f\left (x\right)=\begin {cases}\text {formula 1 if x is in domain 1}\\ \text {formula 2 if x is in domain 2. A piecewise defined function is a function defined by at least two equations ("pieces"), each of which applies to a different part of the domain. piecewise defined functions can take on a variety of forms. their "pieces" may be all linear, or a combination of functional forms (such as constant, linear, quadratic, cubic, square root, cube root.

Piecewise Functions Limits And Continuity Calculus Youtube A piecewise function is a function in which more than one formula is used to define the output. each formula has its own domain, and the domain of the function is the union of all these smaller domains. we notate this idea like this: f\left (x\right)=\begin {cases}\text {formula 1 if x is in domain 1}\\ \text {formula 2 if x is in domain 2. A piecewise defined function is a function defined by at least two equations ("pieces"), each of which applies to a different part of the domain. piecewise defined functions can take on a variety of forms. their "pieces" may be all linear, or a combination of functional forms (such as constant, linear, quadratic, cubic, square root, cube root.

Comments are closed.