Graph Theory 11 Trees
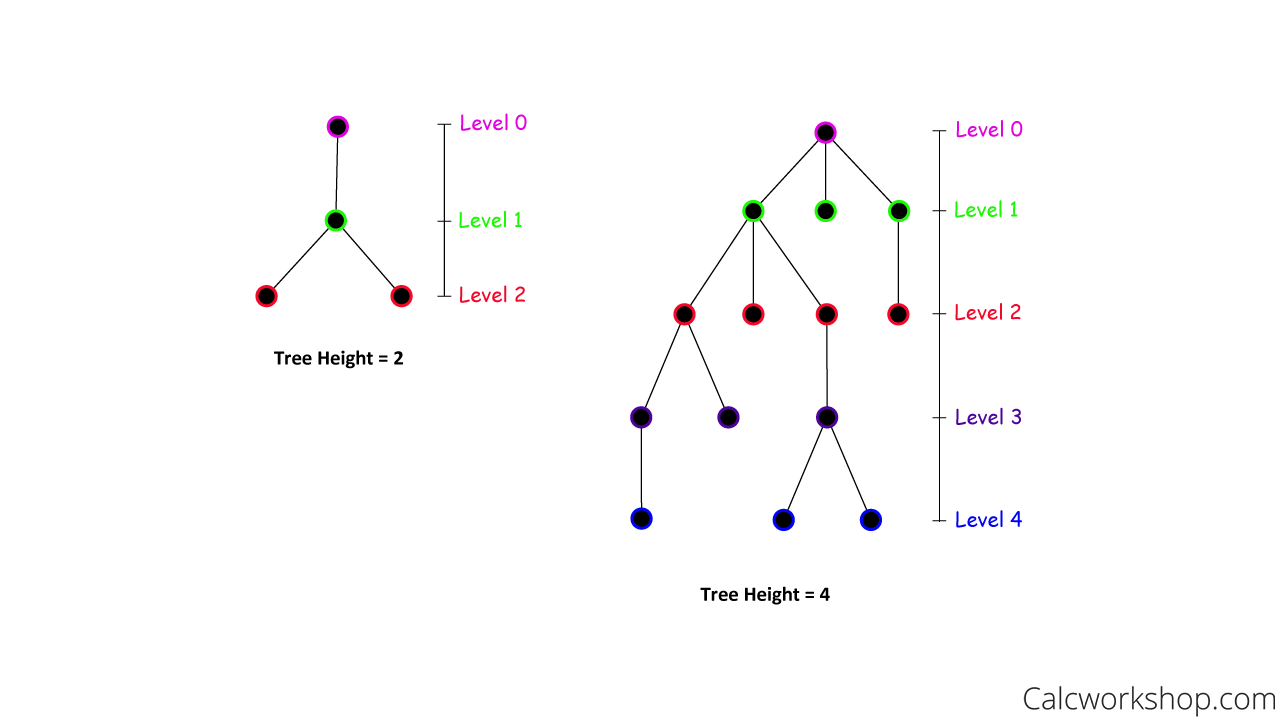
Graph Theory Tree An introduction to trees and their properties. Graph theory in the movies. in the 1997 film good will hunting, the main character, will, played by matt damon, solves what is supposed to be an exceptionally difficult graph theory problem, “draw all the homeomorphically irreducible trees of size n = 10 n = 10.” that sounds terrifying! but don’t panic.
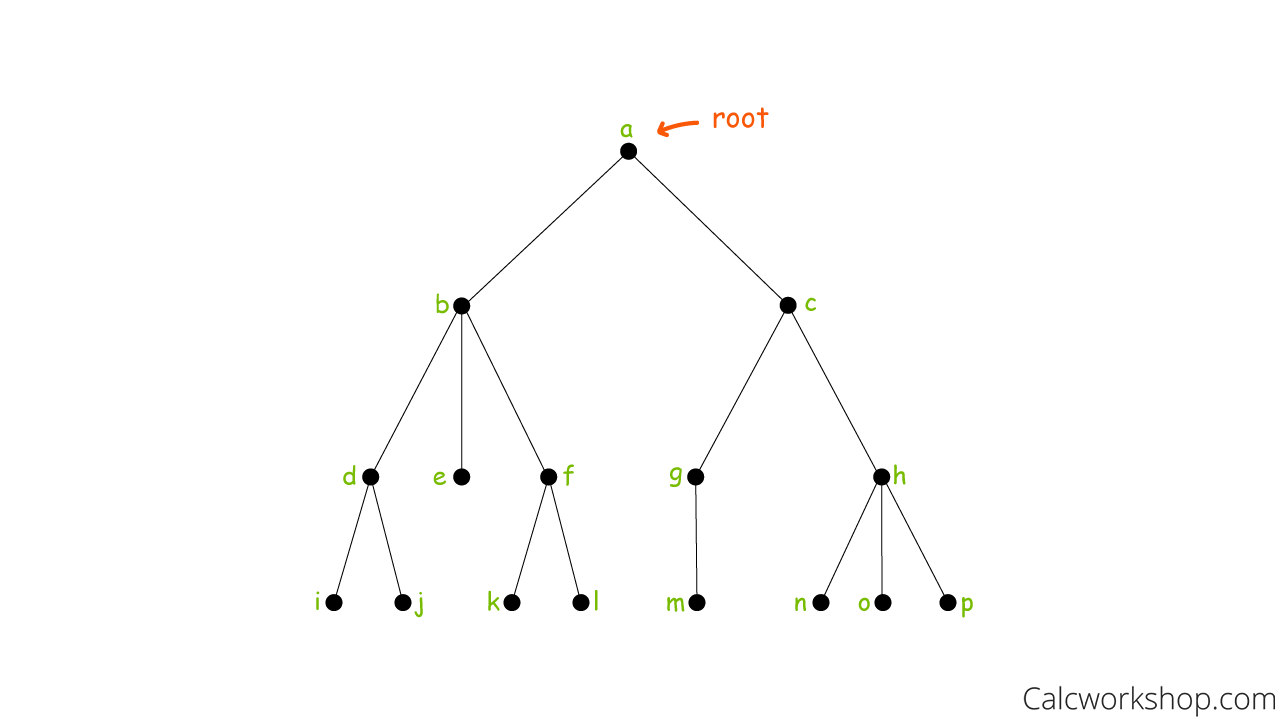
Graph Theory Tree Trees graph theory (fall 2011) rutgers university swastik kopparty 1 some basic de nitions let g = (v;e) be a graph. de nition 1 (degree). the degree of a vertex v 2v, denoted d(v), is the number of e 2e that are incident on v. lemma 2. x v2v d(v) = 2jej: proof. count the number of (v;e) 2v e such that e is incident on v. de nition 3 (walk). V − 1. chromatic number. 2 if v > 1. table of graphs and parameters. in graph theory, a tree is an undirected graph in which any two vertices are connected by exactly one path, or equivalently a connected acyclic undirected graph. [1] a forest is an undirected graph in which any two vertices are connected by at most one path, or equivalently. Fig 4.4 red black tree [8] iv. red black trees are another type of self balancing binary search tree that ensures that no path from the root to a leaf is more than twice as long as any other path. What is a graph? an undirected graph g = (v, e) consists of – a non empty set of vertices nodes v – a set of edges e, each edge being a set of one or two vertices (if one vertex, the edge is a self loop) a directed graph g = (v, e) consists of – a non empty set of vertices nodes v – a set of edges e, each edge being an ordered pair of.
Graph Theory Tree Fig 4.4 red black tree [8] iv. red black trees are another type of self balancing binary search tree that ensures that no path from the root to a leaf is more than twice as long as any other path. What is a graph? an undirected graph g = (v, e) consists of – a non empty set of vertices nodes v – a set of edges e, each edge being a set of one or two vertices (if one vertex, the edge is a self loop) a directed graph g = (v, e) consists of – a non empty set of vertices nodes v – a set of edges e, each edge being an ordered pair of. 1 edges. stil do not know which of two running times (such as m2 and n3) are be er, goal: implement the basic graph search algorithms in time o(m n). this is linear time, since it takes o(m n) time simply to read the input. note that when we work with connected graphs, a running time of o(m n) is the same as o(m), since m n 1. What are trees in graph theory? tree graphs are connected graphs with no cycles. we'll introduce them and some equivalent definitions, with of course example.

Forest With Tree In Graph Theory 11 Youtube 1 edges. stil do not know which of two running times (such as m2 and n3) are be er, goal: implement the basic graph search algorithms in time o(m n). this is linear time, since it takes o(m n) time simply to read the input. note that when we work with connected graphs, a running time of o(m n) is the same as o(m), since m n 1. What are trees in graph theory? tree graphs are connected graphs with no cycles. we'll introduce them and some equivalent definitions, with of course example.
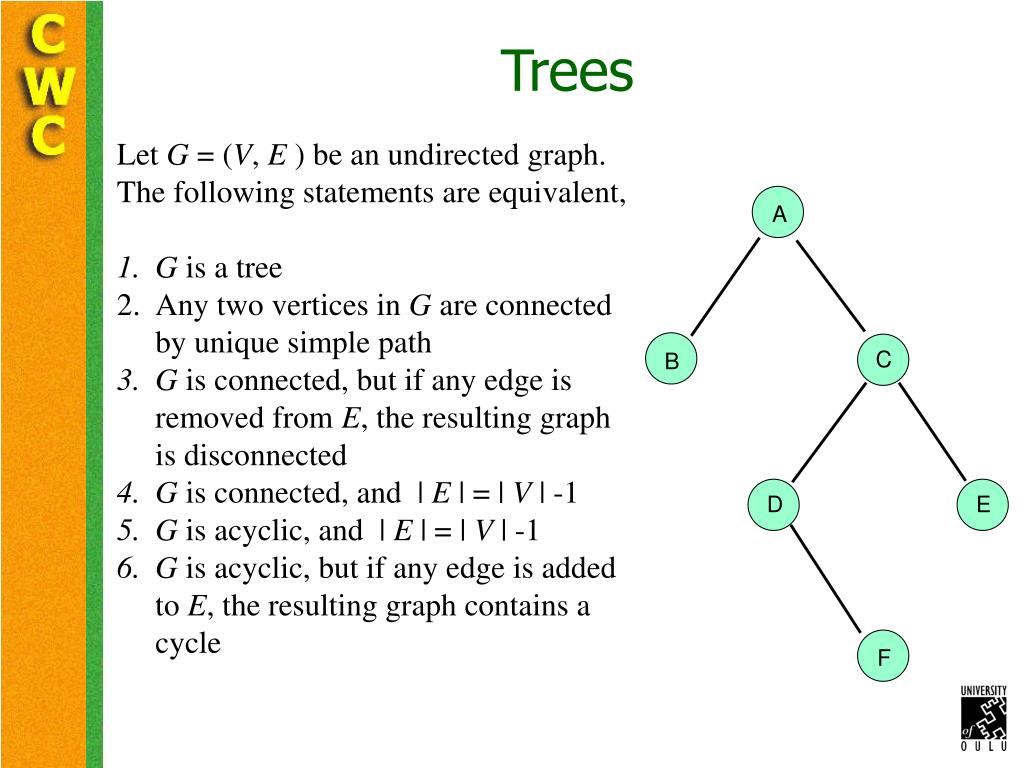
Ppt Overview Of Graph Theory Powerpoint Presentation Free Download

Comments are closed.