Frontiers The Gut Microbiota Microbiome In Cardiovascular Disease
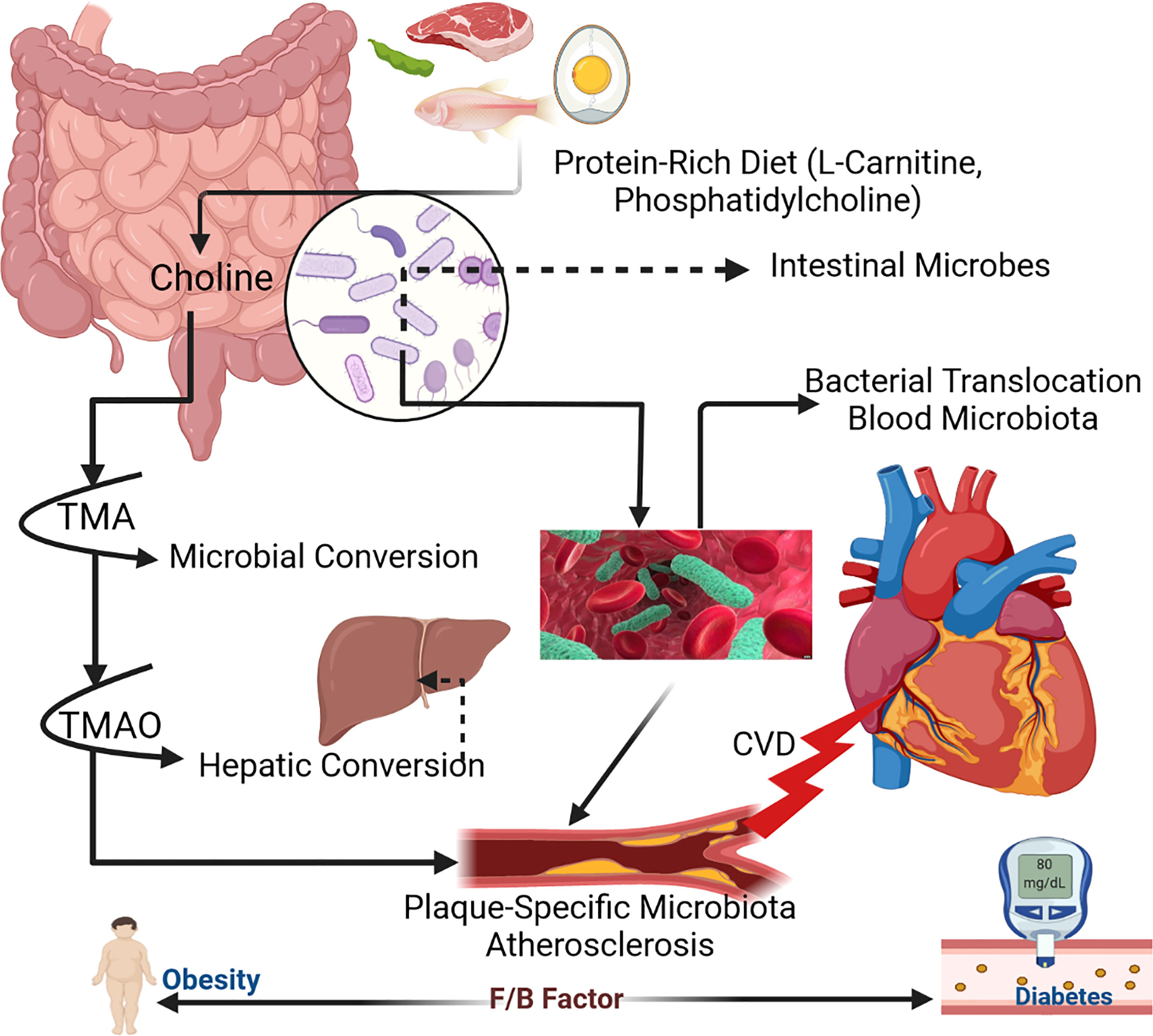
Frontiers The Gut Microbiota Microbiome In Cardiovascular Disease The synthesis of trimethylamine n oxide (tmao) and the development of cardiovascular risk exhibit another dimension to this dynamic activity, i.e., the interplay between the intestinal microbiome and the human host that occurs through the interaction of dietary intake (a type of environmental exposure) with the intestinal microbiota, leading to the production of metabolites that may serve as. By affecting these living cells, the gut microbiota can cause heart failure, atherosclerosis, hypertension, myocardial fibrosis, myocardial infarction, and coronary artery disease. previous studies of the gut microbiota and its relation to stroke pathogenesis and its consequences can provide new therapeutic prospects.
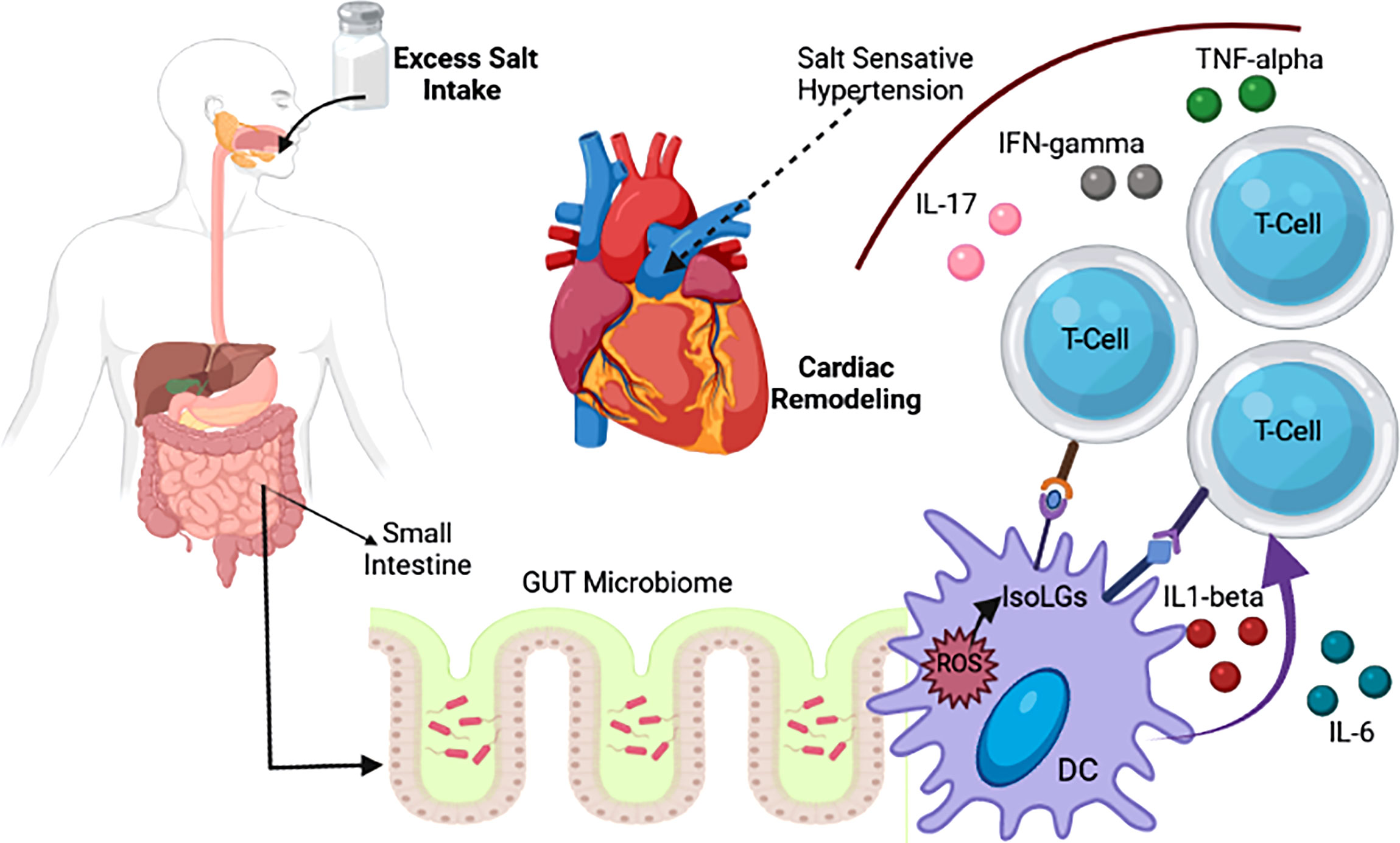
Frontiers The Gut Microbiota Microbiome In Cardiovascular Disease Abstract. in the last two decades, considerable interest has been shown in understanding the development of the gut microbiota and its internal and external effects on the intestine, as well as the risk factors for cardiovascular diseases (cvds) such as metabolic syndrome. the intestinal microbiota plays a pivotal role in human health and disease. Perturbation of the gut microbiota, dysbiosis, can lead to several diseases, not only gastrointestinal conditions, but also disorders of the lung, brain, heart and immune system (5–7). dysbiosis has an important role in cvds, especially by activating a proinflammatory status in the body and favoring the atherosclerotic process ( 8 , 9 ). The gut microbiota has emerged as an environmental risk factor that affects thrombotic phenotypes in several cardiovascular diseases. evidence includes the identification of marker species by. The gut microbiota has recently gained attention due to its association with cardiovascular health, cancers, gastrointestinal disorders, and non communicable diseases. one critical question is how.

Comments are closed.