Food Chain Producers Consumers Decomposers Food Chain In Pond

Food Chain Producers Consumers Decomposers Food Chain In Pond A food chain is one possible path energy takes as it moves through the ecosystem. a pond can contain many different food chains that interconnect and overlap forming a complex food wed. the pond. Pond ecosystem food chain diagram. the typical pond food chain is much more complex than just simple predator prey relationships. it involves microorganisms that must generate their own food when a sufficient set of nutrient building blocks are available. it also involves microbes that are responsible for breaking down waste to free up these.

Pond Ecosystem Types Food Chain Animals And Plants Earth Reminder Jon houston on 07 14 2024. a pond food chain is a fascinating network of energy transfer that occurs in freshwater pond ecosystems. at the base of this chain are the producers, primarily plants and algae, which use sunlight to create energy through photosynthesis. these producers are vital because they support the entire ecosystem by providing. The producer close producer plants that begin food chains by making energy from carbon dioxide and water. provides the basic source of food which other organisms, the consumers close consumer an. All of the living organisms within the pond are broken down into producers, consumers, and decomposers. the four levels of the pond food chain in freshwater ponds. the pond food chain is broken down into four basic trophic levels that take on a linear structure, most often based on the size of the species and the abundance. Trophic levels organisms in food chains are grouped into categories called trophic levels. roughly speaking, these levels are divided into producers (first trophic level), consumers (second, third, and fourth trophic levels), and decomposers. producers, also known as autotrophs, make their own food. they make up the first level of every food chain.

Pond Food Web Consumers Decomposers Producers Lesson Study All of the living organisms within the pond are broken down into producers, consumers, and decomposers. the four levels of the pond food chain in freshwater ponds. the pond food chain is broken down into four basic trophic levels that take on a linear structure, most often based on the size of the species and the abundance. Trophic levels organisms in food chains are grouped into categories called trophic levels. roughly speaking, these levels are divided into producers (first trophic level), consumers (second, third, and fourth trophic levels), and decomposers. producers, also known as autotrophs, make their own food. they make up the first level of every food chain. In addition to the producers and consumers, decomposers are an important part of any food web. decomposers are ecosystem members who have an important role of recycling nutrients back into the soil. they consume waste and decaying plant and animal matter. Further trophic levels are numbered subsequently according to how far the organism is along the food chain. level 1: plants and algae make their own food and are called producers. level 2: herbivores eat plants and are called primary consumers. level 3: carnivores that eat herbivores are called secondary consumers.
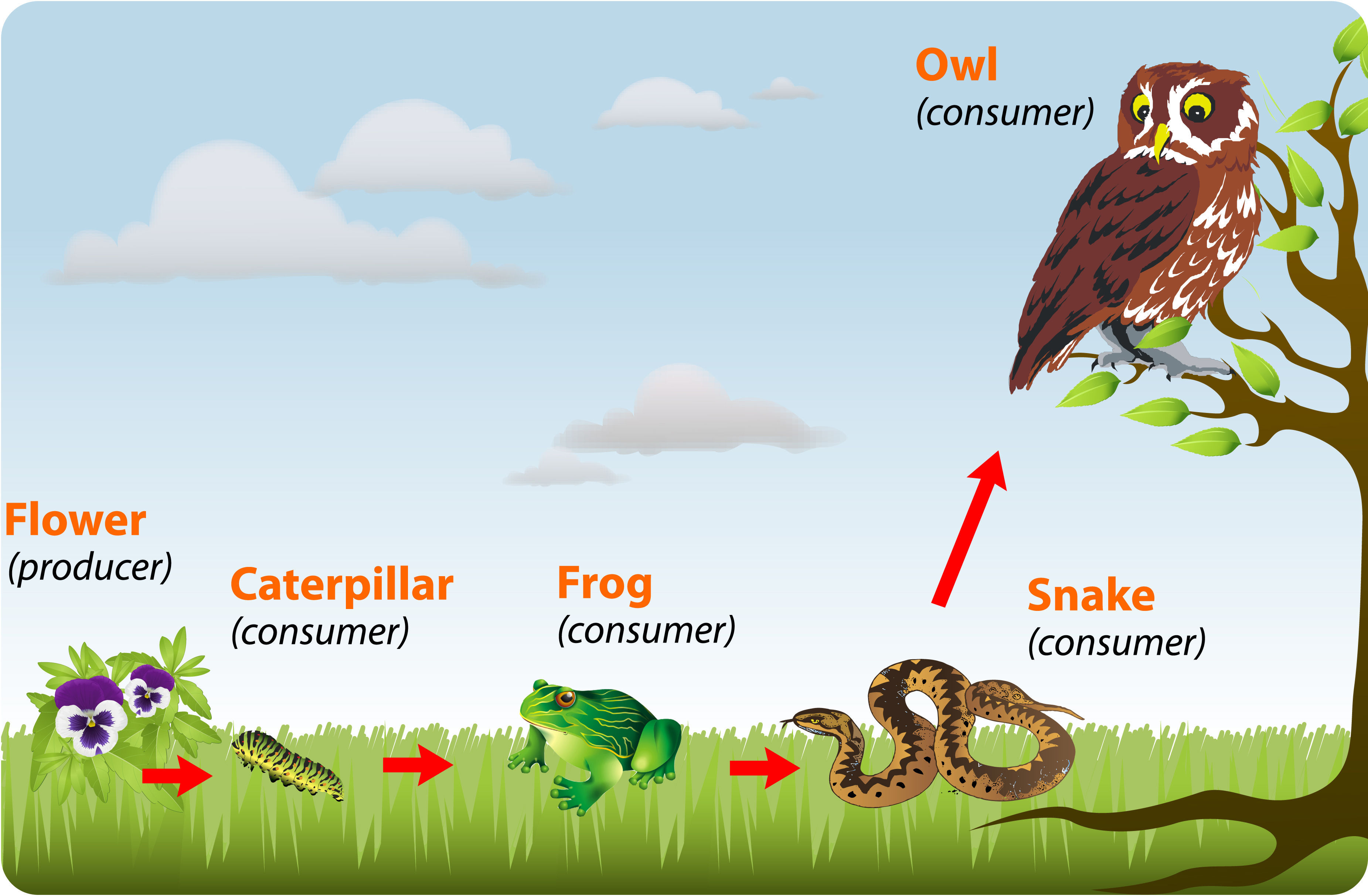
Food Chain In Terrestrial Ecosystem In addition to the producers and consumers, decomposers are an important part of any food web. decomposers are ecosystem members who have an important role of recycling nutrients back into the soil. they consume waste and decaying plant and animal matter. Further trophic levels are numbered subsequently according to how far the organism is along the food chain. level 1: plants and algae make their own food and are called producers. level 2: herbivores eat plants and are called primary consumers. level 3: carnivores that eat herbivores are called secondary consumers.

Comments are closed.