Food Chain 1 Primary Producer A Z Animals
Food Chain 1 Primary Producer A Z Animals Primary producers are autotrophic organisms that utilize inorganic carbon and sunlight to produce food, like grass. 2. primary consumer. primary consumers are animals that directly consume autotrophic animals. for example, an insect could feed on the grass in its environment, gaining nutrition. Simply put, a food chain shows how energy is transferred through an ecosystem, typically by animals consuming other organisms. a forest food chain will always include primary producers and primary consumers, no matter its location. ©thompsma cc by sa 3.0 – original license. food chains always begin with the primary producers: plants.

Animal Food Chain Diagram Noun. one of three positions on the food chain: autotrophs (first), herbivores (second), and carnivores and omnivores (third). volcano. noun. an opening in the earth's crust, through which lava, ash, and gases erupt, and also the cone built by eruptions. the food chain describes who eats whom in the wild. The producers. the primary producers are at the foundation of the rainforest’s ecological system — the sun and the trees. ranging from the oldest largest species to shrubs, trees play an integral part in the rainforest food chain and web. Food chains. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally decomposers. these levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics. A food chain is a list of organisms in a. habitat. that shows their feeding relationship, i.e what eats what. the organisms are joined by arrows which show the transfer of energy in food between.

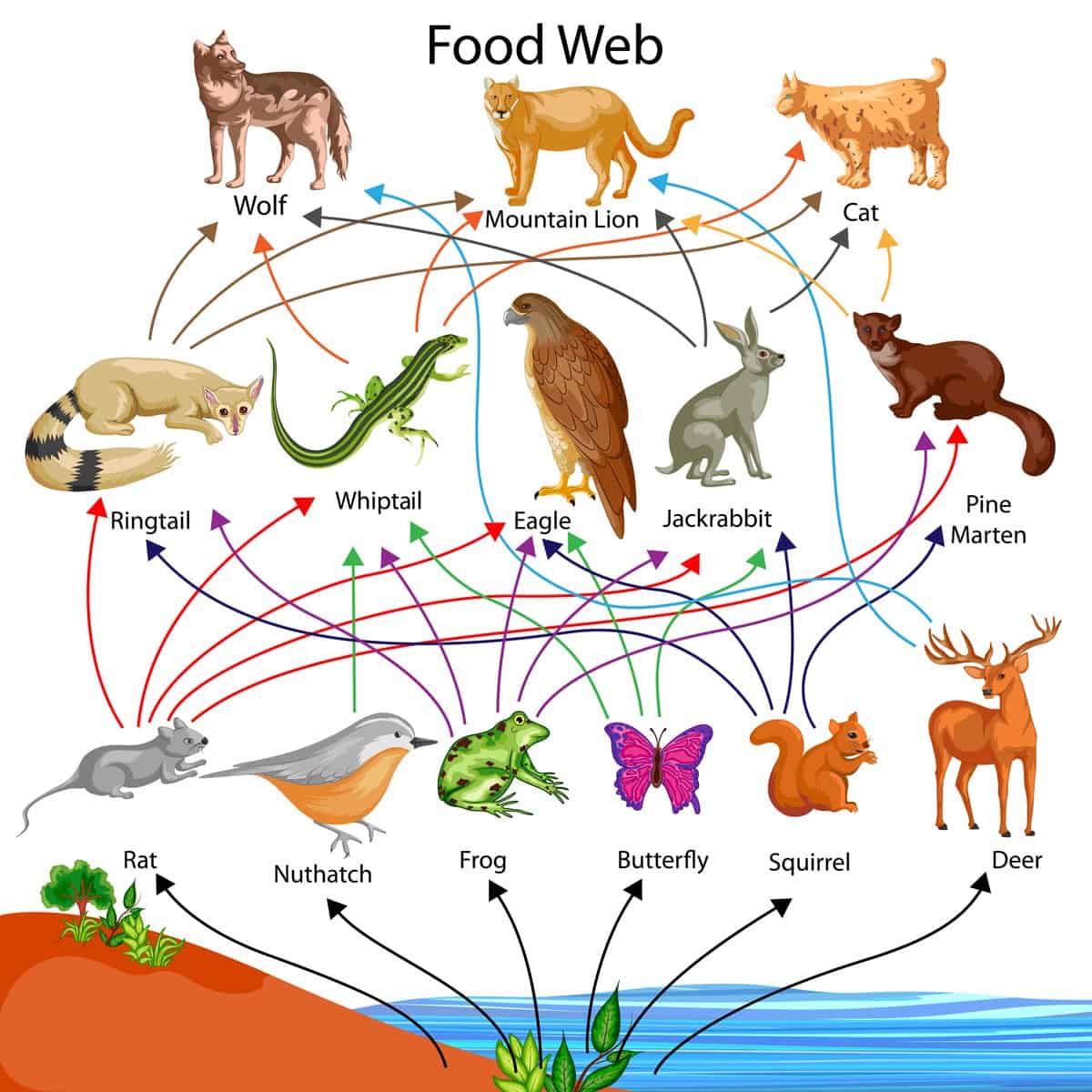
Food Chain 1 Primary Producer A Z Animals Food chains. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally decomposers. these levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics. A food chain is a list of organisms in a. habitat. that shows their feeding relationship, i.e what eats what. the organisms are joined by arrows which show the transfer of energy in food between. Typically, a food chain is represented by a diagram where arrows show the direction of energy and nutrients flow. many herbivores eat grass, and deer can eat other plants besides grass. even a tiger can eat many types of animals and plants. thus, each animal is part of multiple food chains. all interconnected to make a food web. A food web is a graphic representation of a holistic, nonlinear web of primary producers, primary consumers, and higher level consumers used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics (figure 1). figure 1. example of simplified food chains (a) and food webs (b) of terrestrial and marine ecosystems.

Food Pyramid For Animals Typically, a food chain is represented by a diagram where arrows show the direction of energy and nutrients flow. many herbivores eat grass, and deer can eat other plants besides grass. even a tiger can eat many types of animals and plants. thus, each animal is part of multiple food chains. all interconnected to make a food web. A food web is a graphic representation of a holistic, nonlinear web of primary producers, primary consumers, and higher level consumers used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics (figure 1). figure 1. example of simplified food chains (a) and food webs (b) of terrestrial and marine ecosystems.

Comments are closed.