Finding The Probability Of A Binomial Distribution Plus Mean Standard

Finding The Probability Of A Binomial Distribution Plus Mean Standard For our die example we have n = 10 rolls, a success probability of p = 0.1667, and a failure probability of (1 – p) = 0.833. let’s enter these values into the formula. 10 * 0.1667 * 0.8333 = 1.3891. that’s the variance, which uses squared units. to find the standard deviation of the binomial distribution, we need to take the square root. This statistics video tutorial explains how to find the probability of a binomial distribution as well as calculating the mean and standard deviation. you n.

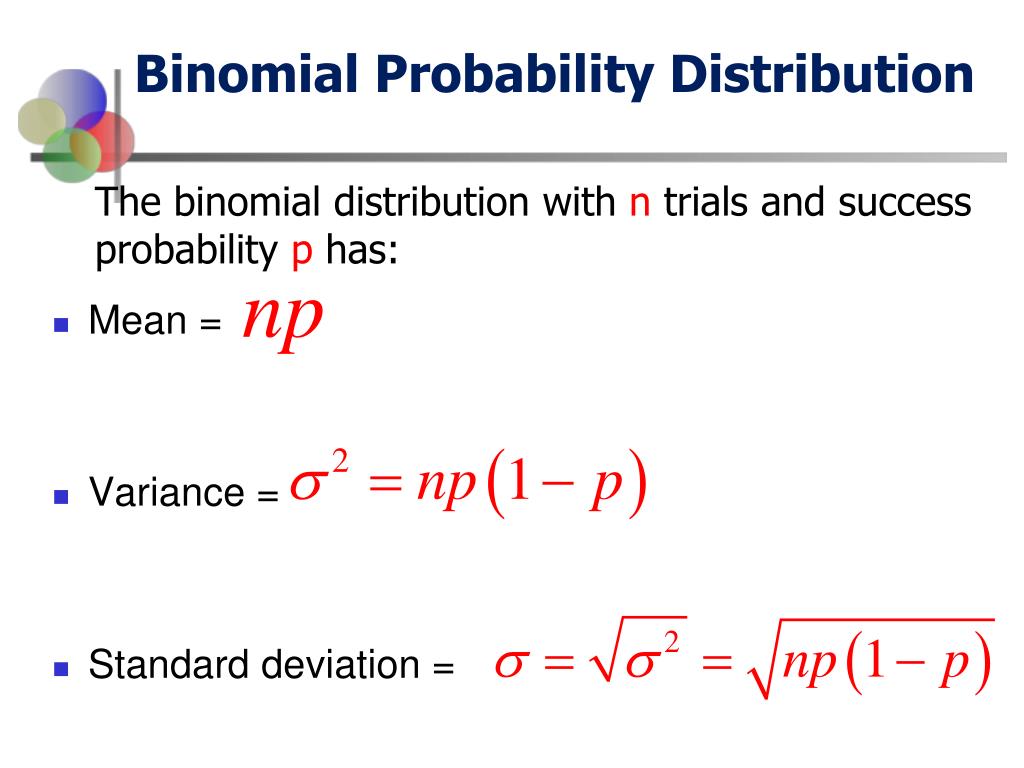
Binomial Distribution Mean Variance Standard Derivation Youtube Example \(\pageindex{1}\) finding the probability distribution, mean, variance, and standard deviation of a binomial distribution. when looking at a person’s eye color, it turns out that 1% of people in the world has green eyes ("what percentage of," 2013). consider a group of 20 people. state the random variable. write the probability. The standard deviation of binomial distribution, another measure of a probability distribution dispersion, is simply the square root of the variance, σ. keep in mind that the standard deviation calculated from your sample (the observations you actually gather) may differ from the entire population's standard deviation. Patreon professorleonardstatistics lecture 5.4: finding the mean and standard deviation of a binomial probability distribution. The outcomes of a binomial experiment fit a binomial probability distribution. the random variable x = the number of successes obtained in the n independent trials. the mean, μ, and variance, σ 2, for the binomial probability distribution are μ = np and σ 2 = npq. the standard deviation, σ, is then σ = n p q n p q.

Find Binomial Probabilities Mean Variance And Standard Deviation Of Patreon professorleonardstatistics lecture 5.4: finding the mean and standard deviation of a binomial probability distribution. The outcomes of a binomial experiment fit a binomial probability distribution. the random variable x = the number of successes obtained in the n independent trials. the mean, μ, and variance, σ 2, for the binomial probability distribution are μ = np and σ 2 = npq. the standard deviation, σ, is then σ = n p q n p q. The binomial distribution describes the probability of having exactly k successes in n independent bernoulli trials with probability of a success p (in example 5.4.1.1 5.4.1. 1, n = 4, k = 1, p = 0.35). we would like to determine the probabilities associated with the binomial distribution more generally, i.e. we want a formula where we can use. The calculator displays a binomial probability of 15.51%, matching our results above for this specific number of sixes. next, change exactly r successes to r or more successes. the calculator displays 22.487, matching the results for our example with the binomial inverse cumulative distribution. now, try one yourself.

Mean Variance And Standard Deviation Of A Binomial Probability The binomial distribution describes the probability of having exactly k successes in n independent bernoulli trials with probability of a success p (in example 5.4.1.1 5.4.1. 1, n = 4, k = 1, p = 0.35). we would like to determine the probabilities associated with the binomial distribution more generally, i.e. we want a formula where we can use. The calculator displays a binomial probability of 15.51%, matching our results above for this specific number of sixes. next, change exactly r successes to r or more successes. the calculator displays 22.487, matching the results for our example with the binomial inverse cumulative distribution. now, try one yourself.
Ppt Binomial Probability Distribution Powerpoint Presentation Free

Comments are closed.