Exploring The 5 Types Of Cyber Security Gitsecurity Trusted

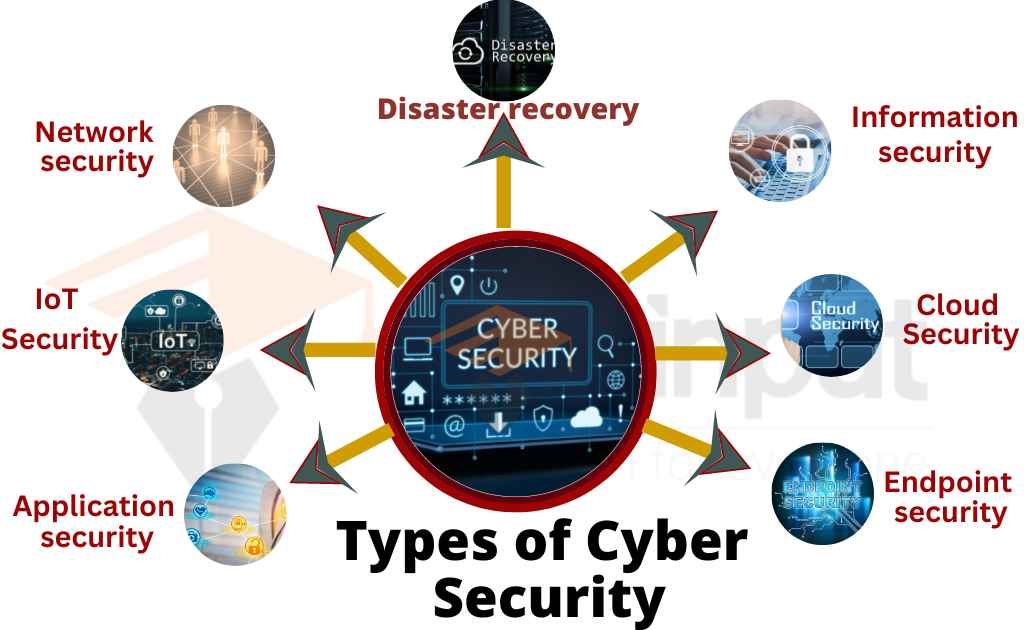
Exploring The 5 Types Of Cyber Security Gitsecurity Trusted Experts say network, application, and operational security are the main parts of a strong cyber security plan. they cover the most important aspects of keeping digital information safe. using these five main types of cyber security, companies can build a strong defense and fight off many cyber threats. Information security models encompass various approaches, including multilevel security models, integrity models, information flow models, state machine models, and more. these models are used to protect subjects and objects, as well as data items. each model offers distinct methods for establishing a secure state within network systems by.

Understanding The 5 Types Of Cyber Security Kmt Pro tips: 1. familiarize yourself with the 8 domains of cybersecurity, which include security and risk management, asset security, security engineering, communications and network security, identity and access management, security assessment and testing, security operations, and software development security. 2. Pro tips: 1. understand the different categories of security: the 7 domains of security include networking, physical, administrative, operations, personnel, application, and information. it is essential to have knowledge of each category to develop a well rounded security strategy. 2. 2. cloud security. 3. internet of things. there is also critical infrastructure security and application security. 1. network security. network security protects your computer network from cyber attacks. utilising different features, these safeguards reduce the risk of cyber threats from inside and outside your business. What is zero trust. zero trust is a network security philosophy that states no one inside or outside the network should be trusted unless their identification has been thoroughly checked. zero trust operates on the assumption that threats both outside and inside the network are an omnipresent factor. zero trust also assumes that every attempt.

Understanding The 5 Types Of Cyber Security Kmt 2. cloud security. 3. internet of things. there is also critical infrastructure security and application security. 1. network security. network security protects your computer network from cyber attacks. utilising different features, these safeguards reduce the risk of cyber threats from inside and outside your business. What is zero trust. zero trust is a network security philosophy that states no one inside or outside the network should be trusted unless their identification has been thoroughly checked. zero trust operates on the assumption that threats both outside and inside the network are an omnipresent factor. zero trust also assumes that every attempt. Examples of advanced cyber threats include advanced persistent threats (apts), ransomware, and zero day. exploits .the 5 most famous threats that exist now are as follows: ransomware attack. a. Zero trust seeks to address the following key principles based on the nist guidelines: continuous verification. always verify access, all the time, for all resources. limit the “blast radius.”. minimize impact if an external or insider breach does occur. automate context collection and response.
Cyber Security Types Threats And Certifications Examples of advanced cyber threats include advanced persistent threats (apts), ransomware, and zero day. exploits .the 5 most famous threats that exist now are as follows: ransomware attack. a. Zero trust seeks to address the following key principles based on the nist guidelines: continuous verification. always verify access, all the time, for all resources. limit the “blast radius.”. minimize impact if an external or insider breach does occur. automate context collection and response.

Comments are closed.