Explainer Making Waves In Science

Explainer Making Waves In Science Making waves. flickr max nathan, cc by nc nd. explainer: making waves in science published: march 1, 2016 2:04pm est. michael hall, griffith university. author. michael hall senior research fellow. For example, when making waves on a rope, it takes more energy to make a higher frequency wave. moving your hand up and down 10 times per second (10 hertz) requires more energy than moving your hand only once per second (1 hertz). and those 10 hertz waves on the rope have a shorter wavelength than ones at 1 hertz.
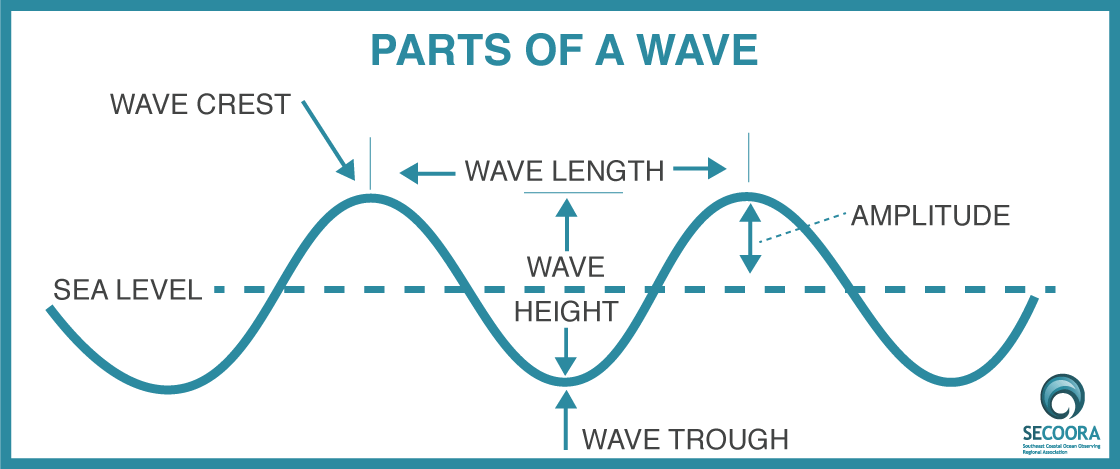
Labelled Diagram Of A Wave Measuring waves. all sound waves are the same: they travel through a medium by making atoms or molecules shake back and forth. but all sound waves are different too. there are loud sounds and quiet sounds, high pitched squeaks and low pitched rumbles, and even two instruments playing exactly the same musical note will produce sound waves that are quite different. Explainer: the doppler effect. when an ambulance passes with its siren blaring, you hear the pitch of the siren change: as it approaches, the siren’s pitch sounds higher than when it is moving. Introduction to waves. transverse and longitudinal waves are two types of mechanical waves, which involve the transfer of energy through a medium (e.g. water, air, a solid). learn about transverse and longitudinal waves through the examples of a rope and a sound wave. explore the difference between a single wave pulse and periodic waves. All kinds of waves have the same fundamental properties of reflection, refraction, diffraction and interference, and all waves have a wavelength, frequency, speed and amplitude. all waves can be thought of as a disturbance that transfers energy. some waves (water waves and sound waves) are formed through the vibration of particles.

Explainer Making Waves In Science Introduction to waves. transverse and longitudinal waves are two types of mechanical waves, which involve the transfer of energy through a medium (e.g. water, air, a solid). learn about transverse and longitudinal waves through the examples of a rope and a sound wave. explore the difference between a single wave pulse and periodic waves. All kinds of waves have the same fundamental properties of reflection, refraction, diffraction and interference, and all waves have a wavelength, frequency, speed and amplitude. all waves can be thought of as a disturbance that transfers energy. some waves (water waves and sound waves) are formed through the vibration of particles. A wave can be described as a disturbance that travels through a medium from one location to another location. consider a slinky wave as an example of a wave. when the slinky is stretched from end to end and is held at rest, it assumes a natural position known as the equilibrium or rest position. Lesson 2 properties of a wave. the anatomy of a wave. frequency and period of a wave. energy transport and the amplitude of a wave. the speed of a wave. the wave equation. lesson 3 behavior of waves. boundary behavior. reflection, refraction, and diffraction.
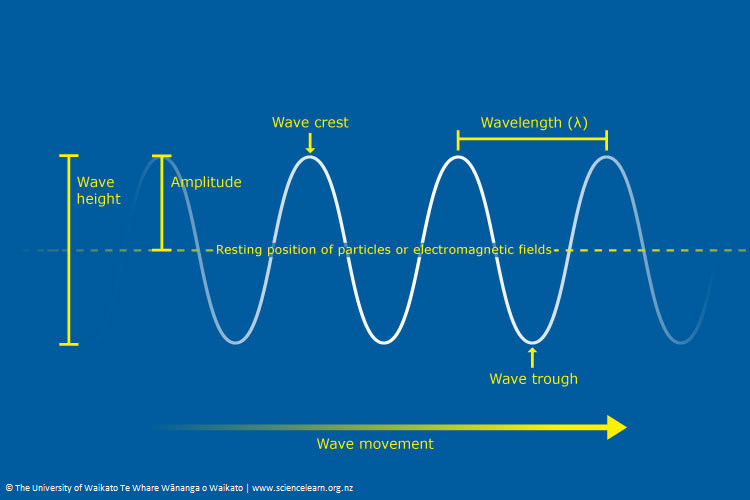
Fundamentals Of Waves вђ Science Learning Hub A wave can be described as a disturbance that travels through a medium from one location to another location. consider a slinky wave as an example of a wave. when the slinky is stretched from end to end and is held at rest, it assumes a natural position known as the equilibrium or rest position. Lesson 2 properties of a wave. the anatomy of a wave. frequency and period of a wave. energy transport and the amplitude of a wave. the speed of a wave. the wave equation. lesson 3 behavior of waves. boundary behavior. reflection, refraction, and diffraction.
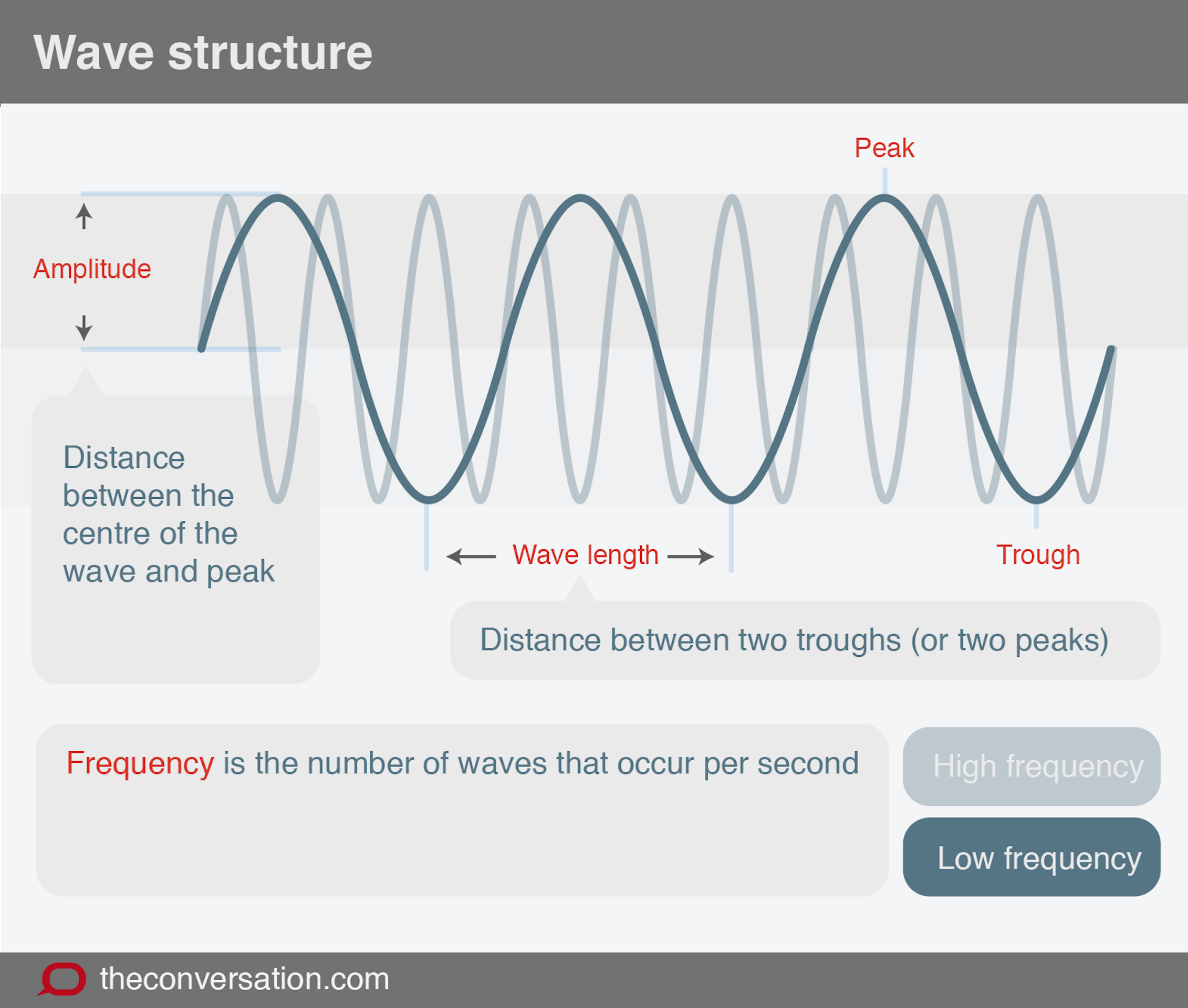
Explainer Making Waves In Science

Comments are closed.