Examples Of A Tertiary Consumer
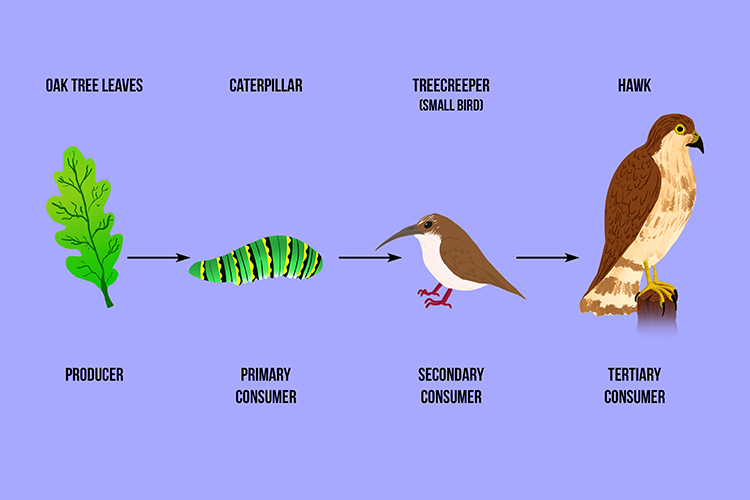
A Tertiary Consumer Eats Secondary Animals In The Food Chain A tertiary consumer is an animal that eats primary and secondary consumers, such as big cats, sharks, whales and humans. learn how tertiary consumers control ecosystems, occupy the top trophic level and take quizzes on this topic. A tertiary consumer is a fourth trophic level after producers, primary consumers, and secondary consumers. tertiary consumers eat primary and secondary consumers as their main source of food. these organisms are sometimes referred to as apex predators as they are normally at the top of food chains, feeding on both primary and secondary consumers.
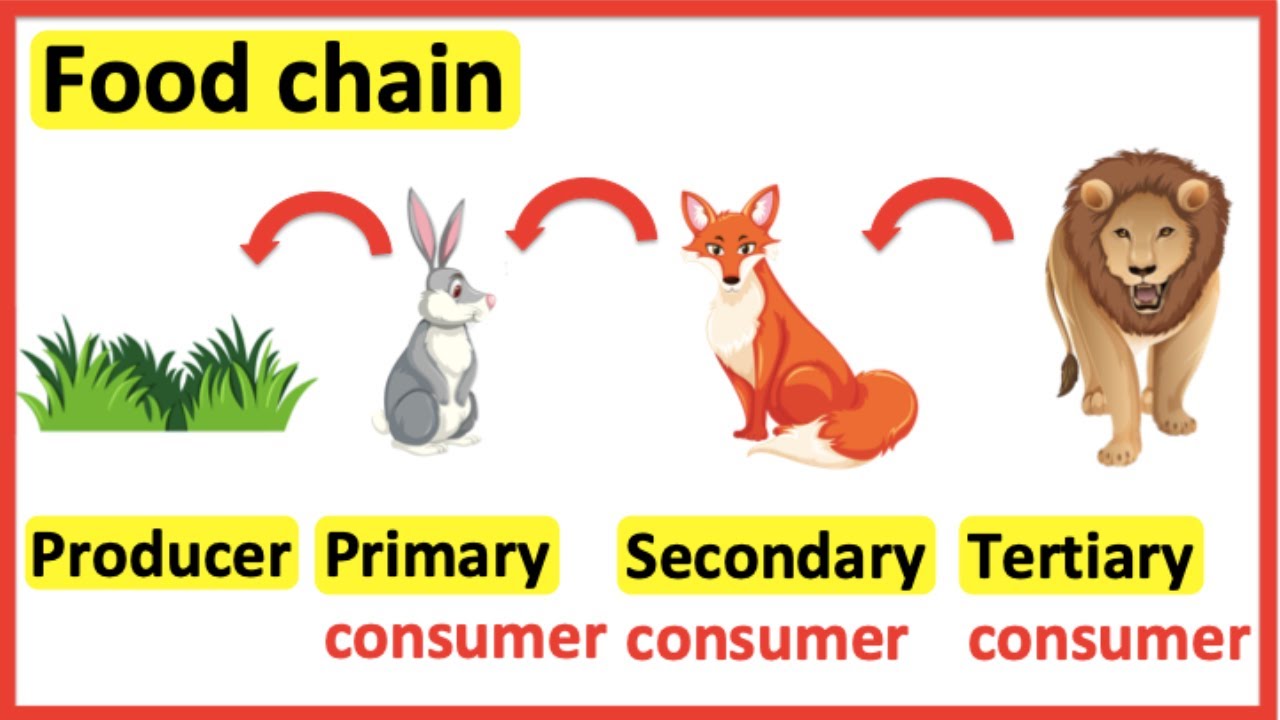
Food Chains Producer Primary Consumer Secondary Consumer Tertiary Examples of tertiary consumer. all big cats are examples of tertiary consumers. for example, lions, tigers, pumas, jaguars, etc. furthermore, they are also apex predators, which imply that in their natural environment there are no other organisms that prey on them. they have features that are atypical of apex predators, including large teeth. Consumers are organisms that consume (eat) other organisms to sustain themselves. organisms that are consumers include heterotrophs like some animals, fungi, and bacteria. a tertiary consumer is an organism that obtains the energy it needs from consuming other consumers at different levels, from eating primary consumers or secondary consumers. Tertiary consumer examples. some examples of tertiary consumers include sharks, sea lions, eagles, hawks, lions, tigers, crocodiles, pythons, and polar bears. these animals rule their range, eating both secondary and primary consumers and easily defending their territories from other species. many tertiary consumers also don’t have to compete. Tertiary consumers are carnivores that eat other carnivores. higher level consumers feed on the next lower trophic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the apex consumers. in the lake ontario food chain, shown in figure \(\pageindex{2}\), the chinook salmon is the apex consumer at the top of this food chain.

Tertiary Consumer Definition And Examples Science Trends Tertiary consumer examples. some examples of tertiary consumers include sharks, sea lions, eagles, hawks, lions, tigers, crocodiles, pythons, and polar bears. these animals rule their range, eating both secondary and primary consumers and easily defending their territories from other species. many tertiary consumers also don’t have to compete. Tertiary consumers are carnivores that eat other carnivores. higher level consumers feed on the next lower trophic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the apex consumers. in the lake ontario food chain, shown in figure \(\pageindex{2}\), the chinook salmon is the apex consumer at the top of this food chain. Secondary consumers are usually carnivores that eat the primary consumers. tertiary consumers are carnivores that eat other carnivores. higher level consumers feed on the next lower tropic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the apex consumers. in the lake ontario food chain shown in figure 1, the chinook salmon. Based on their participation in the food chain, the same animal can assume the role of a tertiary consumer or the highest level predator, the apex consumer. large carnivores include tigers, dogs, cats, jaguars, cougars, leopards, crocodiles, alligators, green anacondas, pythons, philippine eagles, black eagles, and crowned eagles are examples.

Comments are closed.