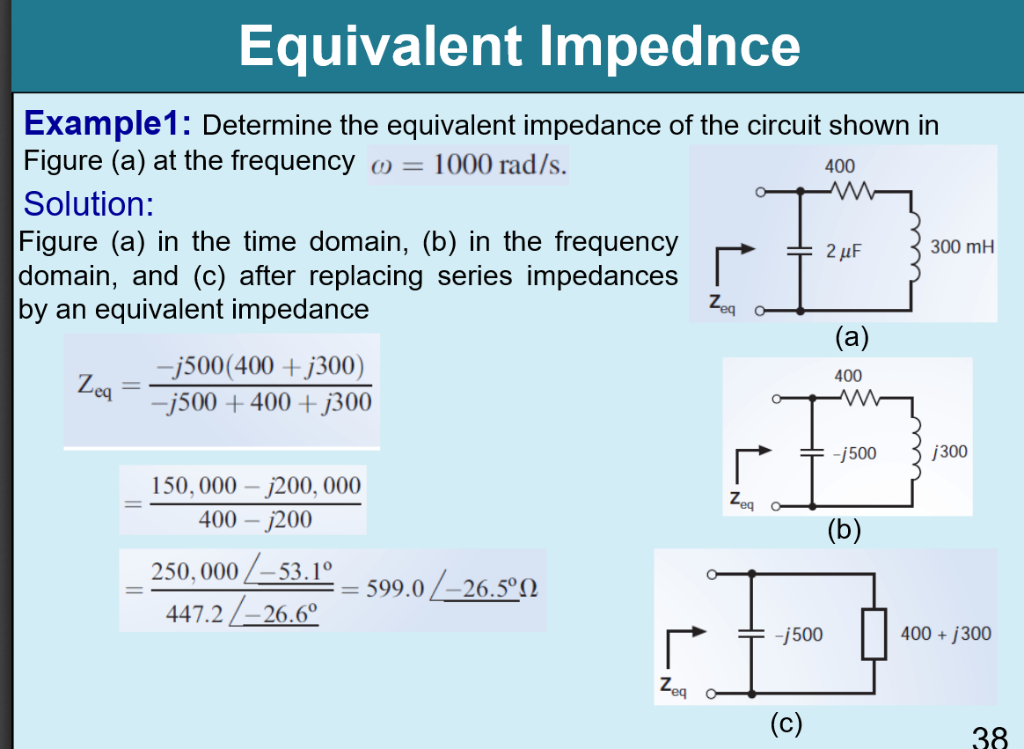
Example 1 Equivalent Impedance
Solved Equivalent Impednce Example1 Determine The Chegg Examples with solutions. example 1 find the equivalent impedance between points a and b in the circuit given below and write it in exponential and polar form. . solution to example 1 let \( z 1 \) be the impedance of resistor r and hence \( z 1 = r\) let \( z 2 \) be the impedance of the capacitor \( c \) and the inductor \( l \) that are in. A delta or wye circuit is said to be balanced if it has equal impedances in all three branches. when a delta wye circuit is balanced, equations. (10) and (11) become. where zy = z1 = z2 = z3 and zΔ = za = zb = zc. as you can see in this post, the principles of voltage division, current division, circuit reduction, impedance equivalence, and.

Example 1 Equivalent Impedance Youtube Calculate the equivalent impedance of a circuit consisiting of a r, l and c. Impedance and admittance (example 1) for the following circuit determine the equivalent impedance and use it to determine i(t) let omega=10 rad s: note that voltage and current are given in phasor notation and that the impedances of the circuit elements have already been provided. angular frequency has also been given as 10 radians per second. The equivalent resistance is defined as a point where the total resistance is measured in a parallel or series circuit (in either the whole circuit or in a part of the circuit). the equivalent resistance is defined between two terminals or nodes of the network. equivalent resistance may sound complicated, but it’s just a technical way to say. Step 1: find thevenin’s resistance. while calculating the thevenin’s equivalent resistance, all voltage sources must be turned off, meaning it acts like a short circuit and all current sources act like an open circuit, as shown in the figure below: let us calculate the thevenin’s resistance for the above circuit: thevenin’s resistance.

How To Easily Find Equivalent Impedance For Ac Circuits Wira Electrical The equivalent resistance is defined as a point where the total resistance is measured in a parallel or series circuit (in either the whole circuit or in a part of the circuit). the equivalent resistance is defined between two terminals or nodes of the network. equivalent resistance may sound complicated, but it’s just a technical way to say. Step 1: find thevenin’s resistance. while calculating the thevenin’s equivalent resistance, all voltage sources must be turned off, meaning it acts like a short circuit and all current sources act like an open circuit, as shown in the figure below: let us calculate the thevenin’s resistance for the above circuit: thevenin’s resistance. Determine the equivalent impedance of the network shown in figure 4.3.1. figure 4.3.1: network for example 4.3.1. looking in from the left side, we note that the inductor and 33 k Ω resistor are in parallel as they are both tied to the same two nodes. also, we can see that the capacitor is in series with the 8.2 k Ω resistor. An equivalent impedance is an equivalent circuit of an electrical network of impedance elements [note 2] which presents the same impedance between all pairs of terminals [note 10] as did the given network. this article describes mathematical transformations between some passive, linear impedance networks commonly found in electronic circuits.

Ac Example Equivalent Impedance Youtube Determine the equivalent impedance of the network shown in figure 4.3.1. figure 4.3.1: network for example 4.3.1. looking in from the left side, we note that the inductor and 33 k Ω resistor are in parallel as they are both tied to the same two nodes. also, we can see that the capacitor is in series with the 8.2 k Ω resistor. An equivalent impedance is an equivalent circuit of an electrical network of impedance elements [note 2] which presents the same impedance between all pairs of terminals [note 10] as did the given network. this article describes mathematical transformations between some passive, linear impedance networks commonly found in electronic circuits.

Comments are closed.