Evidence Synthesis Institute Exploring Different Review Methodologies

Evidence Synthesis Institute Exploring Different Review Methodologies This course brings the core components of the evidence synthesis institute to a self paced open online course. it contains 15 modules guiding learners through the es process from an introduction to review types through writing a methods section for publication, with an emphasis on developing and using systematic search strategies. development of this. Types of evidence synthesis include: systematic review. systematically and transparently collect and categorize existing evidence on a broad question of scientific, policy or management importance. compares, evaluates, and synthesizes evidence in a search for the effect of an intervention. time intensive and often take months to a year or more.
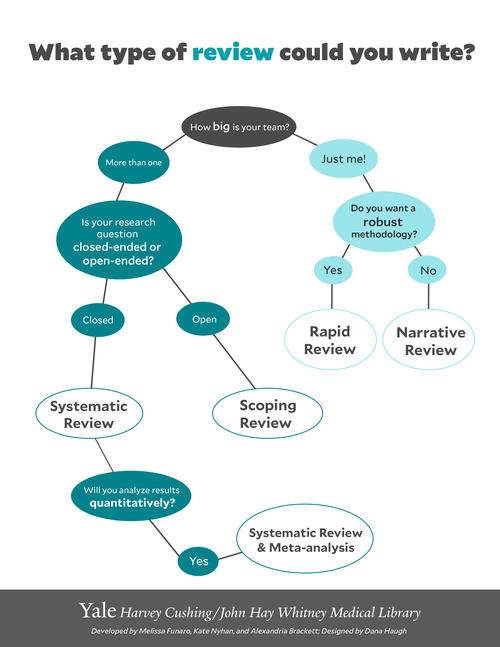
Evidence Synthesis Literature Reviews Education Harvey Cushing John Room 1: adapting systematic review methods for graduate students or researchers working solo (matt) room 2: starting a service (megan) room 3: automation (i.e., using automation and machine learning methods in evidence synthesis) (sarah ) room 4: search filters and hedges: finding and using validated search strings (zahra ) 2:45: break: 3:00: q. Exploring different review methodologies. reproducibility and transparent methods. formulating a research question. guidelines and reporting standards. protocols and registration. databases and search strategies. grey literature. tools for screening and organization. supplementary course videos. introduction to evidence synthesis. registering a. 1. introduction. evidence synthesis is a prerequisite for knowledge translation. 1 a well conducted systematic review (sr), often in conjunction with meta‐analyses (ma) when appropriate, is considered the “gold standard” of methods for synthesizing evidence related to a topic of interest. 2 the central strength of an sr is the transparency of the methods used to systematically search. Scoping reviews are an increasingly common approach to evidence synthesis with a growing suite of methodological guidance and resources to assist review authors with their planning, conduct and reporting. the latest guidance for scoping reviews includes the jbi methodology and the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta analyses—extension for scoping reviews. this paper.
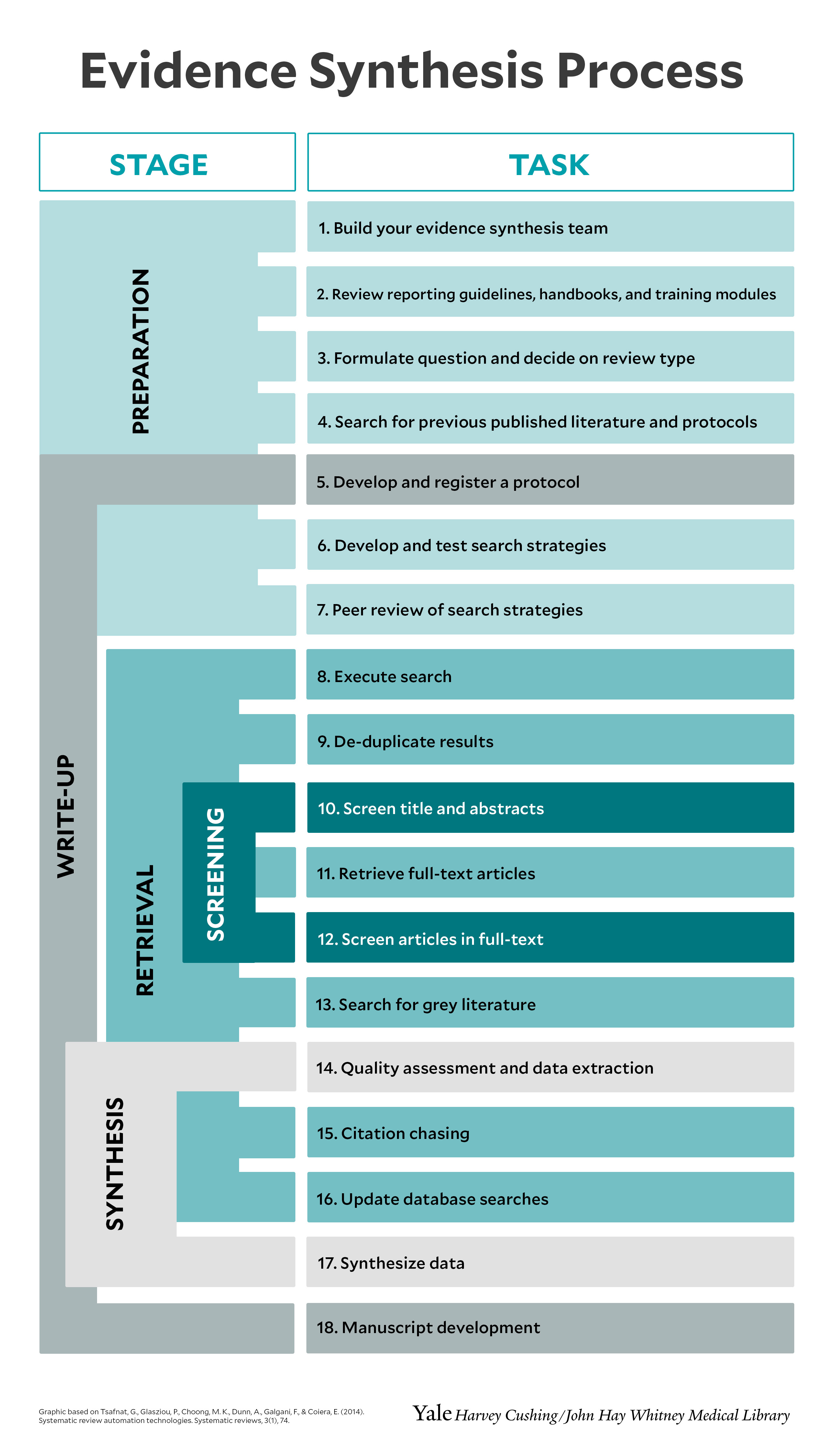
Evidence Synthesis Literature Reviews Education Harvey Cushing John 1. introduction. evidence synthesis is a prerequisite for knowledge translation. 1 a well conducted systematic review (sr), often in conjunction with meta‐analyses (ma) when appropriate, is considered the “gold standard” of methods for synthesizing evidence related to a topic of interest. 2 the central strength of an sr is the transparency of the methods used to systematically search. Scoping reviews are an increasingly common approach to evidence synthesis with a growing suite of methodological guidance and resources to assist review authors with their planning, conduct and reporting. the latest guidance for scoping reviews includes the jbi methodology and the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta analyses—extension for scoping reviews. this paper. Not a true evidence synthesis review, but employs certain elements of a systematic review; no specific methodology; does not require a protocol or critical appraisal of the evidence; conducted by only 1 or 2 people; may be completed in about 2 6 months literature (narrative) review. not a true evidence synthesis review, but a broad term. A scoping review is a type of evidence synthesis that has the objective of identifying and mapping relevant evidence that meets pre determined inclusion criteria regarding the topic, field, context, concept or issue under review. the review question guiding a scoping review is typically broader than that of a traditional systematic review.

A Schematic Showing How The Evidence Synthesis Methods Used In The Case Not a true evidence synthesis review, but employs certain elements of a systematic review; no specific methodology; does not require a protocol or critical appraisal of the evidence; conducted by only 1 or 2 people; may be completed in about 2 6 months literature (narrative) review. not a true evidence synthesis review, but a broad term. A scoping review is a type of evidence synthesis that has the objective of identifying and mapping relevant evidence that meets pre determined inclusion criteria regarding the topic, field, context, concept or issue under review. the review question guiding a scoping review is typically broader than that of a traditional systematic review.
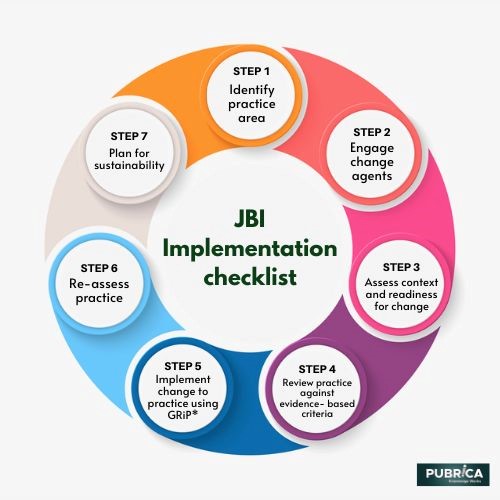
Jbi Manual For Evidence Synthesis Scoping Reviews

Comments are closed.