Evidence Review Nhmrc

Evidence Review Nhmrc 6.1. be informed by well conducted systematic reviews. 6.2. consider the body of evidence for each outcome (including the quality of that evidence) and other factors that influence the process of making recommendations including benefits and harms, values and preferences, resource use and acceptability. 1. plan your approach to assessing certainty. the decisions you make around forming the questions and deciding what evidence to include may influence the body of evidence you uncover. this body of evidence may also have a number of limitations. for example, when the quality or certainty of evidence for the body of evidence is low, it may be.
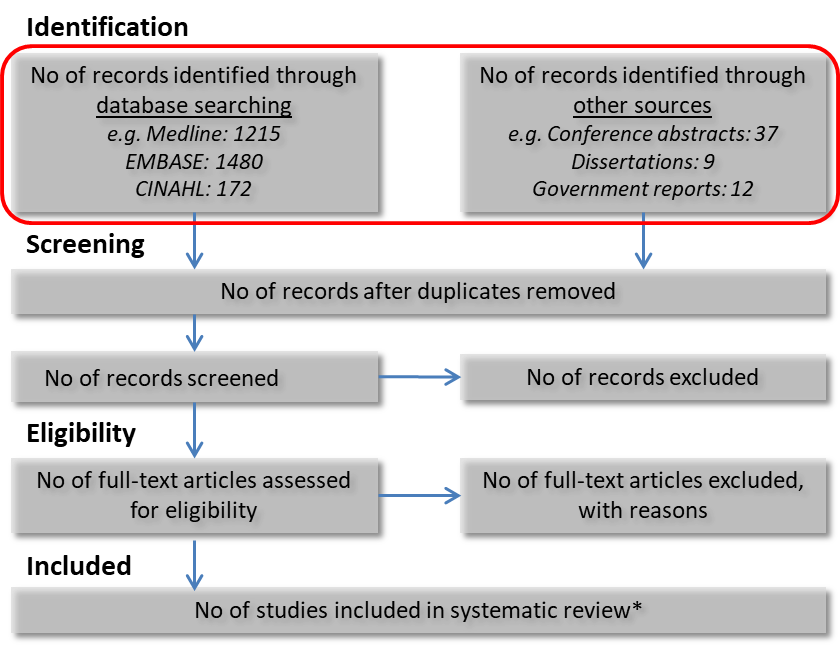
Prisma Hierarchy Of Evidence Evidence review. communication. public call for systematic reviews. nhmrc has rigorous standards in place to ensure that guidelines and public health advice are of a high quality and based on the best available scientific evidence. nhmrc follows a robust and transparent development and decision making process. A systematic review will only be assigned a level of evidence as high as the studies it contains, excepting where those studies are of level ii evidence. systematic reviews of level ii evidence provide more data than the individual studies and any meta analyses will increase the precision of the overall results, reducing the likelihood that the. The following image represents the hierarchy of evidence provided by the national health and medical research council (nhmrc). 1 most experts agree that the higher up the hierarchy the study design is positioned, the more rigorous the methodology and hence the more likely it is that the study design can minimise the effect of bias on the. Review to adequately answer a particular research question, based on the probability that its design has minimised the impact of bias on the results. see page 6–10 of how to use the evidence: assessment and application of scientific evidence (nhmrc 2000b). the currently available nhmrc levels of evidence for intervention studies (nhmrc.

Nhmrc And Nice Levels Of Evidence Download Table The following image represents the hierarchy of evidence provided by the national health and medical research council (nhmrc). 1 most experts agree that the higher up the hierarchy the study design is positioned, the more rigorous the methodology and hence the more likely it is that the study design can minimise the effect of bias on the. Review to adequately answer a particular research question, based on the probability that its design has minimised the impact of bias on the results. see page 6–10 of how to use the evidence: assessment and application of scientific evidence (nhmrc 2000b). the currently available nhmrc levels of evidence for intervention studies (nhmrc. Nnt is the number of patients who have to be treated to prevent one event occurring (see information point in vol. 10, no. 6, p. 783). another hierarchy used a scale of level i through to level iv [national health and medical research council (nhmrc), 1995]. level i was assigned to evidence obtained from a systematic review of all relevant. An example of the evolution toward more transparent considerations of internal validity of individual studies within a levels of evidence framework is seen in the progression of the australian national health and medical research council (nhmrc) system for evaluating evidence in the development of clinical practice guidelines.

Natural Therapies Review Nhmrc Nnt is the number of patients who have to be treated to prevent one event occurring (see information point in vol. 10, no. 6, p. 783). another hierarchy used a scale of level i through to level iv [national health and medical research council (nhmrc), 1995]. level i was assigned to evidence obtained from a systematic review of all relevant. An example of the evolution toward more transparent considerations of internal validity of individual studies within a levels of evidence framework is seen in the progression of the australian national health and medical research council (nhmrc) system for evaluating evidence in the development of clinical practice guidelines.

Comments are closed.