Enzymes Cells Biology Fuseschool

Enzymes Cells Biology Fuseschool Youtube Enzymes | cells | biology | fuseschoolenzymes are really important proteins that speed up the rates of reactions such as in photosynthesis, respiration and p. How enzymes denature | cells | biology | fuseschoolenzymes have optimal conditions under which they operate. temperature, ph, enzyme concentration and substr.
Enzyme Molecules make you think of chemistry, right? well, they also are very important in biology too. in this video we are going to look at carbohydrates, protein. Enzymes | cells | biology | fuseschool. Through a specific reaction pathway, enzymes allow a reaction to proceed rapidly by providing an alternate reaction pathway in the cell which has a lower free energy of activation can direct different substrates to different particular rxn pathways. Study with quizlet and memorise flashcards containing terms like define enzyme, define catalyst, enzymes | cells | biology | fuseschool and others.

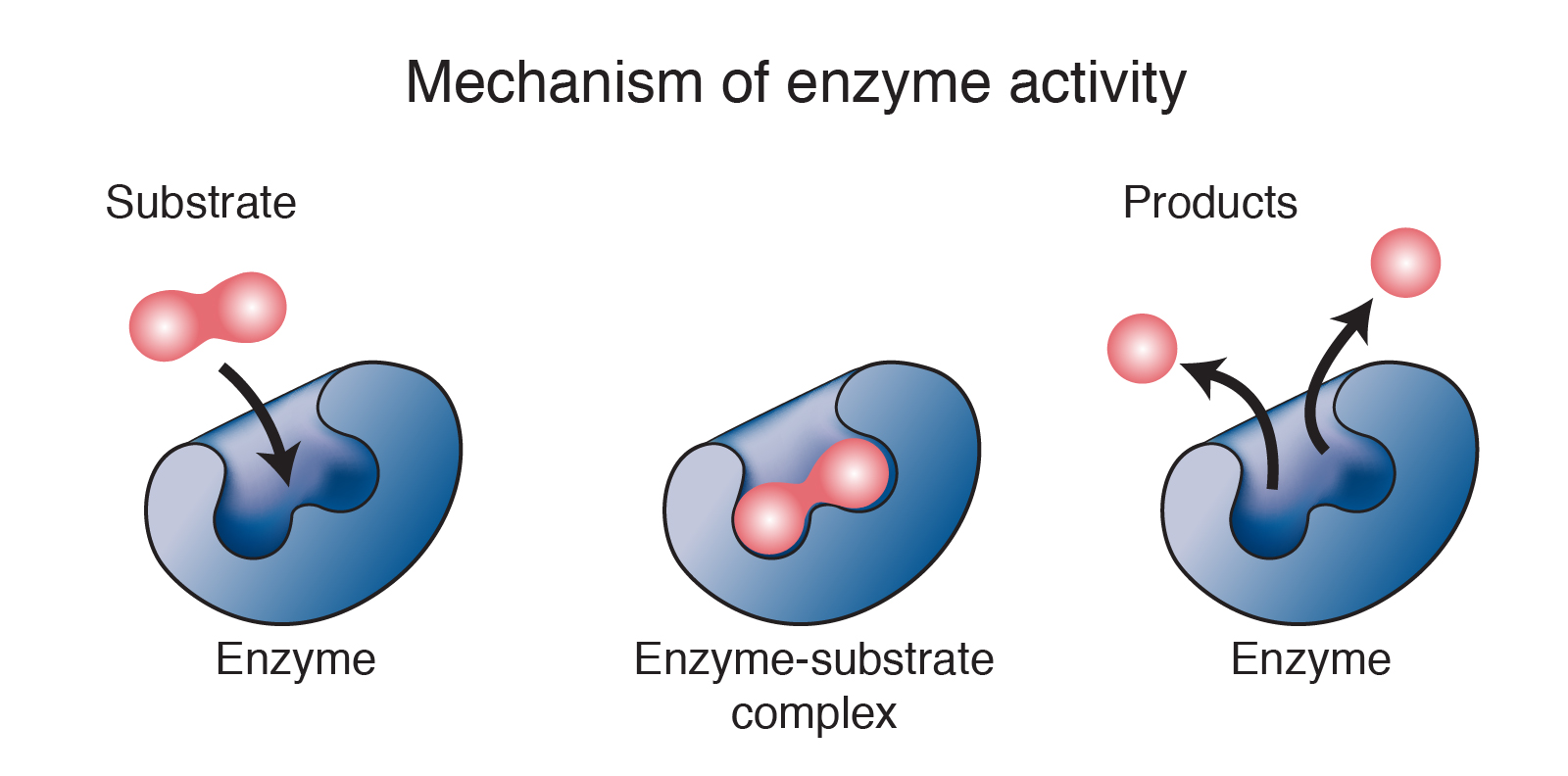
Enzymes Cells Biology Fuseschool вђ Alugha Through a specific reaction pathway, enzymes allow a reaction to proceed rapidly by providing an alternate reaction pathway in the cell which has a lower free energy of activation can direct different substrates to different particular rxn pathways. Study with quizlet and memorise flashcards containing terms like define enzyme, define catalyst, enzymes | cells | biology | fuseschool and others. A) a lactase enzyme breaking down lactose sugar in the small intestine. b) a dna polymerase enzyme synthesizing new strands of dna. c) a lipase enzyme breaking down fats (lipids) in the small intestine. d) a helicase enzyme unraveling dna so it can be replicated. e) all of the above. Enzymes are specialised; their active site matches the shape of the specific substrate that they react with. the enzyme and the substrate fit together using a lock and key mechanism. once the substrate is in the active site, the reaction takes place. the required product is produced and the enzyme releases itself and carries on moving around.

Enzymes Definition Classification Functions A) a lactase enzyme breaking down lactose sugar in the small intestine. b) a dna polymerase enzyme synthesizing new strands of dna. c) a lipase enzyme breaking down fats (lipids) in the small intestine. d) a helicase enzyme unraveling dna so it can be replicated. e) all of the above. Enzymes are specialised; their active site matches the shape of the specific substrate that they react with. the enzyme and the substrate fit together using a lock and key mechanism. once the substrate is in the active site, the reaction takes place. the required product is produced and the enzyme releases itself and carries on moving around.

Comments are closed.