Enzymes And Catalysts
Catalytic Modes Of Enzymes Creative Enzymes Like all other catalysts, enzymes are characterized by two fundamental properties. first, they increase the rate of chemical reactions without themselves being consumed or permanently altered by the reaction. second, they increase reaction rates without altering the chemical equilibrium between reactants and products. Structure of catalysts and enzymes. a catalyst is any substance that can cause significant alterations to the rate of a chemical reaction. thus it could be a pure element like nickel or platinum, a pure compound like silica, manganese dioxide, dissolved ions like copper ions or even a mixture like iron molybdenum.

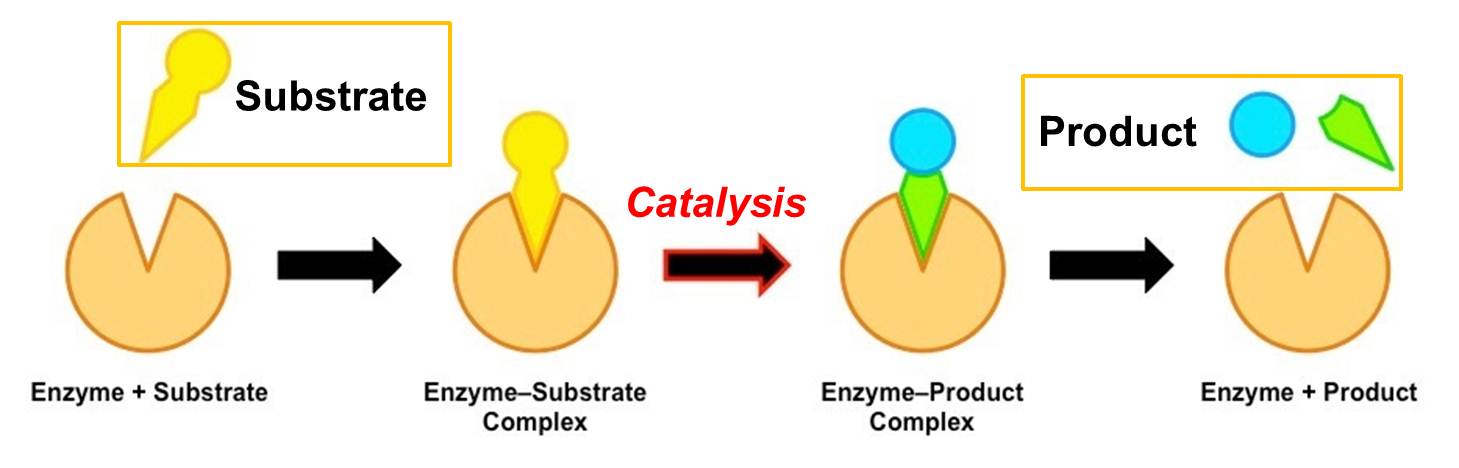
Enzyme Catalysis Mechanism Characteristics Enzyme Catalyst Enzyme, a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being altered in the process. a brief treatment of enzymes follows. for full treatment, see protein: enzymes. the biological processes that occur within all living organisms are chemical reactions, and most are. Enzymes are biological catalysts (also known as biocatalysts) that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms, and which can be extracted from cells and then used to catalyse a wide range of commercially important processes. this chapter covers the basic principles of enzymology, such as classification, structure, kinetics and. After an enzyme is done catalyzing a reaction, it releases its product (s). figure 6.4.2 6.4. 2: according to the induced fit model, both enzyme and substrate undergo dynamic conformational changes upon binding. the enzyme contorts the substrate into its transition state, thereby increasing the rate of the reaction. 5.2: enzymes is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by libretexts. enzymes are biological catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy. enzymes are proteins consisting of one or more polypeptide chains. enzymes have an active site ….

Catalysts Enzymes вђ Overview Examples Expii After an enzyme is done catalyzing a reaction, it releases its product (s). figure 6.4.2 6.4. 2: according to the induced fit model, both enzyme and substrate undergo dynamic conformational changes upon binding. the enzyme contorts the substrate into its transition state, thereby increasing the rate of the reaction. 5.2: enzymes is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by libretexts. enzymes are biological catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy. enzymes are proteins consisting of one or more polypeptide chains. enzymes have an active site …. The main difference between catalyst and enzyme is that catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction whereas enzyme is a globular protein that can increase the rate of biochemical reactions. the inorganic catalysts include mineral ions or small molecules. in contrast, enzymes are complex macromolecules with 3d. Enzymes ( ˈɛnzaɪmz ) are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. the molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products.

Enzymes And Catalysts Reaction At Vincent Miller Blog The main difference between catalyst and enzyme is that catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction whereas enzyme is a globular protein that can increase the rate of biochemical reactions. the inorganic catalysts include mineral ions or small molecules. in contrast, enzymes are complex macromolecules with 3d. Enzymes ( ˈɛnzaɪmz ) are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. the molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products.

Comments are closed.