Enzyme Key Stage Wiki
Enzyme Key Stage Wiki 1.2 about enzymes; 2 key stage 4. 2.1 meaning; 2.2 about enzymes; 2.3 denaturation; key stage wiki. this page was last edited on 6 december 2019, at 14:56. Key stage 4 meaning. a digestive enzyme is an enzyme which is used to break down large insoluble molecules into smaller soluble molecules. about digestive enzymes digestive enzymes, like all enzymes, are made of proteins. digestive enzymes work as a catalyst for the breakdown of large molecules. digestive enzymes are shaped to work on only one.
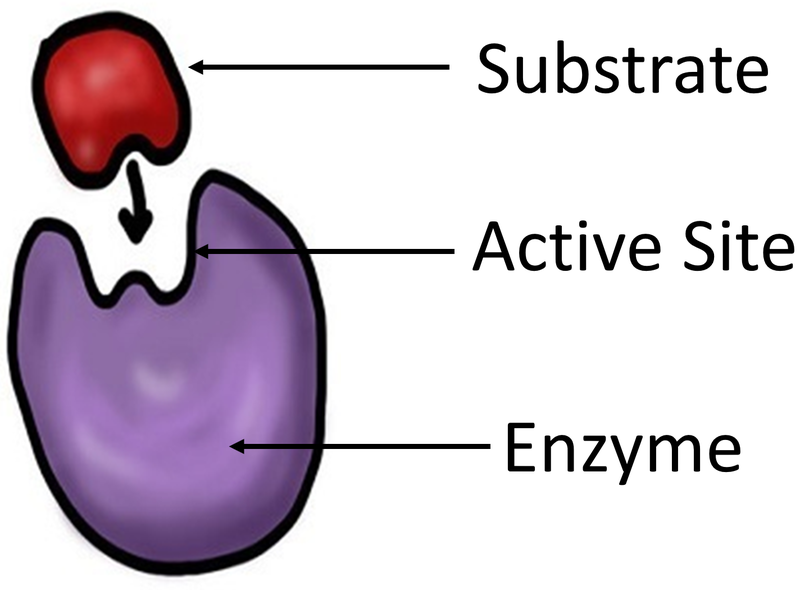
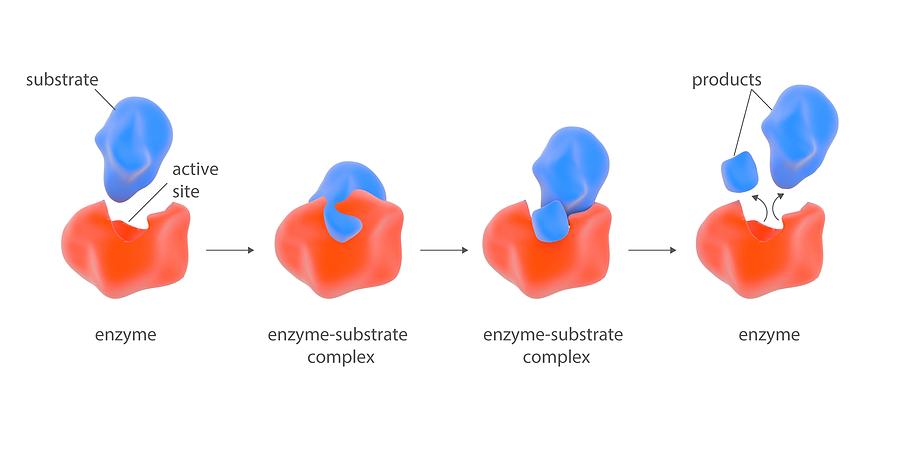
Enzyme Key Stage Wiki E. enzymes ( ˈɛnzaɪmz ) are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. the molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. The citric acid cycle is a metabolic pathway that connects carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism. the reactions of the cycle are carried out by eight enzymes that completely oxidize acetate (a two carbon molecule), in the form of acetyl coa, into two molecules each of carbon dioxide and water. through catabolism of sugars, fats, and. Without enzymes, many reactions would happen too slowly to support life. enzymes catalyse reactions essential to life, including digestion and reactions in photosynthesis and respiration. each enzyme has a 3d shape with an active site that a specific substrate fits into. the lock and key model to explain enzyme substrate interactions. 5.2: enzymes. enzymes are biological catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy. enzymes are proteins consisting of one or more polypeptide chains. enzymes have an active site that provides a unique chemical environment, made up of certain amino acid r groups (residues).

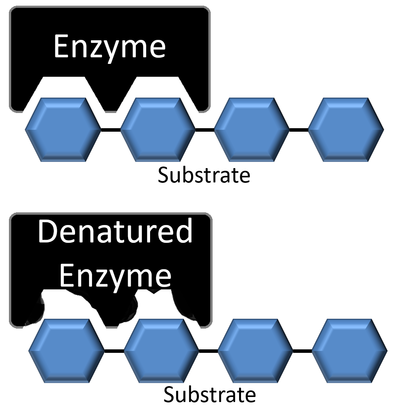
Enzyme Key Stage Wiki Without enzymes, many reactions would happen too slowly to support life. enzymes catalyse reactions essential to life, including digestion and reactions in photosynthesis and respiration. each enzyme has a 3d shape with an active site that a specific substrate fits into. the lock and key model to explain enzyme substrate interactions. 5.2: enzymes. enzymes are biological catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy. enzymes are proteins consisting of one or more polypeptide chains. enzymes have an active site that provides a unique chemical environment, made up of certain amino acid r groups (residues). Oxidative phosphorylation (uk ɒkˈsɪd.ə.tɪv , us ˈɑːk.sɪˌdeɪ.tɪv [1]) or electron transport linked phosphorylation or terminal oxidation is the metabolic pathway in which cells use enzymes to oxidize nutrients, thereby releasing chemical energy in order to produce adenosine triphosphate (atp). Your home for online study. use the links below or search for the subject you're interested in for a break down of each topic by key stage. use the planner to help guide you through your education journey. and if you're a teacher, ta or parent please use the puzzle generator to create your own puzzles. all wiki and puzzle generator pages are.

Enzyme Key Stage Wiki Oxidative phosphorylation (uk ɒkˈsɪd.ə.tɪv , us ˈɑːk.sɪˌdeɪ.tɪv [1]) or electron transport linked phosphorylation or terminal oxidation is the metabolic pathway in which cells use enzymes to oxidize nutrients, thereby releasing chemical energy in order to produce adenosine triphosphate (atp). Your home for online study. use the links below or search for the subject you're interested in for a break down of each topic by key stage. use the planner to help guide you through your education journey. and if you're a teacher, ta or parent please use the puzzle generator to create your own puzzles. all wiki and puzzle generator pages are.
Enzyme

Comments are closed.