Entropy

What Is Entropy Definition And Examples Entropy is a scientific concept that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. the term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the microscopic description of nature in statistical physics, and to the principles of information theory. Entropy is a measure of the disorder or the energy unavailable to do work of a system. learn how to calculate entropy, see examples of entropy in physics and chemistry, and explore the second law of thermodynamics and the heat death of the universe.
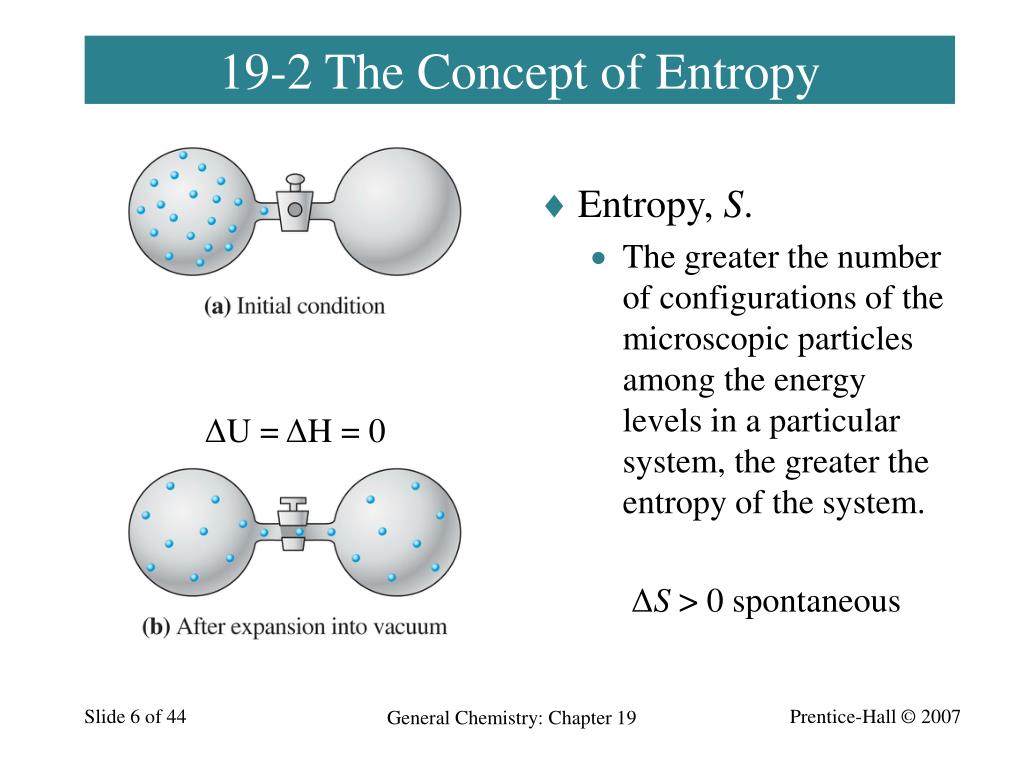
Ppt Chapter 19 Spontaneous Change Entropy And Free Energy Entropy is a measure of the unavailable energy or disorder in a system, especially in thermodynamics and communication theory. learn the etymology, history, examples, and related words of entropy from merriam webster dictionary. Entropy is a measure of the thermal energy unavailable for doing useful work and the molecular disorder of a system. learn how entropy relates to the second law of thermodynamics, heat engines, and spontaneous processes with examples and equations. Thermodynamic entropy is a measure of the disorder in a closed system. according to the second law, when entropy increases, internal energy usually rises as well. if it isn't harnessed somehow, that thermal energy gets dispersed. because the measure of entropy is based on probabilities, it is, of course, possible for the entropy to decrease in. Hence, the entropy change in going from a to b is the same for paths i and ii. since paths i and ii are arbitrary, reversible paths, the entropy change in a transition between two equilibrium states is the same for all the reversible processes joining these states. entropy, like internal energy, is therefore a state function.

Comments are closed.