Energies Free Full Text Dynamic Modeling Of A Decarbonized District
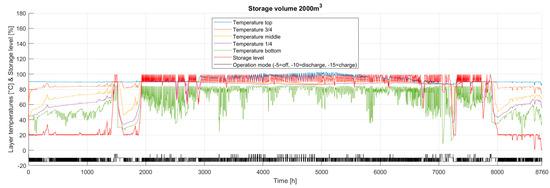
Energies Free Full Text Dynamic Modeling Of A Decarbonized District The targets of global co2 reduction outline the importance of decarbonizing the heating and cooling sector, which consume half of the final energy in the european union (eu). consequently, heating network operators must adapt to growing requirements for carbon neutrality. energy system modeling allows the simulation of individual network compositions and regulations, while considering. The aim of this paper is to implement the flexible mode of biomass plant operation in a modeled heating grid with reduced carbon intensity. the use of a long‐term heat storage and the implementation of a biomass boiler allows the replacement of the peak load boiler supply.

Energies Free Full Text Dynamic Modeling Of A Decarbonized District The definition, characterization and implementation of positive energy districts is crucial in the path towards urban decarbonization and energy transition. however, several issues still must be addressed: the need for a clear and comprehensive definition, and the settlement of a consistent design approach for positive energy districts. as emerged throughout the workshop held during the fourth. Download full text pdf read full text. dynamic modeling of a decarbonized district. plant in flexible district heating with a dynamic simulation model. energy 2020, 202, 117710. The use of an external program such as matlab in combination with modelica’s object oriented structure suits the purpose of building models of district heating networks well, as large system can be built by a few standard components with a high degree of automation. 6. further work. A review of current and future district cooling (dc) technologies, operational, economic, and environmental aspects, and analysis and optimization methodologies is presented, focusing on the demands of cooling dominated regions. sustainable energy sources (i.e., renewable, waste excess electricity and heat, natural artificial cold) and cooling storage technology options with emphasis on heat.

Energies Free Full Text Dynamic Modeling Of A Decarbonized District The use of an external program such as matlab in combination with modelica’s object oriented structure suits the purpose of building models of district heating networks well, as large system can be built by a few standard components with a high degree of automation. 6. further work. A review of current and future district cooling (dc) technologies, operational, economic, and environmental aspects, and analysis and optimization methodologies is presented, focusing on the demands of cooling dominated regions. sustainable energy sources (i.e., renewable, waste excess electricity and heat, natural artificial cold) and cooling storage technology options with emphasis on heat. Dagdougui et al. [22] stated that hybrid energy systems with res can help improve the economic and environmental sustainability to fulfill the energy demand and they developed a dynamic model to integrate different res and one storage device to feed a “green” building for its thermal and electrical energy demands in a sustainable way. Energy system modeling allows the simulation of individual network compositions and regulations, while considering electricity market signals for a more efficient plant operation. the district heating model, programmed for this work, covers a measured heat demand with peak load boiler, biomass fired combined heat and power (chp) plant, and.

Comments are closed.