Employment Macro Economics Labor Market
Labor Market Explained Theories And Who Is Included The bottom line. the labor market is an economic term for the availability of workers and the cost of employment. it plays a major role in the overall economy. the price for labor is largely. The market supply of labor is the horizontal summation of all individuals’ supplies of labor. figure 14.7 the market wage rate in a competitive labor market, the equilibrium wage and employment level are determined where the market demand for labor equals the market supply of labor. like all equilibrium prices, the market wage rate is.

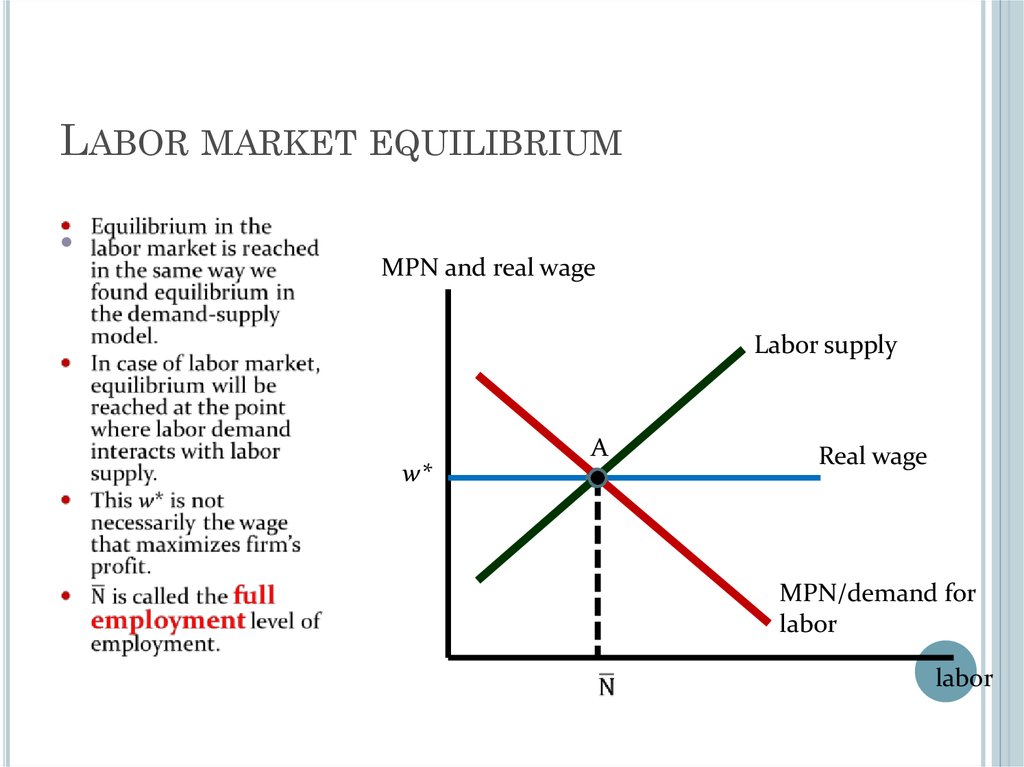
Labour Market Equilibrium Excess supply of labour (involuntary unemployment) is a feature of labour markets, even in equilibrium. if economy wide demand for goods and services is too low, unemployment will be higher than its equilibrium level and may persist. unions and public policies can affect labour market equilibrium. As we have seen, the marginal product of labor could rise because of an increase in the use of other factors of production, an improvement in technology, or an increase in human capital. figure 12.11 changes in the demand for and supply of labor. panel (a) shows an increase in demand for labor; the wage rises to w2 and employment rises to l2. Lectures in labor economics chapter 11. basic equilibrium search framework 229 1. motivation 229 2. the basic search model 229 3. efficiency of search equilibrium 239 4. endogenous job destruction 242 5. a two sector search model 247 chapter 12. composition of jobs 253 1. endogenous composition of jobs with homogeneous workers 253 2. Labor market equilibrium (long run) we define long run equilibrium in macroeconomics as occurring when the labor market clears. by definition, long run macro equilibrium exists when n = n* n = n*. at n*, l abor demand = labor supply. so, by definition, all workers who want a job (the suppliers) are able to find a firm looking for a worker (the.
Macroeconomics Productivity Output Employment Lecture 5 Lectures in labor economics chapter 11. basic equilibrium search framework 229 1. motivation 229 2. the basic search model 229 3. efficiency of search equilibrium 239 4. endogenous job destruction 242 5. a two sector search model 247 chapter 12. composition of jobs 253 1. endogenous composition of jobs with homogeneous workers 253 2. Labor market equilibrium (long run) we define long run equilibrium in macroeconomics as occurring when the labor market clears. by definition, long run macro equilibrium exists when n = n* n = n*. at n*, l abor demand = labor supply. so, by definition, all workers who want a job (the suppliers) are able to find a firm looking for a worker (the. Central question for labor and macro: what determines the level of employment and unemployment in the economy? textbook answer: labor supply, labor demand, and unemployment as fileisurefl. neither realistic nor a useful framework for analysis. alternative: labor market frictions related questions raised by the presence of frictions:. The onset of the covid pandemic was a severe shock to the u.s. economy. unemployment reached 14.8% in april 2020, the highest since the government began measuring it in 1948, while the labor force.

Comments are closed.