Economics Ch 7 2 Monopoly Describing Monopoly A Monopoly

Economics Ch 7 2 Monopoly Describing Monopoly A Monopoly Economics chapter 7 section 2 monopoly. monopoly. click the card to flip 👆. a market in which there are many buyers but only one seller. click the card to flip 👆. 1 9. Factors that cause a producers average cost per unit to fall as output rises. natural monopoly. market that runs most efficiently when one large firms supplies all of the output. government monopoly. monopoly created by the government. patent. license that gives the inventor of a new product the exclusive right to sell it for a certain period.
A Good Example Of Monopoly Chapter 7, section 2: monopoly. monopoly. click the card to flip 👆. a market in which a single seller dominates. click the card to flip 👆. 1 9. This chapter begins by describing how monopolies are protected from competition, including laws that prohibit competition, technological advantages, and certain configurations of demand and supply. it then discusses how a monopoly will choose its profit maximizing quantity to produce and what price to charge. This page titled 7.2: monopoly is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by via that was edited to the style and standards of the libretexts platform. often, the main deterrent to a highly competitive market is market power possessed by sellers. in this section, we will consider the strongest form of seller market. Monopoly: a market in which a single seller dominates. economies of scale: factors that cause a producer’s average cost per unit to fall as output rises. natural monopoly: a market that runs most efficiently when one large firm supplies all of the output. government monopoly: a monopoly created by the government.
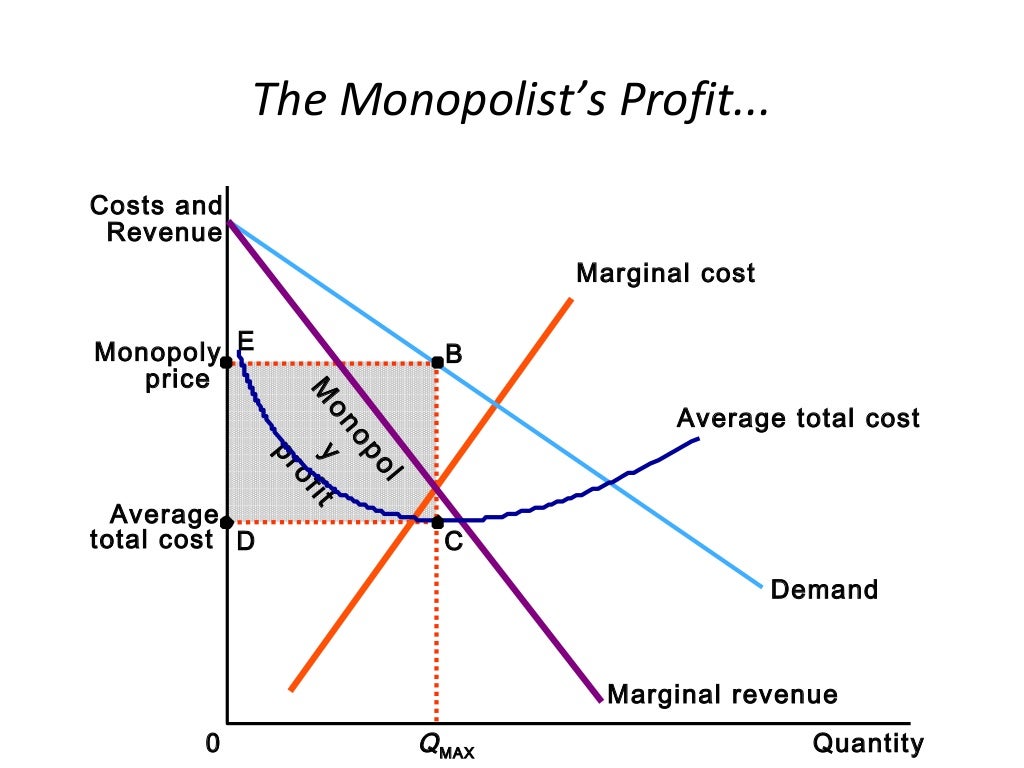
Monopoly Profit Maximization In Monopoly Economics This page titled 7.2: monopoly is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by via that was edited to the style and standards of the libretexts platform. often, the main deterrent to a highly competitive market is market power possessed by sellers. in this section, we will consider the strongest form of seller market. Monopoly: a market in which a single seller dominates. economies of scale: factors that cause a producer’s average cost per unit to fall as output rises. natural monopoly: a market that runs most efficiently when one large firm supplies all of the output. government monopoly: a monopoly created by the government. Define what is meant by a natural monopoly. monopoly is at the opposite end of the spectrum of market models from perfect competition. a monopoly firm has no rivals. it is the only firm in its industry. there are no close substitutes for the good or service a monopoly produces. not only does a monopoly firm have the market to itself, but it. Show solution. the correct answer is that the optimal quantity produced for a monopolist is defined at the point where the marginal cost is equal to the marginal revenue. it is not the case that the marginal cost is equal to the price. this is accurate in a competitive market, where marginal revenue and price are equivalent, but not in a monopoly.

Monopoly Economics Define what is meant by a natural monopoly. monopoly is at the opposite end of the spectrum of market models from perfect competition. a monopoly firm has no rivals. it is the only firm in its industry. there are no close substitutes for the good or service a monopoly produces. not only does a monopoly firm have the market to itself, but it. Show solution. the correct answer is that the optimal quantity produced for a monopolist is defined at the point where the marginal cost is equal to the marginal revenue. it is not the case that the marginal cost is equal to the price. this is accurate in a competitive market, where marginal revenue and price are equivalent, but not in a monopoly.

Chapter 7 Monopoly Pdf Monopoly Microeconomics

Comments are closed.